【Machine Learning 学习笔记】Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent for SVM 代码实现
通过本篇博客记录一下Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent for SVM 代码实现,数据集使用sklearn的breast cancer。
Dual representation of the optimal hyperplane
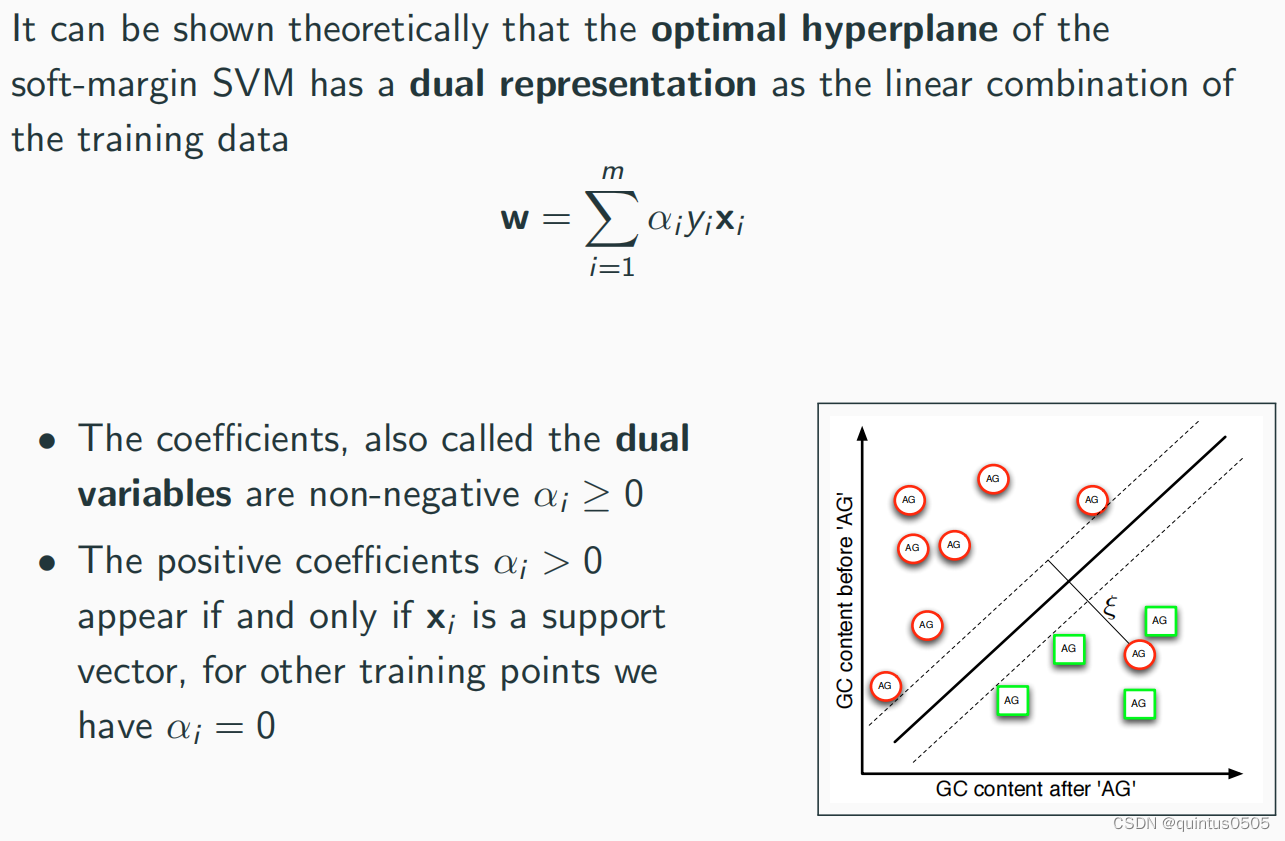
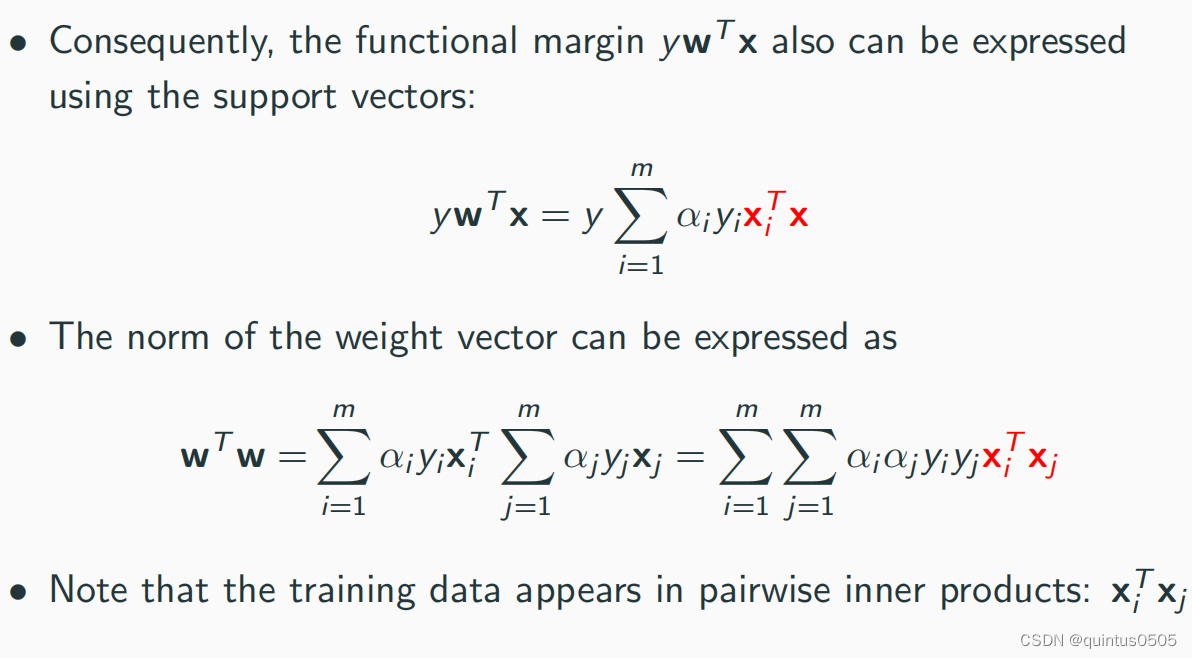
Dual Soft-Margin SVM
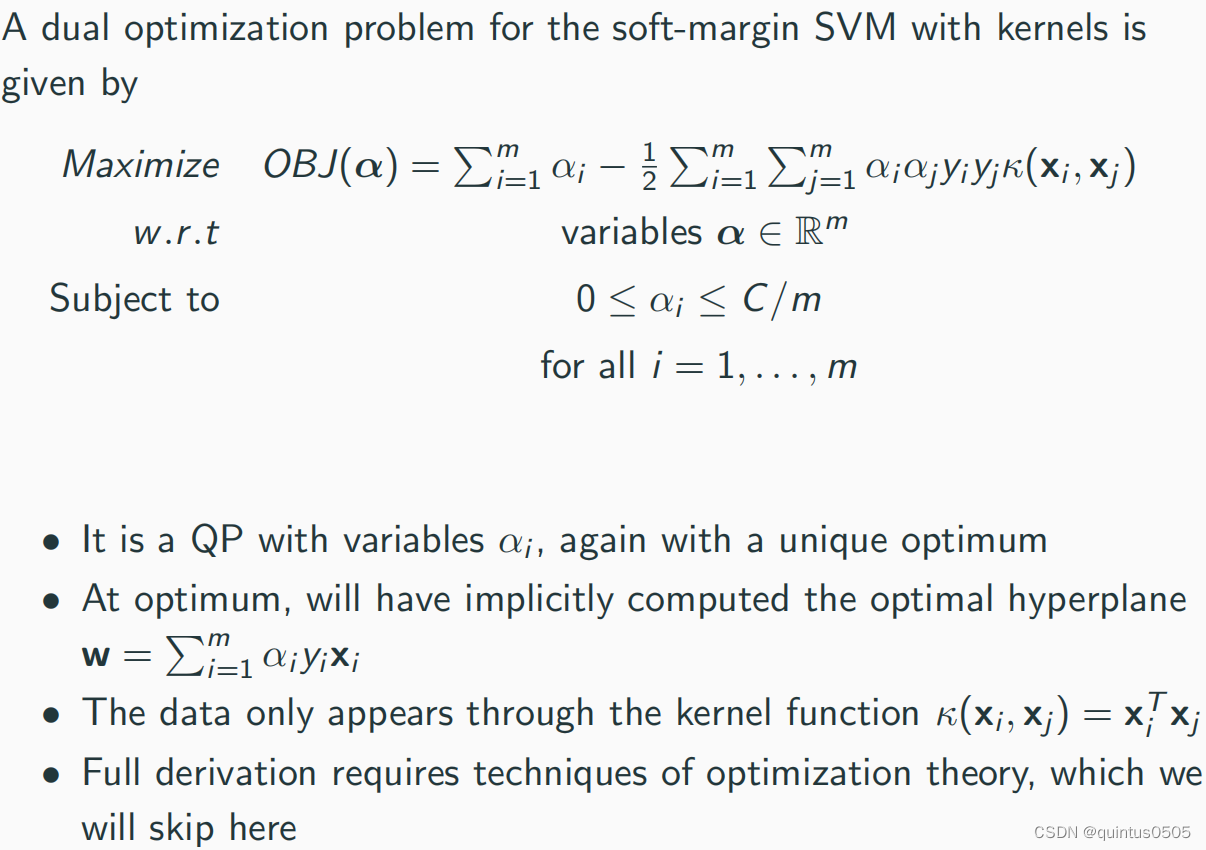
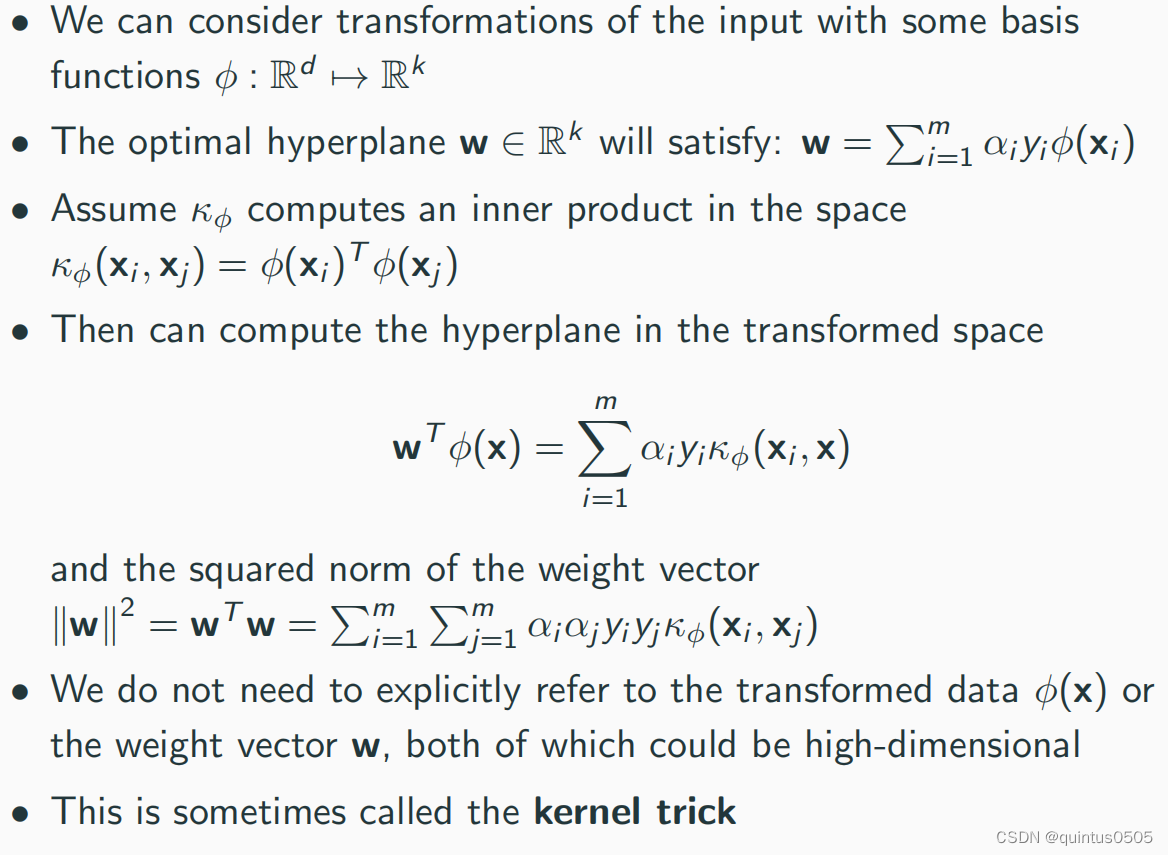
Kernel trick
Algorithm
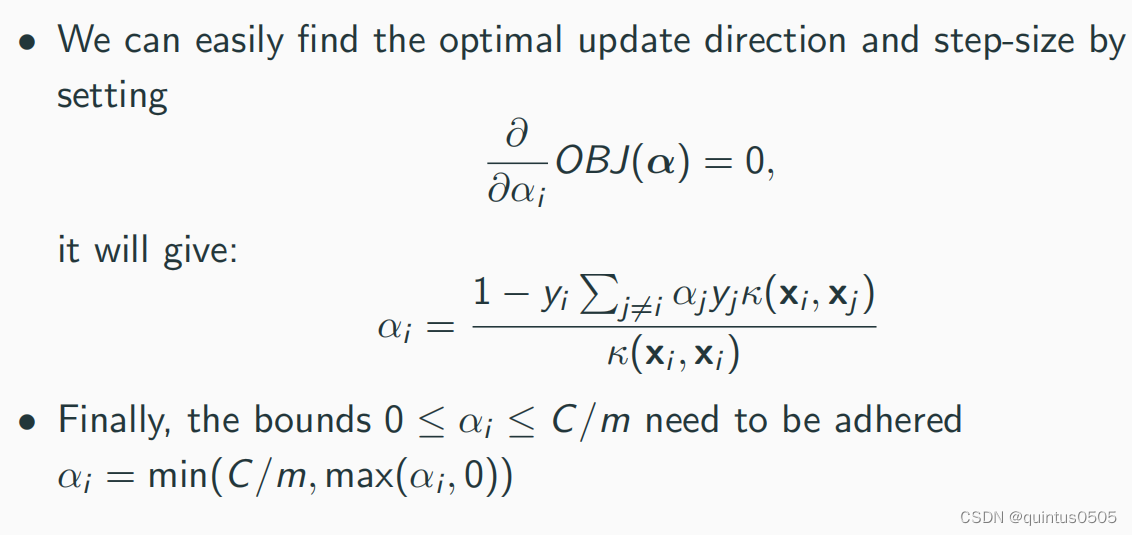

import sys
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, auc, roc_curve, roc_auc_score
# load the data
X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) # X input, y output
print(X.shape, y.shape)
# to convert the {0,1} output into {-1,+1}
y = 2 * y - 1
# X is the input matrix
mdata, ndim = X.shape
# normalization by L infinity norm
scaling = 1
if scaling == 1: # L infinity norm
X /= np.outer(np.ones(mdata), np.max(np.abs(X), 0))
elif scaling == 2: # L2 norm
x_norm = np.sqrt(np.sum(X ** 2, 1))
x_norm += (x_norm == 0)
X /= np.outer(x_norm, np.ones(X.shape[1]))
# number of iteration
niter = 10
# penalty constant for the of the Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent algorithm
C = 1000
# dual stochastic gradient algorithm
# initialize alpha
alpha = np.zeros(mdata)
# compute the linear kernel
K = np.dot(X, X.T)
for iter in range(niter):
for i in range(mdata):
# process all sample examples sequentially
# sum on i!=j
alpha[i] = (1-y[i]*(np.sum(K[i]*y*alpha)-alpha[i]*y[i]*K[i,i]))/K[i, i]
# Clip to satisfy the constraints
alpha[i] = min(C/mdata, max(0, alpha[i]))
# accuracy of the full data
X_test = X
m_test = X.shape[0]
# Linear kernel
K_cross = np.dot(X, X_test.T)
# Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent for SVM prediction
ysdca = np.sign(np.sum(np.outer(y*alpha, np.ones(m_test))*K_cross, 0))
sdca_f1 = f1_score(y, ysdca)
sdca_auc = roc_auc_score(y, ysdca)
tsdca_roc = roc_curve(y, ysdca)
sdca_auc2 = auc(tsdca_roc[0], tsdca_roc[1])
# result
print("Dual stochastic gradient F1: {}".format(sdca_f1))
print("Dual stochastic gradient AUC: {}".format(sdca_auc))
print("Dual stochastic gradient AUC2: {}".format(sdca_auc2))
result
Dual stochastic gradient F1: 0.9633649932157395
Dual stochastic gradient AUC: 0.9382366154008773
Dual stochastic gradient AUC2: 0.9382366154008773








 该篇博客详细记录了使用StochasticDualCoordinateAscent(SDCA)算法实现支持向量机(SVM)的代码过程,数据集选用了sklearn的breastcancer。文章涵盖了SVM的对偶表示、软间隔以及核技巧,并提供了Python代码示例,包括数据预处理、SDCA算法迭代以及性能评估(F1分数和AUC)。
该篇博客详细记录了使用StochasticDualCoordinateAscent(SDCA)算法实现支持向量机(SVM)的代码过程,数据集选用了sklearn的breastcancer。文章涵盖了SVM的对偶表示、软间隔以及核技巧,并提供了Python代码示例,包括数据预处理、SDCA算法迭代以及性能评估(F1分数和AUC)。

















 1329
1329

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










