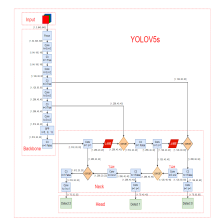
定义
利用了四张图片,对四张图片进行拼接,每一张图片都有其对应的框框,将四张图片拼接之后就获得一张新的图片,同时也获得这张图片对应的框框,然后我们将这样一张新的图片传入到神经网络当中去学习,相当于一下子传入四张图片进行学习了。论文中说这极大丰富了检测物体的背景!且在标准化BN计算的时候一下子会计算四张图片的数据!
PyTorch实现
def load_mosaic(self, index):
"""
将四张图片拼接在一张马赛克图像中
:param self:
:param index: 需要获取的图像索引
:return:
"""
# loads images in a mosaic
labels4 = [] # 拼接图像的label信息
s = self.img_size
# 随机初始化拼接图像的中心点坐标
xc, yc = [int(random.uniform(s * 0.5, s * 1.5)) for _ in range(2)] # mosaic center x, y
# 从dataset中随机寻找三张图像进行拼接
indices = [index] + [random.randint(0, len(self.labels) - 1) for _ in range(3)] # 3 additional image indices
# 遍历四张图像进行拼接 4张不同大小的图像 => 1张[1472, 1472, 3]的图像
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# load image
img, _, (h, w) = load_image(self, index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
# 创建马赛克图像 [1472, 1472, 3]
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第一张图像的右下角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第二张图像的左下角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第三张图像的右上角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, max(xc, w), min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
# 计算马赛克图像中的坐标信息(将图像填充到马赛克图像中)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
# 计算截取的图像区域信息(以xc,yc为第四张图像的左上角坐标填充到马赛克图像中,丢弃越界的区域)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
# 将截取的图像区域填充到马赛克图像的相应位置
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# 计算pad(图像边界与马赛克边界的距离,越界的情况为负值)
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels 获取对应拼接图像的labels信息
x = self.labels[index]
labels = x.copy() # 深拷贝,防止修改原数据
if x.size > 0: # Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
# 计算标注数据在马赛克图像中的
labels[:, 1] = w * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 2] = h * (x[:, 2] - x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels[:, 3] = w * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + padw
labels[:, 4] = h * (x[:, 2] + x[:, 4] / 2) + padh
labels4.append(labels)
# Concat/clip labels 把labels4([(3, 5), (3, 5), (1, 5), (1, 5)] => (8, 5))压缩到一起
if len(labels4):
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
# np.clip(labels4[:, 1:] - s / 2, 0, s, out=labels4[:, 1:]) # use with center crop
np.clip(labels4[:, 1:], 0, 2 * s, out=labels4[:, 1:]) # use with random_affine 防止越界
# affine Augment 随机仿射变换 [1472, 1472, 3] => [736, 736, 3]
# img4 = img4[s // 2: int(s * 1.5), s // 2:int(s * 1.5)] # center crop (WARNING, requires box pruning)
img4, labels4 = random_affine(img4, labels4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
border=-s // 2) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
Reference
- 链接: 代码.























 8827
8827

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








