1.定义
map<int,map<int,int> > mp1;
map<string,map<string,int> > mp2;
map此时的value值也是一个map对象
赋值:
这是比较直接的赋值操作,相当于是一个二维数组赋值
mp1[1][2]=5;
mp2["s1"]["t1"]=7;
mp2["s2"]["t2"]=8;
mp2["s3"]["t3"]=9;
mp2["s4"]["t4"]=10;
2.遍历,两个迭代器,一个外迭代器,一个内迭代器
for(map<string,map<string,int>>::iterator it1=mp2.begin();it1!=mp2.end();it1++)
{
cout<<it1->first<<endl;
for(map<string,int>::iterator it2=it1->second.begin();it2!=it1->second.end();it2++)
cout<<it2->first<<" "<<it2->second<<endl;
}
运行结果:

洛谷 P3613 寄包柜
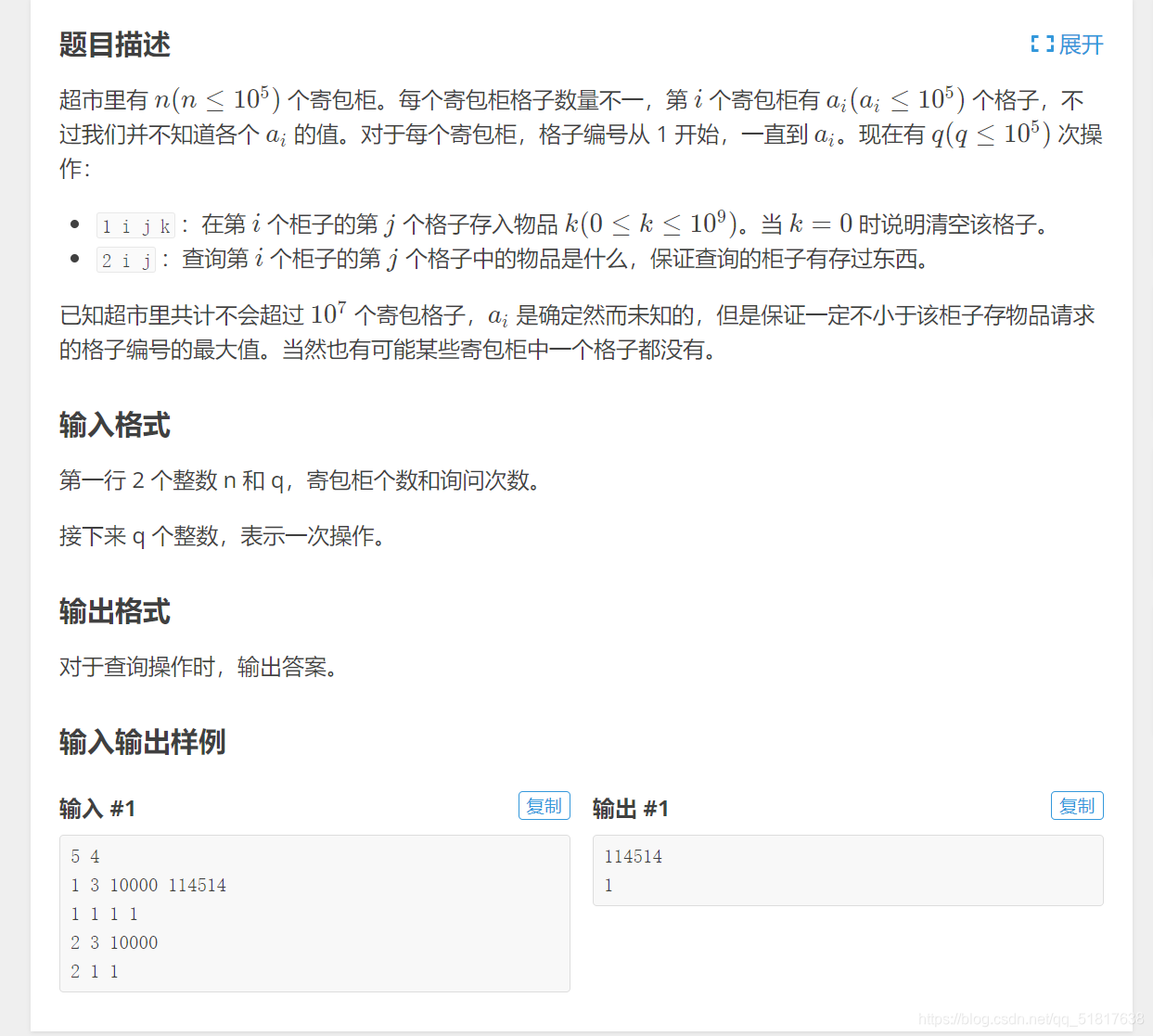
分析:还不会二维map的时候,想到是用结构体,现在直接用上文提到的赋值操作即可
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
map<int,map<int,int> > mp;
int main()
{
int n,q;
int a,b,c,d,e,f;
cin>>n>>q;
for(int i=0;i<q;i++)
{
cin>>a;
if(a==1)
{
cin>>b>>c>>d;
mp[b][c]=d;
}
else if(a==2)
{
cin>>e>>f;
cout<<mp[e][f]<<endl;
}
}
}
hdu 1213
水果

分析:和上题区别不大,这题是计总数,所以计数的时候要累加,一开始还有点卡,没想到应该怎么去计算总数,其实直接在map后叠加就可以了
注意格式,每组数据之间有一个空行,最后一组数据没有空行
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
map<string,map<string,int> > mp;
int main()
{
int t,n;
cin>>t;
string ch1,ch2;
int sum;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
mp.clear();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>ch1>>ch2>>sum;
mp[ch2][ch1]+=sum;//因为要计算总数,所以要累加
}
for(map<string,map<string,int> >::iterator it1=mp.begin();it1!=mp.end();it1++)
{
cout<<it1->first<<endl;//外迭代器
for(map<string,int>::iterator it2=it1->second.begin();it2!=it1->second.end();it2++)
{
cout<<" |----"<<it2->first<<"("<<it2->second<<")"<<endl; //内迭代器
}
}
if(t!=0)
cout<<endl;
}
}
























 1531
1531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








