TO BE OR NOT TO BE
划分数据子集的算法和划分原始数据集的方法相同,直到所有具有相同类型的数据均在一个数据子集内。
通过最大特征值的选择和识别从而划分出目的数据组。
初始化选择二元切获取最简的答案,ID3,如果用CART树回归,可以跟后期学习的Adaboost
伪代码如下
def createBranch():
if so return 类标签
else
寻找划分数据集的最好特征
划分数据集
创建分支节点
for 每个划分的子集
调用函数createBranch并增加返回结果到分支节点中
return 分支节点
决策树一般流程的封装
构建数据集
def creatDataset():
dataset=[[1,1,'yes'],
[1,1,'no'],
[1,0,'no'],
[0,1,'no'],
[0,1,'no']]
labels=['no surfacing','flippers']
return dataset,labels
def creatTree(dataset,labels):
classList=[example[-1] for example in dataset]
if classList.count(classList[0])==len(classList):
return classList[0]
if len(dataset[0])==1:
return majorityNt(classList)
bestfeat=choosebestfeatureToSplit(dataset)
bestfeatlabel=labels[bestfeat]
mytree={bestfeatlabel:{}}
del(labels[bestfeat])
featValues=[example[bestfeat]for example in dataset]
uniqueVals=set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels=labels[:]
mytree[bestfeatlabel][value]=creatTree(splitDataset/(dataset,bestfeat,value),subLabels)
return mytree
分数据集的大原则 :将无序的数 变得更加 。我们 用多种方法划分数据集,但是每种方法都有各自的章数 与化学的熵增对应
from math import log
import operator
def calcShannoENt(dataset):
numEntries=len(dataset)
labelCounts={}
for featVEc in dataset:
currentLabel=featVEc[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel]=0
labelCounts[currentLabel]+=1
shannoEnt=0
for key in labelCounts:
prob=float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannoEnt-=prob*log(prob,2)
return shannoEnt
划分数据集
使用输入的三个参数:待划分的数据集、划分数据集的特征、特征的返回值。
并且选择最好的数据集划分方式
def splitDataset(dataset,axis,value):
retDataset=[]
for featvec in dataset:
reduceFeature=featvec[:axis]
reduceFeature.extend(featvec[axis+1:])
retDataset.append(reduceFeature)
return retDataset
def choosebestfeatureToSplit(dataset):
numFeature=len(dataset[0])-1
baseEntrpy=calcShannoENt(dataset)
bestinfogain=0;bestfeature=-1
for i in range(numFeature):
featList=[example[i] for example in dataset]
uniqueVals=set(featList)
newEntropy=0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataset=splitDataset(dataset,i,value)
prob=len(subDataset)/float(len(dataset))
newEntropy+=prob*calcShannoENt((subDataset))
infoGain=baseEntrpy-newEntropy
if(infoGain>bestinfogain):
bestinfogain=infoGain
bestinfogain=i
return bestfeature
在运行时并不是总在每次划分分组时候都会消耗特征,由于特征数目并不是在每次划分数据分组都减少,只需要考虑是否使用了所有属性即可,使用多数表决的方法来决定改叶子结点的分类
def majorityNt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote]=0
classCount[vote]+=1
sortedClassCount=sorted(classCount.items(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
使用matplotlib.pyplot as plt文本标注解绘制树节点
decisionNode=dict(boxstyle="Sawtooth",fc="0.8")
leafNode=dict(boxstyle="round4",fc="0.8")
arrow_args=dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt,centerPr,parentPt,nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotata(nodeTxt,xy=parentPt,xycoords='axes fraction',xytext=centerPr,textcoords='axes fraction',va="center",ha="center",bbox=nodeType,arrowprops=arrow_args)
构造注解树
# matlab的生成,未调用
# def createPlot():
# fig=plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
# fig.clf()
# createPlot().ax1=plt.subplot(111,frameon=False)
# plotNode('a decision node',(0.5,0.1),(0.1,0.5),decisionNode)
# plotNode('a leaf node',(0.8,0.1),(0.3,0.8),leafNode)
# plt.show()
def plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,txtString):
xMid=(parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0]/2.0+cntrPt[0])
yMid=(parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1]/2.0+cntrPt[1])
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid,yMid,txtString)
def plotTree(mytree,parentPt,nodeTxt):
numLeafs=getNumLeafs(mytree)
depth=getTreeDepth(mytree)
firstStr=mytree.keys()[0]
cntrPt=(plotTree.xoff+(1.0+float(numLeafs)/2.0/plotTree.yoff))
plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr,cntrPt,parentPt,decisionNode)
secondDict=mytree[firstStr]
plotTree.yoff=plotTree.yoff-1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xoff=plotTree.xoff+1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key],(plotTree.xoff,plotTree.yoff),cntrPt,leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xoff,plotTree.yoff),cntrPt,str(key))
plotTree.yoff=plotTree.yoff+1.0/plotTree.totalD
构建决策树
def createPlot(intree):
fig=plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops=dict(xticks=[],yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1=plt.subplot(111,frameon=False,**axprops)
plotTree.totalW=float(getNumLeafs(intree))
plotTree.totalD=float(getTreeDepth(intree))
plotTree.xoff=-0.5/plotTree.totalW;plotTree.yoff=1.0;
plotTree(intree,(0.5,1.0),'')
plt.show()
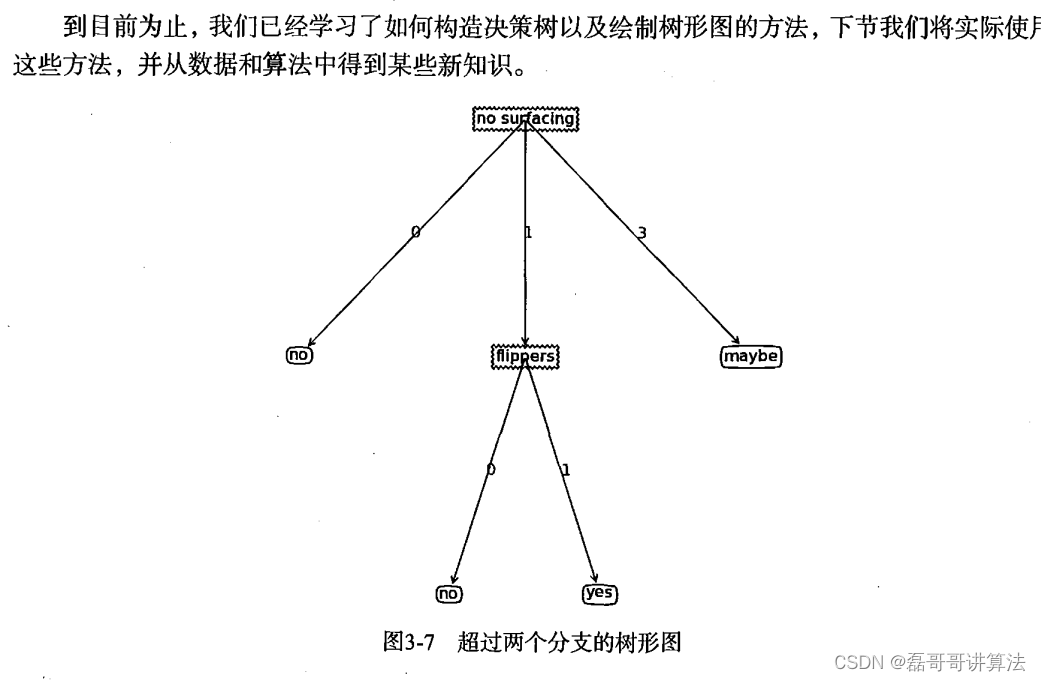
import treePlotter
import branchtree
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def retrieveTree(i):
listofTrees=[{'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flippers':{0:'no',1:'yes'}}}},{'no surfacing':{0:'no',1:{'flippers':{0:{'head':{0:'no',1:'yes'}},1:'no'}}}}]
return listofTrees[i]
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs=0
firstStr=myTree.keys()[0]
secondDict=myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs+=getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs+=1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth=0
firstStr=myTree.keys()[0]
secondDict=myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).name=='dict':
thisDepth=1+getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth=1
if thisDepth>maxDepth:
maxDepth=thisDepth
return maxDepth
总执行调用代码
import branchtree
import treePlotter
dataset,lables=branchtree.creatDataset()
# print(branchtree.splitDataset(dataset,0,0))
# branchtree.calcShannoENt(dataset)
# print(branchtree.choosebestfeatureToSplit(dataset))
# treePlotter.retrieveTree(1)
# mytree=treePlotter.retrieveTree(0)
# treePlotter.getNumLeafs(mytree)
# treePlotter.getTreeDepth(mytree)
mytree=treePlotter.retrieveTree(0)
treePlotter.createPlot(mytree)
myTree=['no surfacing'][3]='maybe'
print(mytree)























 2761
2761











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










