1、使用内存泄漏工具asan需要添加编译选项
-Lasan -fsanitize=address -fsanitize-recover=address -fno-omit-frame-pointer
2、编写代码文件,如添加test_asan.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void test()
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
}
int main()
{
test();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
3、编译代码
gcc -g test_asan.c -o tt -Lasan -fsanitize=address -fsanitize-recover=address -fno-omit-frame-pointer
4、执行结果
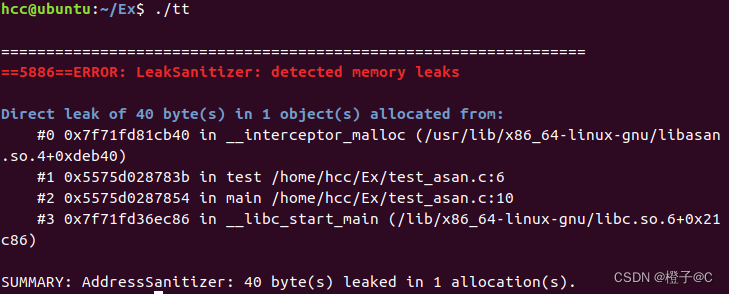
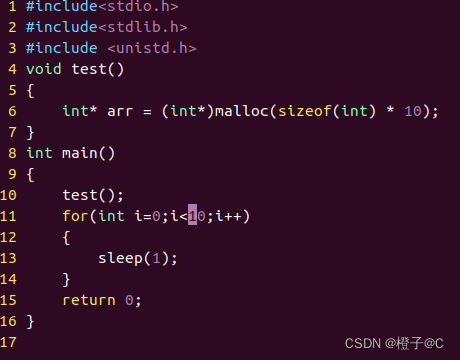
5、常见的错误类型
1、内存泄漏(Memory leaks),即申请的内存未释放,如上图所示
2、栈溢出(Stack buffer overflow),函数中的变量,参数,引用,指针,返回地址等存储在栈中,若超出栈的容量会导致栈溢出,常见情形为递归过深或申请的数组过大。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void test()
{
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 10);
}
void stack_buffer_overflow(){
long long len = 1024*1024*1024;
double a[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
a[i] = -1.0;
}
return;
}
int main()
{
// test();
stack_buffer_overflow();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
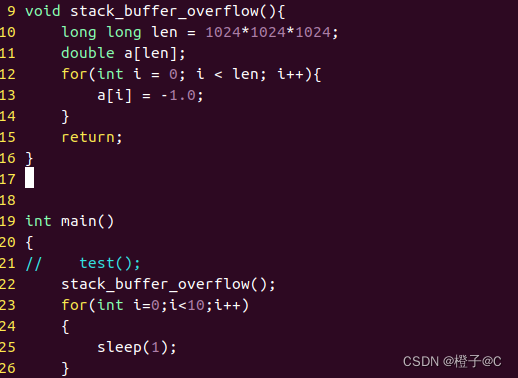
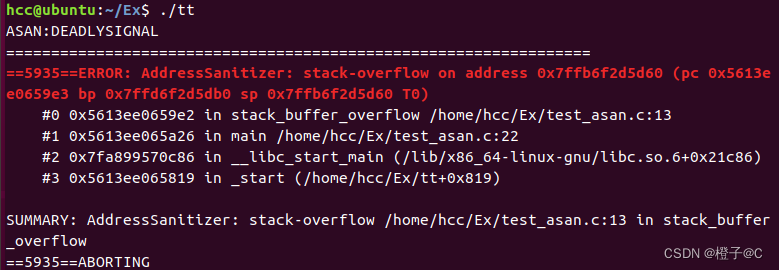
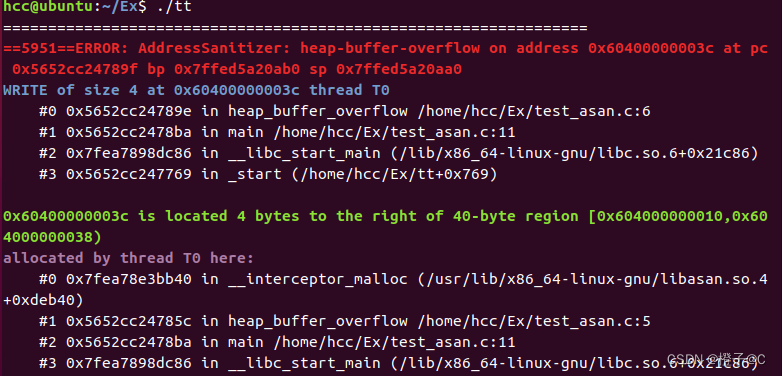
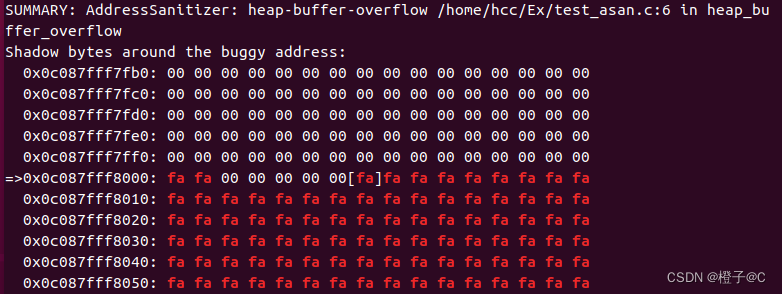
3.堆溢出(heap buffer overflow)。堆中存储动态申请内存,如malloc(), calloc(), new int[]等,常见情况为访问到申请内存之外的地址
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void heap_buffer_overflow(){
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*10);
a[11] = 1;
return;
}
int main(){
heap_buffer_overflow();
return 0;
}
 4.全局溢出(Global buffer overflow)。
4.全局溢出(Global buffer overflow)。
把超大静态数组/放到全局变量中或越界访问静态数组
























 1864
1864

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








