存储结构
采用邻接表保存图的信息,从文本文件中读取相关点的信息,构建邻接表。
文本文件信息保存顺序:第一个int型数字,保存当前点数(V0 还是V1)。第二个字符,保存顶点名称(A或者B)。此处理论上应该可以保存一个字符串,因为在设计时,使用string类型存储。第三个int型数据,保存当前景点票价。第四个int型数据,保存当前顶点和其他顶点存在多少条边,便于在后序构建邻接表时,知道需要循环几次。此后每个数据,依次是和该顶点相关联的顶点的坐标,两者之间的权值。
例如:0 A 100 2 1 5 5 8
表示该顶点是下标为0的顶点,名字为A,票价100¥,与之相连的有两个顶点,分别是下标为1、权值为5和下标为5、权值为8的顶点。
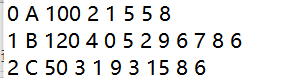
数据结构设计
1. 顶点结构设计
typedef struct VertexNode{
string data;
int money;
EdgeNode *First;
}VertexNode;
2. 边结构设计
typedef struct EdgeNode{
int vertex;
int weight;
struct EdgeNode *next;
}EdgeNode;
3.类设计
class Graph {
private:
//顶点数组
VertexNode G[numVertex];
//保存遍历时已经遍历过的顶点
bool visited[numVertex];
//深度优先递归算法
void Dfs(const int n,string &s);
public:
Graph();
~Graph();
//获取图的顶点
VertexNode getVertex(const int n);
//获得图的顶点和边
void createGraph();
//深度遍历
string DfsTraverse(const int a);
//最短路径
void shortestPath(const int V1,const int V2,QTextEdit* T);
//最小生成树
void minimumSpanningTree(QTextEdit* T);
};
读取函数
void Graph::createGraph()
{
ifstream ifs;
int Vertex = 0;
string s;
ifs.open(R"(D:\CLion\Graph\graph.txt)",ios::in);
if(ifs.is_open()){
int edges = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < numVertex;i++) {
ifs >> Vertex; //读取顶点下标
ifs >> G[Vertex].data; //读取顶点名称 (A、B...)
ifs >> G[Vertex].money; //读取票价
ifs >> edges; //读取边数
//读取边的信息
EdgeNode *e = (EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof (EdgeNode));
ifs >> e->vertex;
ifs >> e->weight;
G[Vertex].First = e;
EdgeNode *p = e;
for (int j = 1;j < edges;j++) {
auto *e = (EdgeNode*)malloc(sizeof (EdgeNode));
ifs >> e->vertex;
ifs >> e->weight;
e->next = nullptr;
p->next = e;
p = e;
}
cout << endl;
}
}else{
cout << "The File is not found!!!" << endl;
}
ifs.close();
}
景点信息查询
景点信息查询实现较为简单,通过输入点的下标,返回对应的顶点的信息
QInputDialog 可以自行百度,此处不多加赘述。
void MainWindow::on_pushButton_2_clicked()
{
bool OK = true;
int n = QInputDialog::getInt(this,"","please input number",1,1,9,1,&OK);
if(OK){
string s = graph.getVertex(n-1).data + "\nTicket prices: " + to_string(graph.getVertex(n-1).money);
ui->textEdit_2->setText(QString::fromStdString(s));
}
}
遍历整个景区
遍历算法,一般有深度遍历以及层序遍历两种。此处采用深度遍历递归算法(学校作业要求)。
深度遍历思路:在当前顶点的邻接顶点中还有未被访问过的顶点时,就访问其中一个未被访问的顶点。
void Graph::Dfs(const int n,string &s)
{
EdgeNode *p = nullptr;
visited[n] = true;
cout << G[n].data << " " ;
s = s + G[n].data + " ";
p = G[n].First;
while (p){
if (! visited[p->vertex]){
Dfs(p->vertex,s);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
string Graph::DfsTraverse(const int a)
{
for (bool & i : visited){
i = false;
}
string s;
cout << "The Traversal path :" << endl;
for (int j = a;j < numVertex + a;j++){
if (! visited[j % numVertex]){
Dfs(j % numVertex,s);
}
}
for (int i = 0;i < numVertex;i++){
if (visited[i]){
cout << i << endl;
}
}
return s;
}
最短路径
最短路径寻求方法:迪杰斯科拉算法 佛洛依德算法
此处采用迪杰斯科拉算法
该算法原理:初始化最短距离数组为起点到其他点的距离,找其中距离最短的加入路径中。并根据加入的点,从起点经过改点到其他点距离是否变短。如果变短,更新当前点的距离。直至所有的点都被访问过。
因为使用距离矩阵更容易实现此算法,所以利用邻接表中的边信息创建一个距离矩阵
利用一个数组来保存路径信息。
void Graph::shortestPath(const int V1,const int V2,QTextEdit* T)
{
//find数组保存当前点是从哪个点过来的,便于恢复路径经过的点
int find[numVertex];
bool visit[numVertex];
for (int i = 0;i < numVertex;i++){
visit[i] = false;
find[i] = V1;
}
//距离矩阵
int path[numVertex][numVertex];
//构建距离矩阵
for (int i = 0;i < numVertex;i++){
for (int j = 0;j <numVertex;j++){
path[i][j] = INF;
}
EdgeNode *p = G[i].First;
while (p != nullptr){
path[i][p->vertex] = p->weight;
p = p->next;
}
path[i][i] = 0;
}
//初始化边的信息
int min = INF;
//选择V1为起始点,将V1的边的信息存入初始d[]中
visit[V1] = true;
int d[numVertex];
for (int i = 0;i < numVertex;i++){
d[i] = path[V1][i];
}
//u存储当前找到的最短路径的中的点
int u = V1;
for (int i = 1;i < numVertex;i++){
min = INF; //最小值初始化为一个较大的值
for (int j = 0;j < numVertex;j++){
if (! visit[j] && d[j] < min){
u = j;
min = d[j];
}
}
//将找到的u的点存为已经访问
visit[u] = true;
for (int k = 0;k < numVertex;k++){
if (! visit[k] && d[k] > d[u] + path[u][k]){
d[k] = d[u] + path[u][k];
find[k] = u;
}
}
}
//输出最短路径
T->setText("");
cout << "The shortest path from " + G[V1].data +" to " + G[V2].data +" :" << endl;
T->append(QString::fromStdString("The shortest path from " + G[V1].data +" to " + G[V2].data +" :"));
int f = V2;
string s;
while ((f != V1) && (f < numVertex)){
cout << G[f].data + " <- ";
s = s + G[f].data + " <- ";
f = find[f];
}
cout << G[V1].data << endl;
s = s + G[V1].data ;
T->append(QString::fromStdString(s));
cout << "The value is : " << d[V2];
T->append(QString::fromStdString("The value is : " + to_string(d[V2]) + "\n"));
cout << endl;
}
最小生成树
(最小成本问题)
最小生成树算法:普利姆算法 克鲁斯卡尔算法
此处采用:普利姆算法
该算法原理:从当前已经访问过的顶点集合中找与之相关联的未访问过的顶点中权值最小的边加入最小生成树,并且将该顶点加入已经访问的顶点集合
void Graph::minimumSpanningTree(QTextEdit* T)
{
bool visit[numVertex];
for (bool & i : visit){
i = false;
}
int min = INF;
visit[0] = true;
EdgeNode *p = nullptr;
int curr_V = 0;
int pre_V = 0;
int find[numVertex];
for (int i = 1;i < numVertex;i++){
min = INF;
for (int j = 0;j < numVertex;j++){
if(visit[j]){
p = G[j].First;
while (p != nullptr){
if (! visit[p->vertex] && min > p->weight){
min = p->weight;
curr_V = p->vertex;
pre_V = j;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
find[curr_V] = pre_V;
visit[curr_V] = true;
}
T->setText("");
for (int i = 1;i < numVertex;i++){
cout << G[i].data << " --> " << G[find[i]].data << endl;
T->append(QString::fromStdString(G[i].data + " --> " + G[find[i]].data));
}
}
本文作者: 小天g
代码链接:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1q5mNebompqzNI_S_bDRKig 提取码: 9r14





















 533
533











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








