Project Quality Management
What is Quality?
- The standard of something as measured against other things of a similar kind; the degree of excellence of something.
- Conformance to requirements: Project’s processes and products meet written specifications
- Fitness for use: Product can be used as it was intended
What is Project Quality Management?
The purpose of project quality management is to ensure that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken.项目质量管理的目的是确保项目能够满足开展项目的需要。
Project quality management processes:
- Planning quality management: identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and how to satisfy them; a metric is a standard of measurement 确定哪些质量标准与该项目有关以及如何满足这些标准;度量是测量标准
- Managing quality: translating the quality management plan into executable quality activities 将质量管理计划转化为可执行的质量活动
- Controlling quality: monitoring specific project results to ensure they comply with the relevant quality standards 监测具体的项目成果,确保其符合相关的质量标准
1.Planning Quality Management
Important scope aspects of IT projects that affect quality
- Functionality: degree to which a system performs its intended function 系统执行其预期功能的程度
- Features: system’s special characteristics that appeal to users 吸引用户的系统特性
- System outputs: screens and reports the system generates 系统生成的屏幕和报告
- Performance: addresses how well a product or service performs the customer’s intended use 解决产品或服务在客户预定用途上的表现。
• Reliability: ability of a product or service to perform as expected under normal conditions 产品或服务在正常条件下按预期执行的能力
• Maintainability: ease of performing maintenance on a product 易于对产品进行维护
2.Managing Quality
Quality assurance includes all the activities related to satisfying the relevant quality standards for a project 质量保证包括与满足项目相关质量标准相关的所有活动
- Another goal is continuous quality improvement 另一个目标是持续改进质量
- Benchmarking generates ideas for quality improvements by comparing specific project practices or product characteristics to those of other projects or products within or outside the performing organization 通过将特定的项目实践或产品特性与执行组织内外的其他项目或产品的特性进行比较,基准测试产生了质量改进的想法
- A quality audit is a structured review of specific quality management activities that help identify lessons learned that could improve performance on current or future projects 质量审计是对特定质量管理活动的结构化审查,有助于确定可以改进当前或未来项目绩效的经验教训
3.Controlling Quality
What would be major outcomes of quality control?
The main outcomes of quality control
- Acceptance decisions determine if the products or services produced as part of the project will be accepted or rejected. 验收决定决定作为项目的一部分而生产的产品或服务是否会被接受或拒绝。
- Rework is action taken to bring rejected items into compliance with product requirements, specifications, or other stakeholder expectations. 返工是为了使被拒绝的项目符合产品要求、规格或其他利益相关者的期望而采取的行动。
- Process adjustments correct or prevent further quality problems based on quality control measurements. 过程调整根据质量控制测量结果,纠正或防止进一步的质量问题。
Tools and Techniques for Quality Control
The Seven Basic Tools of Quality Control
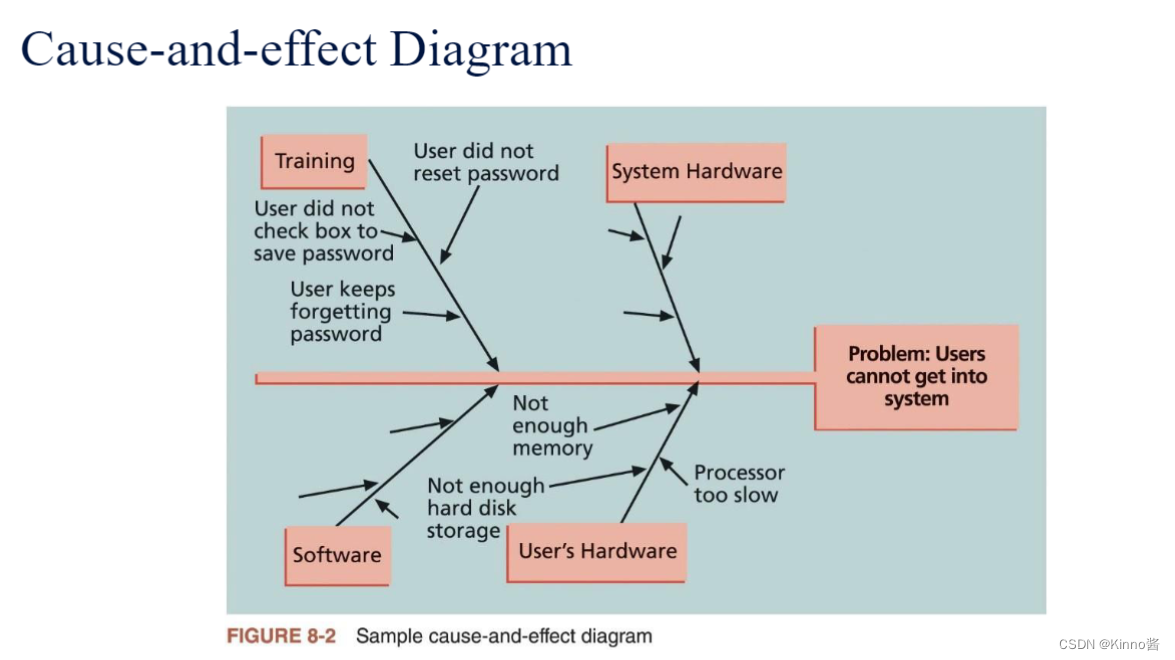
- Cause-and-effect diagrams
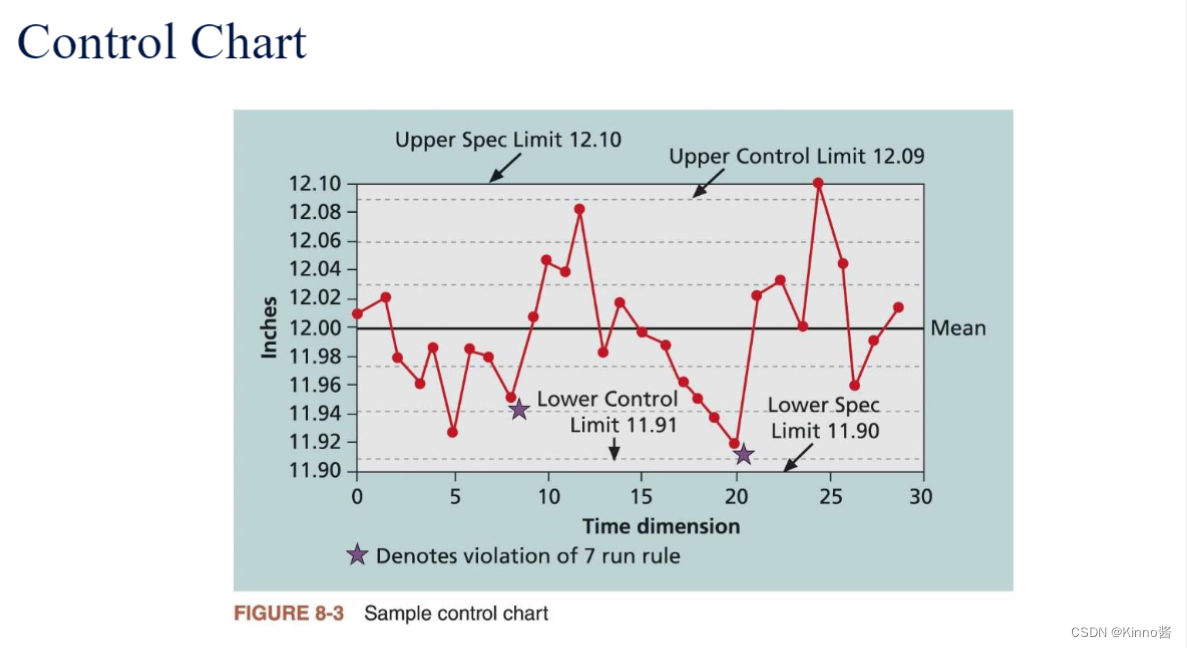
- Control chart
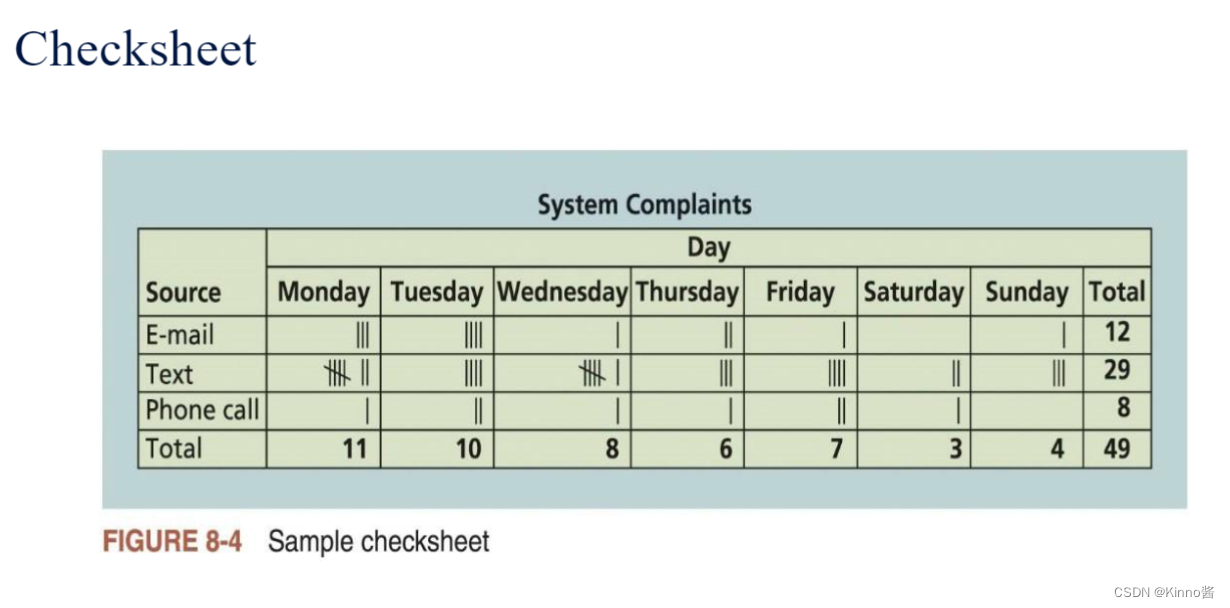
- Checksheet
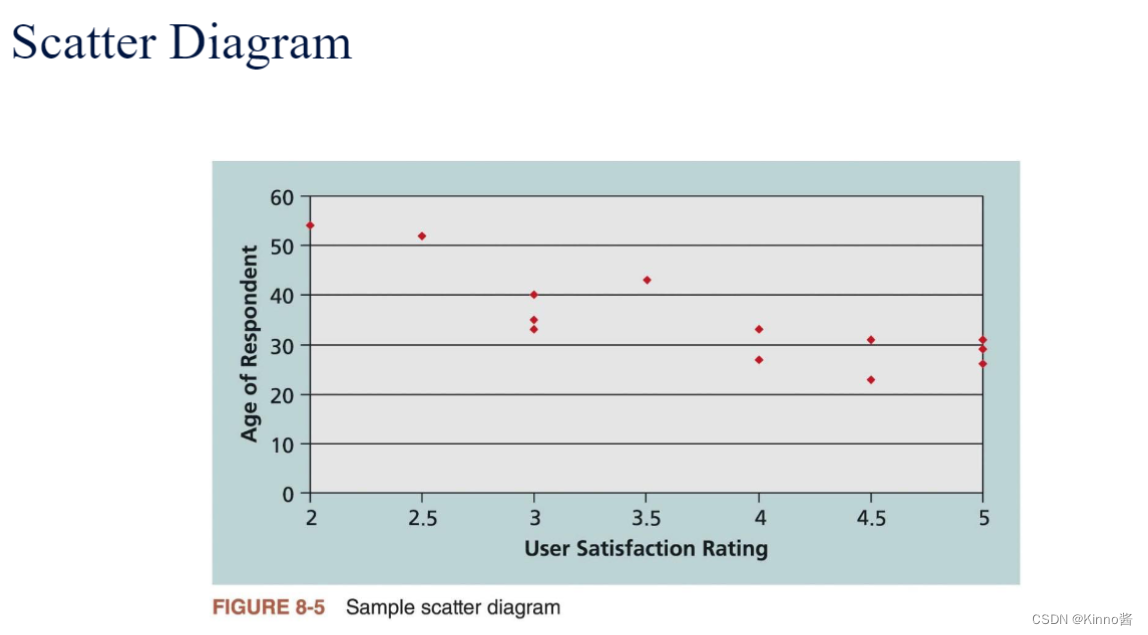
- Scatter diagram
- Histogram
- Flowcharts
- Run charts
1.Cause-and-effect diagrams
2.Control chart
3.Checksheet
4.Scatter diagram
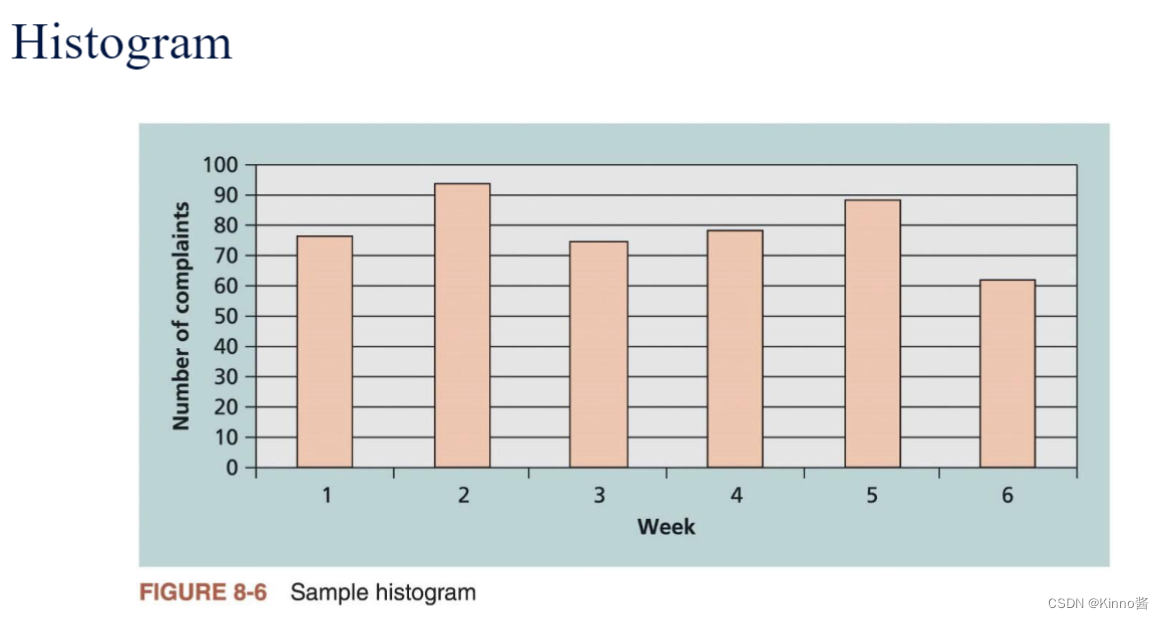
5.Histogram
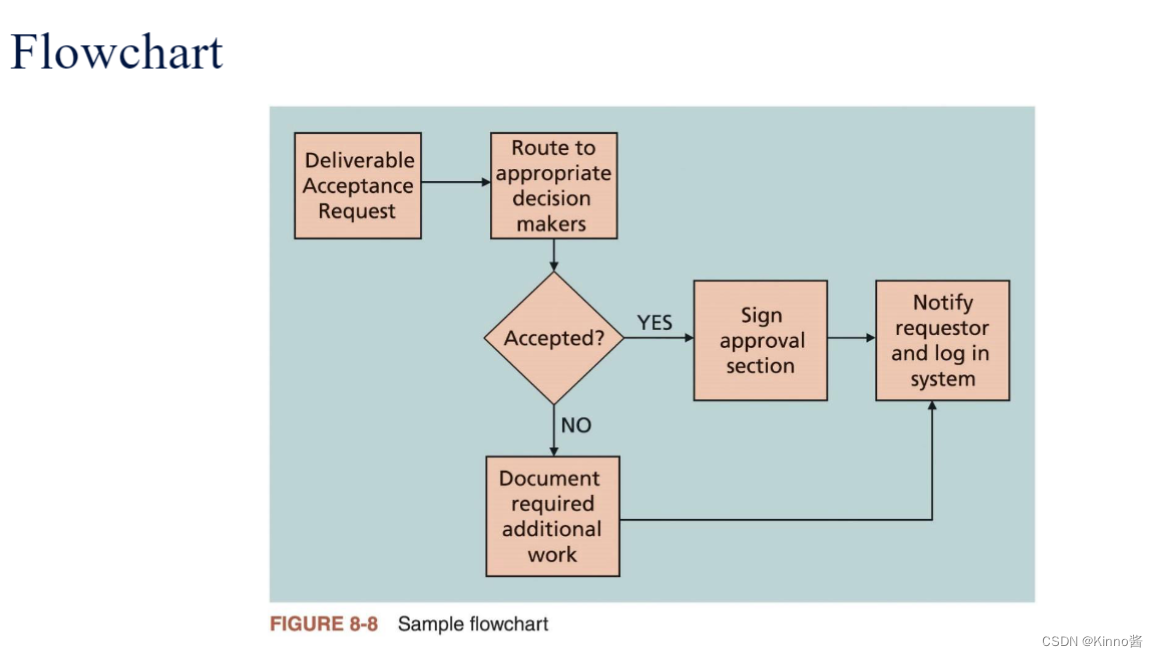
6.Flowcharts
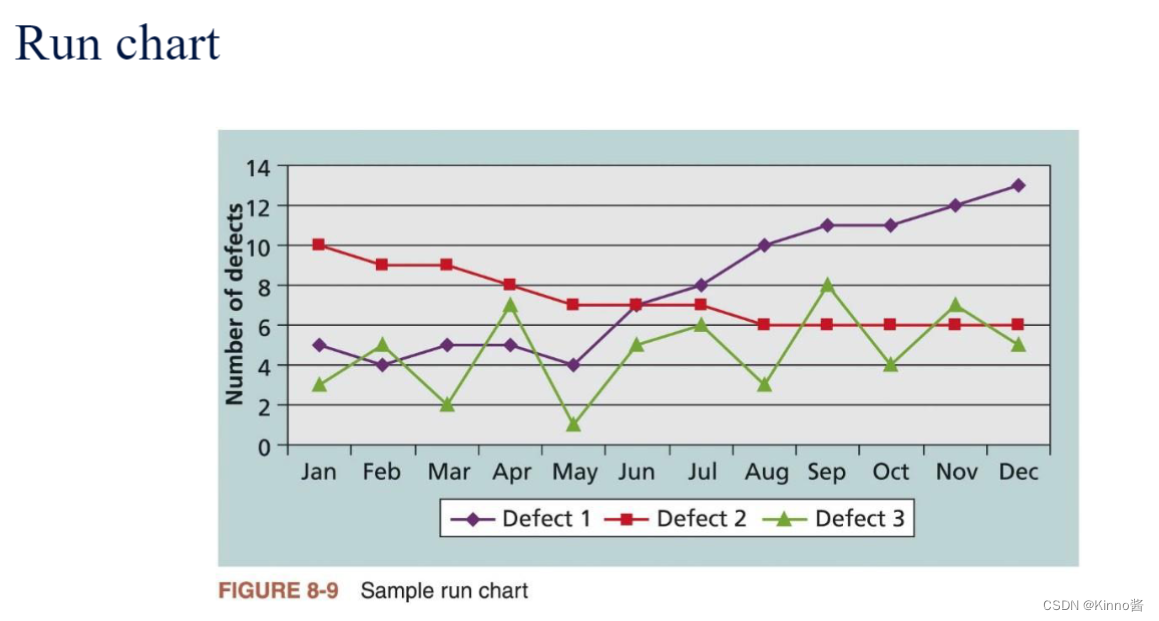
7.Run charts
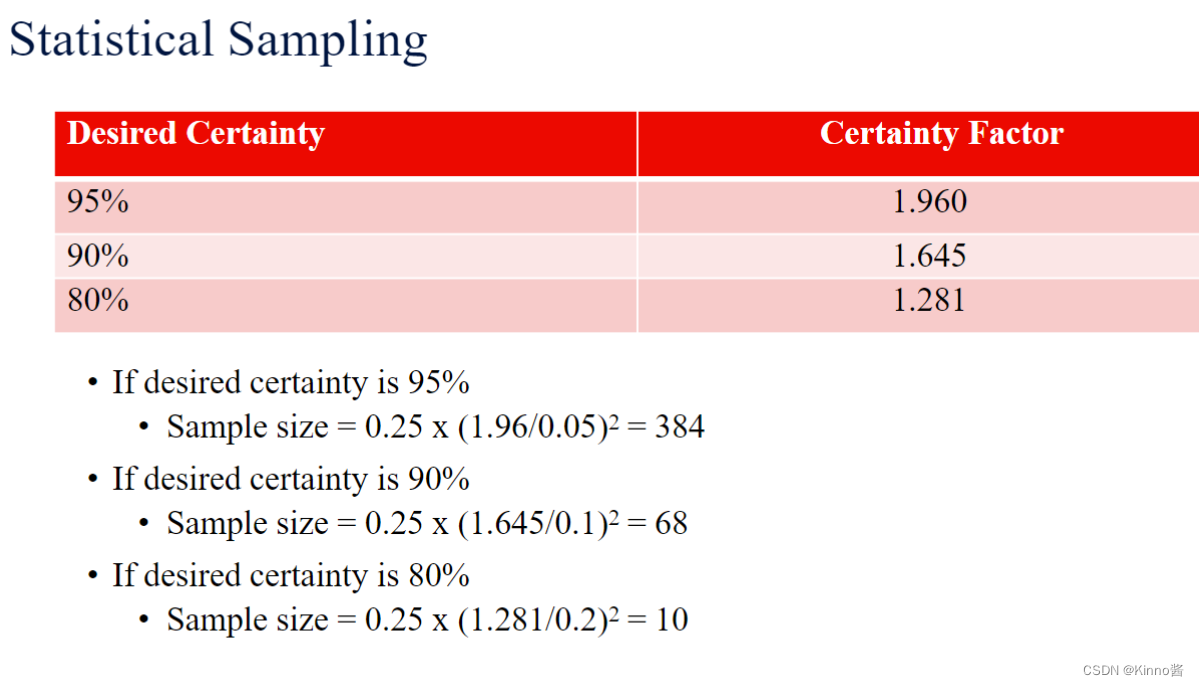
Statistical Sampling
Statistical sampling involves choosing part of a population of interest for inspection. 统计抽样涉及选择感兴趣的人群中的一部分进行检查。
- Size of a sample depends on how representative you want the sample to be 样本的大小取决于你希望样本的代表性如何
- Sample size formula
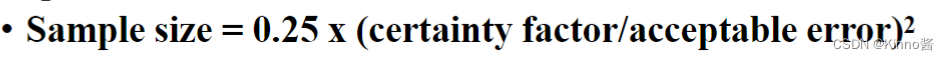
- The certainty factor denotes how confident you want to be that the sampled data includes only variations that naturally exist in the population.
- The acceptable error is related to the desired certainty and is
1
−
p
e
r
c
e
n
t
c
e
r
t
a
i
n
t
y
/
100
1 - percent certainty/100
1−percentcertainty/100. For example, if you set desired certainty to 95%, then the acceptable error is
1
−
95
/
100
=
0.05
1-95/100=0.05
1−95/100=0.05
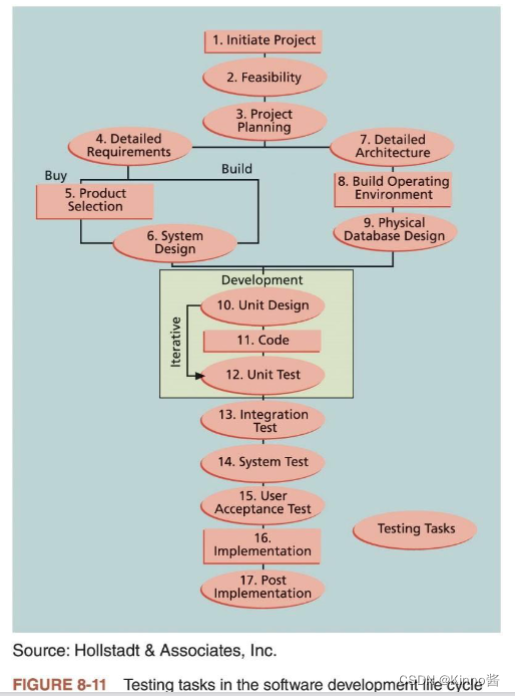
Testing
Testing needs to be done during almost every phase of the systems development life cycle, not just before the organization ships or hands over a product to the customer 测试需要在系统开发周期的几乎每一个阶段进行,而不仅仅是在组织向客户发货或移交产品之前。
Types of Testing
- Unit testing tests each individual component (often a program) to ensure it is as defect-free as possible 单元测试测试每个单独的组件(通常是一个程序)以确保它尽可能没有缺陷
- Integration testing occurs between unit and system testing to test functionally grouped components 集成测试发生在单元测试和系统测试之间,以测试功能分组的组件
- System testing tests the entire system as one entity 系统测试将整个系统作为一个实体进行测试
- User acceptance testing is an independent test performed by end users prior to
accepting the delivered system 用户验收测试是最终用户在接受交付的系统之前执行的独立测试





















 2481
2481











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








