A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles: 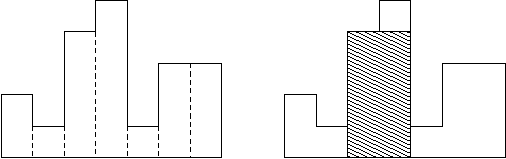
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
思路:
本题特别经典,它充分体现了:在你维护一个单调递增的栈时:
栈中stack[i-1]跟stack[i+1]分别是stack[i]在数组a[]中,
在a[stack[i]]左边离自己最近的小于等于自己的数和在a[stack[i]]右边离自己最近的大于等于自己的数
维持一个单调递增的栈:
一旦出现较小的柱子,后来进栈的柱子高度所维持的最大宽度先知道
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
long long b[1011010];/*模拟一个栈存柱子的位置坐标*/
long long a[111010];
int main()
{
long long n,m,j,i,top=-1,max1,s;
while(~scanf("%lld",&n)&&n)
{
/*题外话:memset也会废不少时间*/
top=-1;
max1=0;/*坑死了,这以后max1赋初值还真不能让乱赋
,最后一个哨兵为0且输入全是0的话根本进不了whlie循环最后还输出是你赋的初值*/
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
a[n+1]=0; /*最后加一个哨兵可以保证清除栈里的东西*/
b[++top]=0;
for(i=1; i<n+2; i++)
{
while(top>0&&a[b[top]]>a[i])
{
s=(i-b[top-1]-1)*a[b[top]];/*注意确定的宽度范围在b[top]跟top跟b[top-1]还有一段*/
max1=max(max1,s);
top--;
}
b[++top]=i;
}
printf("%lld\n",max1);
}
return 0;
}






















 49
49











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








