目录
GEMM Algorithms Numerical Behavior
cuBLAS Helper Function ReferencecublasCreate()
cuBLAS Level-1 Function Reference
使用的cuBLAS相关的API
This section describes how to use the cuBLAS library API.
Errort status
所有cuBLAS库函数调用均返回错误状态cublasStatus_t
cuBLAS 内容
应用程序必须初始化 handle到cuBLAS库上下文,方法是调用 cuBlasCreate() 功能。然后,handle被显式传递给每个后续库函数调用。应用程序使用完库后,必须调用函数cublasDestory()以释放与cuBLAS库上下文关联的资源
这种方法允许用户在使用多个主机线程和多个GPU时显式控制库设置。例如,应用程序可以使用 cudaSetDevice() 以将不同的设备与不同的主机线程相关联,并且在这些主机线程的每一个中,它可以初始化唯一的 cudaSetDevice()到cuBLAS库上下文,它将使用与该主机线程关联的特定设备。然后,使用不同的handle将自动将计算分派到不同的设备。
与特定cuBLAS上下文关联的设备假定在相应的 cublasCreate()以及cublasDestory()调用。为了使cuBLAS库在同一主机线程中使用不同的设备,应用程序必须通过调用cudaSetDevice(),然后创建另一个将与新设备关联的cuBLAS上下文,方法是调用 cublasCreate() 。
cuBLAS库上下文与CUDA上下文紧密耦合,CUDA上下文在cublasCreate() 调用。使用多个CUDA上下文的应用程序需要为每个CUDA上下文创建一个cuBLAS上下文,并确保前者的寿命永远不会超过后者。
Thread Safety
该库是线程安全的,可以从多个宿主线程调用它的函数,即使使用相同的handle也是如此。当多个线程共享同一个句柄时,更改句柄配置时需要格外小心,因为该更改可能会影响所有线程中的后续cuBLAS调用。对于手柄的破坏更是如此。因此不建议多个线程共享同一个cuBLAS handle。
结果重现
根据设计,当在具有相同架构和相同SM数量的GPU上执行时,来自给定工具包版本的所有cuBLAS API例程在每次运行时生成逐位相同的结果。然而,逐位可再现性在工具包版本之间并不保证,因为实现可能会因某些实现变化而有所不同。
这一保证仅在单个CUDA流处于活动状态时有效。如果多个并发流处于活动状态,则库可以通过挑选不同的内部实现来优化总体性能。
- 使用cublasSetWorkspace()函数为每个使用的流创建单独的工作空间,或者
- 每个流有一个cuBLAS句柄,或者
- 使用cublasLtMatmul()而不是 *gemm*()函数,并提供用户拥有的工作空间,或
- 将调试环境变量
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG设置为:16:8(可能会限制整体性能)或:4096:8(将使GPU内存中的库占用空间增加约24MiB)。
即使多个并发流共享一个cuBLAS句柄,这些设置中的任何一个都将允许确定性行为。此行为预计将在将来的版本中更改
对于某些例程,例如cublas<t>symv 以及cublas<t>hemv ,可以使用例程选择替换的明显更快的例程cublasSetAtomicsMode() 。在这种情况下,结果不能保证是逐位可再现的,因为原子用于计算。
Scalar Parameters
使用标量参数的函数有两类:
需要的函数alpha和/或 beta主机或设备上引用的参数作为缩放因子,例如gemm 。
在主机或设备上返回标量结果的函数amax(), amin,,asum(), rotg(),rotmg(),dot() and nrm2()
对于函数使用的标量,当指针模式设置为CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_HOST ,标量参数alpha 和/或 beta 可以在堆栈上或在堆上分配,不应放置在托管内存中。在下面,与这些函数相关的CUDA内核将使用值alpha 和/或 beta 。因此,如果它们是在堆上分配的,那么即使内核启动是异步的,它们也可以在调用返回后立即被释放。当指针模式设置为 CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_DEVICE ,alpha 和/或 beta 他 必须可以在设备上访问,并且在内核完成之前不应修改它们的值。请注意,由于cudaFree() 做了一个隐含的cudaDeviceSynchronize(), cudaFree()仍然可以调用 alpha 和/或 beta但在这种情况下使用此指针模式的目的将落空。
对于第二类函数,当指针模式设置为CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_HOST时,这些函数会阻塞CPU,直到GPU完成其计算并将结果复制回主机。当指针模式设置为CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_DEVICE时,这些函数将立即返回。在这种情况下,与矩阵和向量结果类似,标量结果仅在GPU上的例程执行完成时才准备就绪。这需要正确的同步以便从主机读取结果。
无论哪种情况,指针模式 CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_DEVICE都允许库函数与主机完全异步执行,即使alpha和/或beta是由以前的内核生成的。例如,当使用cuBLAS库实现用于求解线性系统和特征值问题的迭代方法时,可能会出现这种情况。
并发流
如果应用程序使用多个独立任务计算的结果,则CUDA™流可用于重叠这些任务中执行的计算。
应用可以在概念上将每个流与每个任务相关联。为了实现任务之间计算的重叠,用户应使用函数cudaStreamCreate()创建CUDA™流,并在调用实际的cuBLAS例程之前调用cublasSetStream(),设置每个单独的cuBLAS库例程使用的流。注意cublasSetStream()将用户提供的工作空间重置为默认的工作空间池;请参见cublasSetWorkspace()。然后,在GPU上可能的情况下,在单独的流中执行的计算将自动重叠。当单个任务执行的计算量相对较小,不足以填满GPU时,这种方法特别有用。
我们建议使用新的cuBLAS API,在设备内存中使用标量参数和通过引用传递的结果,以在使用流时实现计算的最大重叠。
流的一个特殊应用,批量化的多个kernel 的处理,在下面的部分中描述。
batching Kernels
在本节中,我们将解释如何使用流来批处理小内核的执行。例如,假设我们有一个应用程序,需要用稠密矩阵进行许多小的独立矩阵-矩阵乘法。
很明显,即使有数百万个小的独立矩阵,我们也不能达到同样的效果 GFLOPS 千兆位浮点运算,速率与一个大矩阵相同。例如,单个 n x n的的矩阵进行之间的乘法运算,large matrix-matrix multiplication performs n^3 operations for n^2 input size, while 1024 (n/32)^3× (n/32)^3small matrix-matrix multiplications perform 1024 (n/32)^3× (n/32)^3operations for the same input size. However, it is also clear that we can achieve a significantly better performance with many small independent matrices compared with a single small matrix.
GPU的架构家族允许我们同时执行多个内核。因此,为了批处理独立内核的执行,我们可以在单独的流中运行每个内核。特别是,在上述示例中,我们可以使用函数cudaStreamCreate()创建1024个CUDA™流,然后在每次调用 cublas<t>gemm()之前调用cublasSetStream(),为每次矩阵-矩阵乘法提供不同的流(注意,cublasSetStream()将用户提供的工作空间重置为默认工作空间池,请参见cublasSetWorkspace())。这将确保在可能的情况下同时执行不同的计算。尽管用户可以创建许多流,但实际上不可能同时执行超过32个并发内核。
Cache Configuration()
在某些设备上,一级缓存和共享内存使用相同的硬件资源。该高速缓存配置可直接使用CUDA运行时函数cudaDeviceSetCacheConfig进行设置。也可以使用cudaFuncSetCacheConfig例程专门为某些函数设置该高速缓存配置。有关该高速缓存配置设置的详细信息,请参阅CUDA Runtime API文档。
由于从一种配置切换到另一种配置会影响内核并发性,因此cuBLAS库不会设置任何缓存配置首选项,而是依赖于当前设置。但是,某些cuBLAS例程(尤其是Level-3例程)严重依赖共享内存。因此该高速缓存首选项设置可能会对其性能产生负面影响。
Static Library Support
从6.5版开始,cuBLAS库也以静态形式提供,在Linux和Mac OS上为libcublas_static. a。静态cuBLAS库和所有其他静态数学库都依赖于一个名为libculibos. a的公共线程抽象层库。
例如,在Linux上,要使用cuBLAS针对动态库编译小型应用程序,可以使用以下命令:
例如,在Linux上,要使用cuBLAS针对动态库编译小型应用程序,可以使用以下命令:
nvcc myCublasApp.c -lcublas -o myCublasApp然而,要针对静态cuBLAS库进行编译,必须使用以下命令:
nvcc myCublasApp.c -lcublas_static -lculibos -o myCublasApp也可以使用本机C++编译器。根据主机操作系统的不同,链接行上可能需要一些额外的库,如pthread或dl。建议在Linux上使用以下命令
g++ myCublasApp.c -lcublas_static -lculibos -lcudart_static -lpthread -ldl -I <cuda-toolkit-path>/include -L <cuda-toolkit-path>/lib64 -o myCublasApp注意,在后一种情况下,库cuda是不需要的。如果需要,CUDA运行时将尝试显式打开cuda库。如果系统没有安装CUDA驱动程序,这将允许应用程序妥善处理此问题,并可能在只有CPU的路径可用时运行。
从11.2版开始,使用类型化函数代替扩展函数(cublas**Ex())有助于在链接到静态cuBLAS库时减少二进制大小。
GEMM Algorithms Numerical Behavior
一些GEMM算法沿着维度K分割计算以增加GPU占用,尤其是当维度K与维度M和N相比较大时。当这种类型的算法由cuBLAS启发式算法选择或由用户显式选择时,每次拆分的结果被确定性地求和到结果矩阵中以获得最终结果。
对于例程cublas<t>gemmEx和cublasGemmEx,当计算类型大于输出类型时,分割块的总和可能导致一些中间溢出,从而产生具有一些溢出的最终结果矩阵。如果所有的点积在最后转换为输出类型之前已经在计算类型中累积,则可能不会发生这些溢出。当computeType为CUDA_R_32F且A类型、B类型和C类型为CUDA_R_16F时,这种计算副作用很容易暴露。此行为可使用计算精度模式CUBLAS_MATH_DISALLOW_REDUCED_PRECISION_REDUCTION和cublasSetMathMode()进行控制
Tensor Core Usage
张量最早是在Volta GPU(计算能力7.0或更高)中引入的,并显著加速了矩阵乘法。从cuBLAS版本11.0.0开始,库将尽可能自动使用张量核心功能,除非通过在cuBLAS中选择学究式计算模式显式禁用这些功能(请参见cublasSetMathMode(),cublasMath_t)。
应该注意的是,库将选择启用张量核的实现,只要它确定它将提供最佳性能。
从cuBLAS版本11.0.0开始,使用张量核对矩阵维数和内存对齐不再有任何限制。但是,当矩阵维数和指针满足某些内存对齐要求时,使用张量核可以实现最佳性能。具体而言,必须满足以下所有条件才能从“张量核”中获得最佳性能:
- m % 8 == 0
- k % 8 == 0
- op_B == CUBLAS_OP_N || n%8 == 0
- intptr_t(A) % 16 == 0
- intptr_t(B) % 16 == 0
- intptr_t(C) % 16 == 0
- intptr_t(A+lda) % 16 == 0
- intptr_t(B+ldb) % 16 == 0
- intptr_t(C+ldc) % 16 == 0
CUDA Graphs Support
在大多数情况下,CUBLAS例程可以在CUDA图形流捕获中捕获,而不受限制。
例外情况是将结果输出到主机缓冲区的例程(例如,<t>配置指针模式CUBLAS_POINTER_MODE_HOST时的cublas dot),因为它强制同步。
对于输入系数(如alpha、beta),行为取决于指针模式设置:
在CUBLAS(LT)_POINTER_MODE_HOST的情况下,系数值将被捕获到图形中。
在使用设备指针的指针模式下,在图形执行时使用设备指针访问系数值。
64-bit Integer Interface
cuBLAS版本12引入了支持64位整数的函数。每个64位整数函数等效于32位整数函数,但有以下更改:
-
The function name has
_64suffix. -
The dimension (problem size) data type changed from
inttoint64_t. Examples of dimension:m,n, andk. -
The leading dimension data type changed from
inttoint64_t. Examples of leading dimension:lda,ldb, andldc. -
The vector increment data type changed from
inttoint64_t. Examples of vector increment:incxandincy.
例如,请考虑以下32位整数函数:
cublasStatus_t cublasSetMatrix(int rows, int cols, int elemSize, const void *A, int lda, void *B, int ldb);
cublasStatus_t cublasIsamax(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, const float *x, int incx, int *result);
cublasStatus_t cublasSsyr(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasFillMode_t uplo, int n, const float *alpha, const float *x, int incx, float *A, int lda);等效的64位整数函数为:
cublasStatus_t cublasSetMatrix_64(int64_t rows, int64_t cols, int64_t elemSize, const void *A, int64_t lda, void *B, int64_t ldb);
cublasStatus_t cublasIsamax_64(cublasHandle_t handle, int64_t n, const float *x, int64_t incx, int64_t *result);
cublasStatus_t cublasSsyr_64(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasFillMode_t uplo, int64_t n, const float *alpha, const float *x, int64_t incx, float *A, int64_t lda);cuBLAS Datatypes
cublasHandle_t
该 cublasHandle_t 是指向保存cuBLAS库上下文的不透明结构的指针类型。必须使用以下命令初始化cuBLAS库上下文 cublasCreate() 并且返回的句柄必须被传递给所有后续的库函数调用。上下文应在最后使用 cublasDestroy()
cublasStatus_t
类型用于函数状态返回。所有cuBLAS库函数都返回其状态,这些状态可以具有以下值。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 操作已成功完成。 |
|
| cuBLAS库未初始化。这通常是由于缺少先前的 更正方法:在函数调用之前调用 |
|
| 在cuBLAS库中分配资源失败。这通常是由 更正方法:在函数调用之前,尽可能多地释放以前分配的内存。 |
|
| 向函数传递了不支持的值或参数(例如,负矢量大小)。 更正方法:确保传递的所有参数都具有有效值。 |
|
| 该功能需要器械体系结构中不存在的功能;通常由计算能力低于5.0引起。 更正方法:在具有适当计算能力的设备上编译并运行应用程序。 |
|
| GPU程序执行失败。这通常是由GPU上内核的启动失败引起的,这可能是由多种原因导致的。 纠正方法:检查硬件、适当版本的驱动程序和cuBLAS库是否已正确安装。 |
|
| 内部cuBLAS操作失败。此错误通常是由 纠正方法:检查硬件、适当版本的驱动程序和cuBLAS库是否已正确安装。此外,检查作为参数传递给例程的内存是否在例程完成之前被释放。 |
|
| 不支持请求的功能 |
|
| 请求的功能需要某些许可证,尝试检查当前许可时检测到错误。如果许可证不存在或已过期,或者环境变量NVIDIA_LICENSE_FILE未正确设置,则可能发生此错误。 |
cublasOperation_t
cublasOperation _t 类型指示需要对稠密矩阵执行哪种运算。其值对应于Fortran字符 “N” 或 “n” (非转置)、 “T” 或 “t”(转置)以及“C”或“c”(共轭转置),这些字符通常用作传统BLAS实现的参数。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 则选择非转置操作 |
|
| 选择转置操作 |
|
| 选择共轭转置运算 |
cublasDiagType_t
类型指示稠密矩阵的主对角线是否为单位,因此不应被函数触及或修改。它的值对应于Fortran字符 “N” 或 “n” (非单位)以及“U”或“u”(单位),这些字符通常用作传统BLAS实现的参数。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 矩阵对角线具有非单位元素 |
|
| 矩阵对角线具有单位元素 |
cublasSideMode_t
类型指示稠密矩阵在由特定函数求解的矩阵方程中是位于左侧还是右侧。它的值对应于Fortran字符“L”或“l”(左)以及“R”或“r”(右),这些字符通常用作传统BLAS实现的参数。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the matrix is on the left side in the equation |
|
| the matrix is on the right side in the equation |
cublasPointerMode_t
cublasPointerMode_t类型指示标量值是否通过主机或设备上的引用传递。需要指出的是,如果函数调用中存在多个标量值,则所有标量值都必须符合相同的单指针模式。指针模式可分别使用cublasSetPointerMode()和cublasGetPointerMode()例程进行设置和检索。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the scalars are passed by reference on the host |
|
| the scalars are passed by reference on the device |
cublasAtomicsMode_t
该类型指示是否可以使用具有使用原子的替代实现的cuBLAS例程。原子模式可以分别使用cublasSetAtomicsMode()和cublasGetAtomicsMode()以及例程来设置和查询。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 不允许使用原子 |
|
| 允许使用原子 |
cublasGemmAlgo_t
cublasGemmAlgo_t类型是一个枚举项,用于指定sm_75以下GPU架构上的矩阵-矩阵乘法算法。在sm_80和更新的GPU架构上,此枚举不起作用。cuBLAS具有以下算法选项:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 应用启发式技术选择GEMM算法 |
|
| 明确选择算法[0,23]。注:对NVIDIA Ampere架构GPU和更新版本没有影响。 |
|
| 此模式已弃用,并将在未来版本中删除。应用启发式来选择GEMM算法,同时允许使用精度降低的CUBLAS_COMPUTE_32F_FAST_16F内核(用于向后兼容)。 |
|
| 这些值已弃用,并将在未来版本中删除。显式选择张量核GEMM算法[0,15]。允许使用精度降低的CUBLAS_COMPUTE_32F_FAST_16F内核(用于向后兼容)。注:对NVIDIA Ampere架构GPU和更新版本没有影响。 |
cublasMath_t
cublasMath_t枚举类型在cublasSetMathMode()中用于选择计算精度模式,定义如下。由于此设置不直接控制“张量”的使用,因此不建议使用CUBLAS_TENSOR_OP_MATH模式,并将在未来版本中删除。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 这是默认且性能最高的模式,它使用计算和中间存储精度,且尾数和指数位数至少与请求的尾数和指数位数相同。将尽可能使用张量核。 |
|
| 此模式在计算的所有阶段使用规定的精度和标准化算法,主要用于数值稳健性研究、测试和调试。此模式的性能可能不如其他模式 |
|
| 使用TF32张量核启用单精度例程加速。 |
|
| 强制矩阵乘法期间的任何约简使用累加器类型(即,计算类型),而在输出类型精度小于计算类型精度的混合精度例程的情况下,不是输出类型。这是一个可以与任何其他值一起设置(使用按位或运算)的标志。 |
|
| 此模式已弃用,并将在未来版本中删除。允许库尽可能使用“张量核”操作。对于单精度GEMM例程,cuBLAS将使用CUBLAS_COMPUTE_32F_FAST_16F计算类型。 |
cublasComputeType_t
cublasComputeType_t枚举类型用于cublasGemmEx和cublasLtMatmul(包括所有批处理和跨距批处理变体),以选择计算精度模式,如下所述。
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 这是16位半精度浮点以及至少具有16位半精度的所有计算精度和中间存储精度的默认和最高性能模式。将尽可能使用张量核 |
|
| 此模式在计算的所有阶段使用16位半精度浮点标准化算法,主要用于数值鲁棒性研究、测试和调试。此模式的性能可能不如其他模式,因为它禁用张量核。 |
|
| 这是默认的32位单精度浮点,并且使用至少32位的计算和中间存储精度。. |
|
| 在计算的所有阶段使用32位单精度浮点算法,同时禁用算法优化,如高斯复杂性降低(3M)。 |
|
| 允许库使用具有自动下变频和16位半精度计算功能的张量核,用于32位输入和输出矩阵。 |
|
| 允许库使用具有自动下转换和bfloat16计算功能的张量核心,用于32位输入和输出矩阵。见 替代浮点部分了解有关bfloat16的更多详细信息。 |
|
| 允许库将张量核心与TF32计算一起用于32位输入和输出矩阵。见 替代浮点部分了解有关TF32计算的更多详细信息。 |
|
| 这是默认的64位双精度浮点,并且使用至少64位的计算和中间存储精度。 |
|
| 在计算的所有阶段使用64位双精度浮点算法,同时禁用算法优化,如高斯复杂性降低(3M)。 |
|
| Th这是默认的32位整数模式,并且使用至少32位的计算和中间存储精度。 |
|
| 在计算的所有阶段使用32位整数算法。 |
CUDA Datatypes Reference
本章介绍了由多个CUDA库共享并在头文件library_types. h中定义的类型。
cudaDataType_t
cudaDataType_t 类型是用于指定数据精度的枚举项。当数据引用本身不携带类型时使用(例如void *)
例如,它用于例程 cublasSgemmEx
| value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 数据类型是16位真实的半精度浮点 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个半精度浮点组成的32位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是16位真实的bfloat16浮点 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个bfloat16浮点组成的32位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是32位真实的单精度浮点 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个单精度浮点组成的64位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是64位真实的双精度浮点 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个双精度浮点组成的128位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是8位带符号实整数 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个8位有符号整数组成的16位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是8位无符号真实的整数 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个8位无符号整数组成的16位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是32位带符号实整数 |
|
| 数据类型是由表示复数的两个32位有符号整数组成的64位结构。 |
|
| 数据类型是E4M3格式的8位真实的浮点 |
|
| 数据类型是E5M2格式的8位真实的浮点 |
libraryPropertyType_t
该 libraryPropertyType_t 用作参数,指定使用例程时请求哪个属性cublasGetProperty
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 用于查询主版本的枚举项 |
|
| 用于查询次版本的枚举项 |
|
| 用于标识修补程序级别的编号 |
cuBLAS Helper Function Reference
cublasCreate()
cublasStatus_t
cublasCreate(cublasHandle_t *handle)此函数用于初始化cuBLAS库,并为保存cuBLAS库上下文的不透明结构创建句柄。它分配主机和设备上的硬件资源,必须在调用任何其它cuBLAS库之前调用。cuBLAS库上下文绑定到当前CUDA设备。要在多个设备上使用库,需要为每个设备创建一个cuBLAS handel。此外,对于给定的设备,可以创建具有不同配置的多个cuBLAS handel。因为 cublasCreate() 分配一些内部资源,并通过调用cublasDestroy() 将隐式调用 cublasDeviceSynchronize() ,建议尽量减少cublasCreate()/cublasDestroy()事件。对于从不同线程使用相同设备的多线程应用程序,建议的编程模型是为每个线程创建一个cuBLAS句柄,并在线程的整个生命周期中使用该cuBLAS句柄。
| Return Value | Meaning 意义 |
|---|---|
|
| 初始化成功 |
|
| CUDA™运行时初始化失败 |
|
| 无法分配资源 |
|
|
|
cublasDestroy()
cublasStatus_t
cublasDestroy(cublasHandle_t handle)此函数用于释放cuBLAS库使用的硬件资源。此函数通常是使用特定句柄对cuBLAS库进行的最后一次调用。因为cublasCreate() 分配一些内部资源,并通过调用 cublasDestroy() 将隐式调用 cublasDeviceSynchronize() ,建议尽量减少cublasCreate()/cublasDestroy() 事件。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 关闭成功 |
|
| 存储库未初始化 |
cublasGetVersion()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetVersion(cublasHandle_t handle, int *version)
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| 操作成功完成 |
|
| 为库版本号提供的存储未初始化(NULL) |
cublasGetProperty()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetProperty(libraryPropertyType type, int *value)此函数返回value指向的内存中所请求属性的值。参考libraryPropertyType用于支持的类型
| Return Value 返回值 | Meaning 意义 |
|---|---|
|
| 操作已成功完成 |
|
| 类型值无效
|
cublasGetProperty()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetProperty(libraryPropertyType type, int *value)此函数返回value指向的内存中所请求属性的值。参考 libraryPropertyType用于支持的类型。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| The operation completed successfully |
|
| Invalid type value
|
cublasGetStatusName()
const char* cublasGetStatusName(cublasStatus_t status)This function returns the string representation of a given status.
cublasGetStatusString()
const char* cublasGetStatusString(cublasStatus_t status)This function returns the description string for a given status.
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NULL-terminated string | The description of the |
cublasSetStream()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetStream(cublasHandle_t handle, cudaStream_t streamId)此函数用于设置cuBLAS库流,该库流将用于执行对cuBLAS库函数的所有后续调用。如果未设置cuBLAS库流,则所有内核都使用defaultNULL流。特别是,此例程可用于在内核启动之间更改流,然后将cuBLAS库流重置回NULL。此外,此函数无条件地将cuBLAS库工作空间重置回默认工作空间池(请参见cublasSetWorkspace())。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the stream was set successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
cublasGetStream()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetStream(cublasHandle_t handle, cudaStream_t *streamId)此函数用于获取cuBLAS库流,该库流用于执行对cuBLAS库函数的所有调用。如果未设置cuBLAS库流,则所有内核都使用defaultNULL流。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the stream was returned successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
|
|
cublasGetPointerMode()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetPointerMode(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasPointerMode_t *mode)此函数用于获取cuBLAS库使用的指针模式。更多细节请参见cublasPointerMode_t类型部分。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the pointer mode was obtained successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
|
|
cublasSetPointerMode()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetPointerMode(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasPointerMode_t mode)此函数用于设置cuBLAS库使用的指针模式。默认情况下,这些值将通过主机上的引用传递。更多细节请参见cublasPointerMode_t类型部分。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the pointer mode was set successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
|
|
cublasSetVector()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetVector(int n, int elemSize,
const void *x, int incx, void *y, int incy)This function supports the 64-bit Integer Interface.
此函数将主机内存空间中的向量x的n个元素复制到GPU内存空间中的向量y。假设两个向量中的元素都具有elemSize字节的大小。连续元素之间的存储间隔对于源向量x由incx给出,对于目标向量y由incy给出。
由于假定二维矩阵采用以列为主的格式,因此如果向量是矩阵的一部分,则向量增量等于1时将访问该矩阵的(部分)列。类似地,使用等于矩阵的前导维度的增量导致对该矩阵的(部分)行的访问。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasGetVector()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetVector(int n, int elemSize,
const void *x, int incx, void *y, int incy)此函数支持64位整数接口。
此函数将GPU内存空间中的向量x中的n个元素复制到主机内存空间中的向量y。假设两个向量中的元素都具有elemSize字节的大小。连续元素之间的存储间隔由源向量的incx和目标向量y的incy给出。
由于假定二维矩阵采用以列为主的格式,因此如果向量是矩阵的一部分,则向量增量等于1时将访问该矩阵的(部分)列。类似地,使用等于矩阵的前导维度的增量导致对该矩阵的(部分)行的访问。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasSetMatrix()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetMatrix(int rows, int cols, int elemSize,
const void *A, int lda, void *B, int ldb)此函数支持64位整数接口。
此函数将行x列元素的平铺从主机内存空间中的矩阵A复制到GPU内存空间中的矩阵B。假设每个元素需要存储elemSize字节,并且两个矩阵都以列为主格式存储,源矩阵A和目标矩阵B的前导维度分别以lda和ldb给出。前导维指示分配的矩阵的行数,即使仅使用其子矩阵。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasGetMatrix()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetMatrix(int rows, int cols, int elemSize,
const void *A, int lda, void *B, int ldb)此函数支持64位整数接口。
此函数将行x列元素的瓦片从GPU内存空间中的矩阵A复制到主机内存空间中的矩阵B。假设每个元素需要存储elemSize字节,并且两个矩阵都以列为主格式存储,源矩阵A和目标矩阵B的前导维度分别以lda和ldb给出。前导维指示分配的矩阵的行数,即使仅使用其子矩阵。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasGetVectorAsync()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetVectorAsync(int n, int elemSize, const void *devicePtr, int incx,
void *hostPtr, int incy, cudaStream_t stream)该函数与cublasGetVector()具有相同的功能,不同之处在于数据传输是使用给定的CUDA™流参数异步完成的(相对于主机)。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasSetVectorAsync()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetVectorAsync(int n, int elemSize, const void *hostPtr, int incx,
void *devicePtr, int incy, cudaStream_t stream)此函数支持64位整数接口。
该函数与cublasSetVector()具有相同的功能,不同之处在于数据传输是使用给定的CUDA™流参数异步完成的(相对于主机)。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasSetMatrixAsync()
cublasStatus_t
cublasSetMatrixAsync(int rows, int cols, int elemSize, const void *A,
int lda, void *B, int ldb, cudaStream_t stream)此函数支持64位整数接口。
该函数与cublasSetMatrix()具有相同的功能,不同之处在于数据传输是使用给定的CUDA™流参数异步完成的(相对于主机)。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasGetMatrixAsync()
cublasStatus_t
cublasGetMatrixAsync(int rows, int cols, int elemSize, const void *A,
int lda, void *B, int ldb, cudaStream_t stream)此函数支持64位整数接口。
该函数与cublasGetMatrix()具有相同的功能,不同之处在于数据传输是使用给定的CUDA™流参数异步完成的(相对于主机)。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the parameters |
|
| there was an error accessing GPU memory |
cublasSetAtomicsMode()
cublasStatus_t cublasSetAtomicsMode(cublasHandlet handle, cublasAtomicsMode_t mode)一些例程,如<t>cublassymv和cublashemv<t>,有一个替代的实现,使用原子来累积结果。这种实现通常明显更快,但可能生成的结果在一次运行与其他运行之间并不完全相同。从数学上讲,这些不同的结果并不重要,但在调试时,这些差异可能是有害的。
此函数允许或不允许在cuBLAS库中为具有替代实现的所有例程使用原子。如果未在任何cuBLAS例程的文档中明确指定,则意味着此例程没有使用原子的替代实现。禁用原子模式时,当在同一硬件上使用相同参数调用时,每个cuBLAS例程从一次运行到另一次运行应产生相同的结果。
默认初始化的cublasHandle_t对象的默认原子模式为CUBLAS_ATOMICS_NOT_ALLOWED。有关详细信息,请参阅类型部分。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the atomics mode was set successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
cublasGetAtomicsMode()
cublasStatus_t cublasGetAtomicsMode(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasAtomicsMode_t *mode)此函数用于查询特定cuBLAS上下文的原子模式。
默认初始化的cublasHandle_t对象的默认原子模式为CUBLAS_ATOMICS_NOT_ALLOWED。有关详细信息,请参阅类型部分。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the atomics mode was queried successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the argument |
cublasSetMathMode()
cublasStatus_t cublasSetMathMode(cublasHandle_t handle, cublasMath_t mode)cublasSetMathMode函数用于选择cublasMath_t定义的计算精度模式(请参见cublasMath_t)。允许用户将计算精度模式设置为它们的逻辑组合(不推荐使用的CUBLAS_TENSOR_OP_MATH除外)。例如,cublasSetMathMode(handle, CUBLAS_DEFAULT_MATH | CUBLAS_MATH_DISALLOW_REDUCED_PRECISION_REDUCTION)。请注意,默认数学模式为CUBLAS_DEFAULT_MATH。
有关cublasGemmEx()和cublasLtMatmul()API及其跨距变体允许的矩阵和计算精度,请参阅:立方GemmEx()、立方GemmBatchedEx()、立方GemmStridedBatchedEx()和立方LtMatmul()。
cublasGetSmCountTarget()
cublasStatus_t cublasGetSmCountTarget(cublasHandle_t handle, int *smCountTarget)此函数获取先前编程到库句柄的值。
| Return Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| SM count target was set successfully. |
|
| smCountTarget is NULL. |
|
| the library was not initialized. |
cublasLoggerConfigure()
cublasStatus_t cublasLoggerConfigure(
int logIsOn,
int logToStdOut,
int logToStdErr,
const char* logFileName)此函数用于在运行时配置日志记录。除了这种类型的配置之外,还可以使用特殊的环境变量来配置日志记录,这些变量将由libcublas进行检查:
CUBLAS_LOGINFO_DBG -设置环境变量为“1”表示打开日志记录(默认情况下日志记录关闭)。
CUBLAS_LOGDEST_DBG -设置环境变量编码如何记录。“stdout”、“stderr”分别表示将日志消息输出到stdout或stderr。在另一种情况下,它指定文件的“文件名”。
参数
logIsOn
输入。完全打开/关闭日志记录。默认情况下处于禁用状态,但通过调用cublasSetLoggerCallback到用户定义的回调函数可以启用。
logToStdOut
输入。打开/关闭标准错误I/O流的日志记录。默认情况下处于禁用状态。
logToStdErr
输入。打开/关闭标准错误I/O流的日志记录。默认情况下处于禁用状态。
logFileName
输入。打开/关闭记录到文件系统中由文件名指定的文件。cublasLogger配置logFileName的复制内容。如果您对这种类型的日志记录不感兴趣,则应该提供空指针。
返回
立方体_状态_成功
成功。
cublasGetLoggerCallback()
cublasStatus_t cublasGetLoggerCallback(
cublasLogCallback* userCallback)此函数通过cublasSetLoggerCallback或其他方式获取指向先前安装的自定义用户定义回调函数的函数指针。
参数
userCallback
输出。指向用户定义的回调函数的指针。
下面列出了此函数返回的可能错误值及其含义。
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
|
|
cublasSetLoggerCallback()
cublasStatus_t cublasSetLoggerCallback(
cublasLogCallback userCallback)此函数通过cublas C公共API安装自定义回调函数。
参数
userCallback
输入。指向用户定义的回调函数的指针。
Returns
立方体_状态_成功
成功。
cuBLAS Level-1 Function Reference
在本章中,我们将介绍执行标量和向量运算的一级基本线性代数子程序(BLAS1)函数。我们将使用缩写<type>表示type,<t>表示相应的短类型,以便更简洁、更清楚地表示所实现的函数。除非另有说明<,类型>和<t>具有以下含义:
| <type> | <t> | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
| ‘s’ or ‘S’ | real single-precision |
|
| ‘d’ or ‘D’ | real double-precision |
|
| ‘c’ or ‘C’ | complex single-precision |
|
| ‘z’ or ‘Z’ | complex double-precision |
当函数的参数和返回值不同时(复杂输入时有时会发生这种情况),<t>也可以具有以下含义Sc、Cs、Dz和Zd。


cublasI<t>amax()
cublasStatus_t cublasIsamax(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIdamax(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIcamax(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIzamax(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx, int *result)此函数支持64位整数接口。

| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with elements. |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| result | host or device | output | the resulting index, which is |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the reduction buffer could not be allocated |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
|
|
|
cublasI<t>amin()
cublasStatus_t cublasIsamin(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIdamin(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIcamin(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx, int *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasIzamin(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx, int *result)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with elements. |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| result | host or device | output | the resulting index, which is |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the reduction buffer could not be allocated |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
|
|
|
cublas<t>asum()
cublasStatus_t cublasSasum(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx, float *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasDasum(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx, double *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasScasum(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx, float *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasDzasum(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx, double *result)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with elements. |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| result | host or device | output | the resulting index, which is |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the reduction buffer could not be allocated |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
|
|
|
cublas<t>axpy()
cublasStatus_t cublasSaxpy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *alpha,
const float *x, int incx,
float *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasDaxpy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *alpha,
const double *x, int incx,
double *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasCaxpy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *alpha,
const cuComplex *x, int incx,
cuComplex *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasZaxpy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *alpha,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| alpha | host or device | input | <type> scalar used for multiplication. |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
#include <iostream>
#include "cublas_v2.h"
#define N 10
int main() {
float a[N], b[N], c[N];
float *dev_a, *dev_b, *dev_c;
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i) // 为数组a、b赋值
{
float tmp = 1.0 * i;
a[i] = tmp;
b[i] = tmp * tmp;
}
cublasHandle_t handle; // 申明句柄
cublasCreate_v2(&handle); // 创建句柄
cudaMalloc(&dev_a, sizeof(float) * N);
cudaMalloc(&dev_b, sizeof(float) * N);
//
float alpha = 1.0;
cublasSetVector(N, sizeof(float), a, 1, dev_a, 1); // H2D host to device
cublasSetVector(N, sizeof(float), b, 1, dev_b, 1);
cublasSaxpy_v2(handle, N, &alpha, dev_a, 1, dev_b, 1); //实现向量+
cublasGetVector(N, sizeof(float), dev_b, 1, c, 1); // D2H
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
cublasDestroy(handle); // 销毁句柄
for(int i=0; i<N; ++i)
{
printf("%f + %f * %f = %f \n", a[i], b[i],b[i], c[i]);
}
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
cublas<t>copy()
cublasStatus_t cublasScopy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx,
float *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasDcopy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx,
double *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasCcopy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx,
cuComplex *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasZcopy(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | output | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
cublas<t>dot()
cublasStatus_t cublasSdot (cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx,
const float *y, int incy,
float *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasDdot (cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx,
const double *y, int incy,
double *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasCdotu(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx,
const cuComplex *y, int incy,
cuComplex *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasCdotc(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx,
const cuComplex *y, int incy,
cuComplex *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasZdotu(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
const cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy,
cuDoubleComplex *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasZdotc(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
const cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy,
cuDoubleComplex *result)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vectors | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | input | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| result | host or device | output | the resulting dot product, which is |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the reduction buffer could not be allocated |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
cublas<t>nrm2()
cublasStatus_t cublasSnrm2(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *x, int incx, float *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasDnrm2(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *x, int incx, double *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasScnrm2(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *x, int incx, float *result)
cublasStatus_t cublasDznrm2(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx, double *result)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | input | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| result | host or device | output | the resulting norm, which is |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the reduction buffer could not be allocated |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
|
|
|
cublas<t>rot()
cublasStatus_t cublasSrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
float *x, int incx,
float *y, int incy,
const float *c, const float *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasDrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
double *x, int incx,
double *y, int incy,
const double *c, const double *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasCrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
cuComplex *x, int incx,
cuComplex *y, int incy,
const float *c, const cuComplex *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasCsrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
cuComplex *x, int incx,
cuComplex *y, int incy,
const float *c, const float *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasZrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy,
const double *c, const cuDoubleComplex *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasZdrot(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx,
cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy,
const double *c, const double *s)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vectors | |
| x | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| c | host or device | input | cosine element of the rotation matrix. |
| s | host or device | input | sine element of the rotation matrix. |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
cublas<t>rotg()
cublasStatus_t cublasSrotg(cublasHandle_t handle,
float *a, float *b,
float *c, float *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasDrotg(cublasHandle_t handle,
double *a, double *b,
double *c, double *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasCrotg(cublasHandle_t handle,
cuComplex *a, cuComplex *b,
float *c, cuComplex *s)
cublasStatus_t cublasZrotg(cublasHandle_t handle,
cuDoubleComplex *a, cuDoubleComplex *b,
double *c, cuDoubleComplex *s)此函数支持64位整数接口。
此函数用于构造Givens旋转矩阵

| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| a | host or device | in/out | <type> scalar that is overwritten with r. |
| b | host or device | in/out | <type> scalar that is overwritten with z. |
| c | host or device | output | cosine element of the rotation matrix. |
| s | host or device | output | sine element of the rotation matrix. |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
For references please refer to:
cublas<t>rotm()
cublasStatus_t cublasSrotm(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, float *x, int incx,
float *y, int incy, const float* param)
cublasStatus_t cublasDrotm(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, double *x, int incx,
double *y, int incy, const double* param)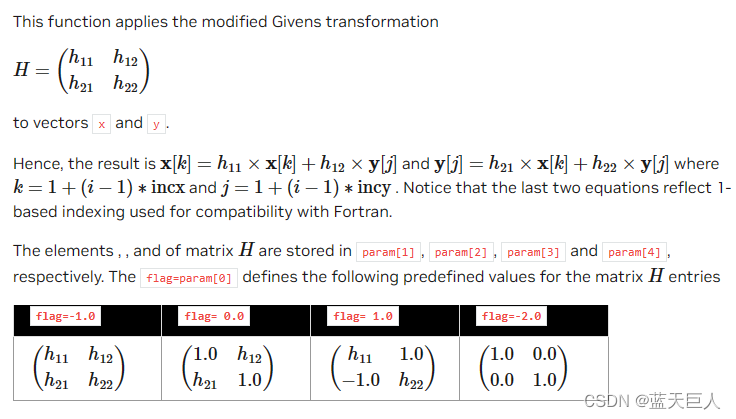
Notice that the values -1.0, 0.0 and 1.0 implied by the flag are not stored in param.
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vectors | |
| x | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| param | host or device | input | <type> vector of 5 elements, where |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
For references please refer to:
cublas<t>rotmg()
cublasStatus_t cublasSrotmg(cublasHandle_t handle, float *d1, float *d2,
float *x1, const float *y1, float *param)
cublasStatus_t cublasDrotmg(cublasHandle_t handle, double *d1, double *d2,
double *x1, const double *y1, double *param)此函数支持64位整数接口。
此函数用于构造修改后的Givens变换
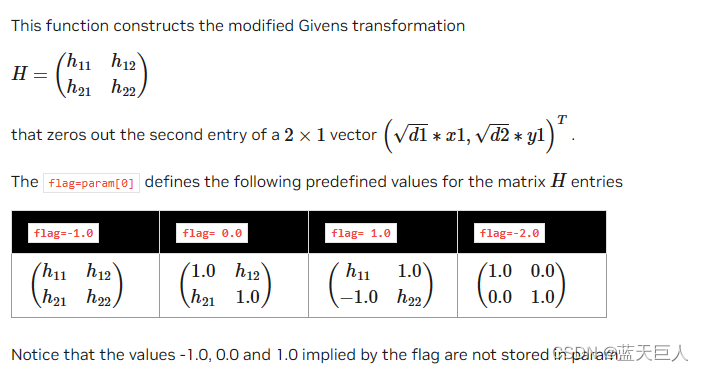
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| d1 | host or device | in/out | <type> scalar that is overwritten on exit. |
| d2 | host or device | in/out | <type> scalar that is overwritten on exit. |
| x1 | host or device | in/out | <type> scalar that is overwritten on exit. |
| y1 | host or device | input | <type> scalar. |
| param | host or device | output | <type> vector of 5 elements, where |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |
cublasStatus_t cublasSscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *alpha,
float *x, int incx)
cublasStatus_t cublasDscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *alpha,
double *x, int incx)
cublasStatus_t cublasCscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuComplex *alpha,
cuComplex *x, int incx)
cublasStatus_t cublasCsscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const float *alpha,
cuComplex *x, int incx)
cublasStatus_t cublasZscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const cuDoubleComplex *alpha,
cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx)
cublasStatus_t cublasZdscal(cublasHandle_t handle, int n,
const double *alpha,
cuDoubleComplex *x, int incx)
| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| alpha | host or device | input | <type> scalar used for multiplication. |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
:class: table-no-stripes
Error Value
Meaning
CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS
the operation completed successfully
CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED
the library was not initialized
CUBLAS_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED
the function failed to launch on the GPU
cublas<t>swap()
cublasStatus_t cublasSswap(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, float *x,
int incx, float *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasDswap(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, double *x,
int incx, double *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasCswap(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, cuComplex *x,
int incx, cuComplex *y, int incy)
cublasStatus_t cublasZswap(cublasHandle_t handle, int n, cuDoubleComplex *x,
int incx, cuDoubleComplex *y, int incy)

| Param. | Memory | In/out | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| handle | input | handle to the cuBLAS library context. | |
| n | input | number of elements in the vector | |
| x | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incx | input | stride between consecutive elements of | |
| y | device | in/out | <type> vector with |
| incy | input | stride between consecutive elements of |
The possible error values returned by this function and their meanings are listed below.
| Error Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
| the operation completed successfully |
|
| the library was not initialized |
|
| the function failed to launch on the GPU |





















 7851
7851











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








