前言
通过之前的文章SystemUI通知流程,我们一家对通知有了初步的了解,后续我们将从Android 15源码对通知相关动画进行一系列分析。
视图结构
目前通知相关的视图主要分为2种,一种是谷歌源码为主的通知中心和控制中心合并为一起,在通知中心继续往下拉出现控制中心。另一种是通知中心和控制中心分开,通过左右滑动进行切换的。


本文我们先忽略这个样式,后续文章再对这个样式进行分析。
而不管是使用哪种样式,通知的收起和展开基本是类似的,可以简单的拆成下面的结构

简单的说就是每条通知组就是一个ExpandableNotificationRow,ExpandableNotificationRow里面包含了一系列的通知NotificationChildrenContainer(即通知组包含了一系列通知),每条通知又包含了标题NotificationHeaderView和内容NotificationContentView
结构上看这些通知摆放的方式有点类似堆叠在一起的扑克牌,点击展开时,叠在一起的扑克牌向下伸展开,同时实现显示和隐藏
点击通知展开动画分析
总体的时序图如下
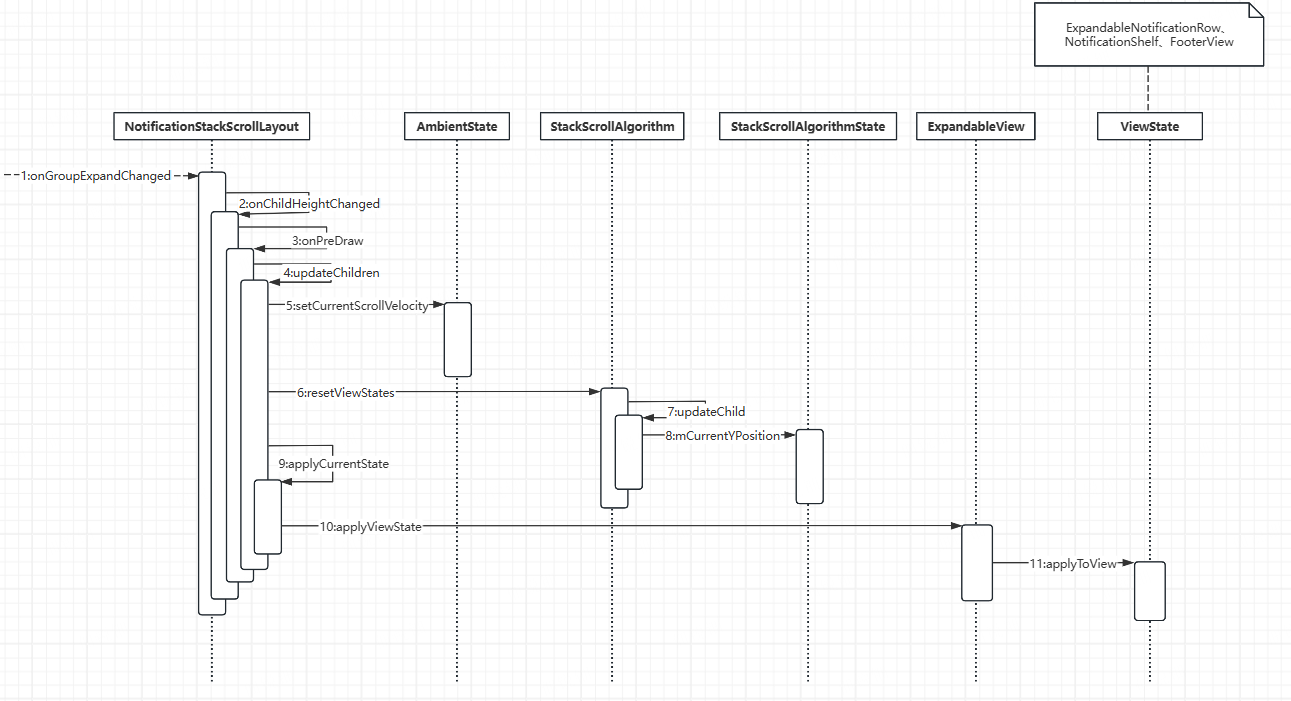
- 点击的时候直接调用onGroupExpandChanged对标题背景和展开状态进行标记
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
void onGroupExpandChanged(ExpandableNotificationRow changedRow, boolean expanded) {
boolean animated = mAnimationsEnabled && (mIsExpanded || changedRow.isPinned());
if (animated) {
mExpandedGroupView = changedRow;
mNeedsAnimation = true;
}
//设置背景及子view的展开状态
changedRow.setChildrenExpanded(expanded);
//高度变化
onChildHeightChanged(changedRow, false /* needsAnimation */);
runAfterAnimationFinished(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
changedRow.onFinishedExpansionChange();
}
});
}
- 通过requestChildrenUpdate发起视图更新
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
void onChildHeightChanged(ExpandableView view, boolean needsAnimation) {
boolean previouslyNeededAnimation = mAnimateStackYForContentHeightChange;
if (needsAnimation) {
mAnimateStackYForContentHeightChange = true;
}
//更新内容高度
updateContentHeight();
updateScrollPositionOnExpandInBottom(view);
clampScrollPosition();
notifyHeightChangeListener(view, needsAnimation);
ExpandableNotificationRow row = view instanceof ExpandableNotificationRow
? (ExpandableNotificationRow) view
: null;
NotificationSection firstSection = getFirstVisibleSection();
ExpandableView firstVisibleChild =
firstSection == null ? null : firstSection.getFirstVisibleChild();
if (row != null) {
if (row == firstVisibleChild
|| row.getNotificationParent() == firstVisibleChild) {
updateAlgorithmLayoutMinHeight();
}
}
if (needsAnimation) {
requestAnimationOnViewResize(row);
}
requestChildrenUpdate();
notifyHeadsUpHeightChangedForView(view);
mAnimateStackYForContentHeightChange = previouslyNeededAnimation;
}
- 通过注册一个OnPreDrawListener,然后通过invalidate() 方法发起刷新,在OnPreDrawListener.onPreDraw() 进行视图的更新操作
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
void requestChildrenUpdate() {
if (!mChildrenUpdateRequested) {
getViewTreeObserver().addOnPreDrawListener(mChildrenUpdater);
mChildrenUpdateRequested = true;
invalidate();
}
}
- 通过实现OnPreDrawListener.onPreDraw() 对子View进行更新
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
private final ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener mChildrenUpdater
= new ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener() {
@Override
public boolean onPreDraw() {
if (SceneContainerFlag.isEnabled()) {
getViewTreeObserver().removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
return true;
}
updateForcedScroll();
//更新所有子view
updateChildren();
mChildrenUpdateRequested = false;
getViewTreeObserver().removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
return true;
}
};
- 在更新View的时候,重点是标记每个View的起始位置,最后通过applyCurrentState()进行更新
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
private void updateChildren() {
Trace.beginSection("NSSL#updateChildren");
updateScrollStateForAddedChildren();
//获取滚动速度设置到mAmbientState中
mAmbientState.setCurrentScrollVelocity(mScroller.isFinished()
? 0
: mScroller.getCurrVelocity());
//循环更新所有子view位置
mStackScrollAlgorithm.resetViewStates(mAmbientState, getSpeedBumpIndex());
if (!isCurrentlyAnimating() && !mNeedsAnimation) {
//将当前状态应用的视图上去
applyCurrentState();
} else {
//以动画的形式将视图更新到对应的状态
startAnimationToState();
}
Trace.endSection();
}
- 在标记View的位置的时候通过AmbientState进行记录和传递
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/StackScrollAlgorithm.java
public void resetViewStates(AmbientState ambientState, int speedBumpIndex) {
// The state of the local variables are saved in an algorithmState to easily subdivide it
// into multiple phases.
StackScrollAlgorithmState algorithmState = mTempAlgorithmState;
//初始化子view 信息,如何view的state是null, 则创建。数据包含height、gone、alpha等
resetChildViewStates();
//初始化可见的view等
initAlgorithmState(algorithmState, ambientState);
//更新所有view的起始位置
updatePositionsForState(algorithmState, ambientState);
updateZValuesForState(algorithmState, ambientState);
updateHeadsUpStates(algorithmState, ambientState);
updatePulsingStates(algorithmState, ambientState);
updateDimmedAndHideSensitive(ambientState, algorithmState);
updateClipping(algorithmState, ambientState);
updateSpeedBumpState(algorithmState, speedBumpIndex);
//更新NotificationShelf的状态
updateShelfState(algorithmState, ambientState);
updateAlphaState(algorithmState, ambientState);
//更新每个子view的状态
getNotificationChildrenStates(algorithmState);
}
- 通过updateChild对View的位置参数进行计算
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/StackScrollAlgorithm.java
protected void updatePositionsForState(StackScrollAlgorithmState algorithmState,
AmbientState ambientState) {
float scrimTopPadding = getScrimTopPaddingOrZero(ambientState);
algorithmState.mCurrentYPosition += scrimTopPadding;
algorithmState.mCurrentExpandedYPosition += scrimTopPadding;
int childCount = algorithmState.visibleChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
//更新每个子view的位置参数等
updateChild(i, algorithmState, ambientState);
}
}
- 计算View的位置着重是标记当前Y值的偏移量mCurrentYPosition,这是连接上下2个View的重点
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/StackScrollAlgorithm.java
protected void updateChild(
int i,
StackScrollAlgorithmState algorithmState,
AmbientState ambientState) {
ExpandableView view = algorithmState.visibleChildren.get(i);
ExpandableViewState viewState = view.getViewState();
viewState.location = ExpandableViewState.LOCATION_UNKNOWN;
float expansionFraction = getExpansionFractionWithoutShelf(
algorithmState, ambientState);
// Add gap between sections.
final boolean applyGapHeight =
childNeedsGapHeight(
ambientState.getSectionProvider(), i,
view, getPreviousView(i, algorithmState));
if (applyGapHeight) {
final float gap = getGapForLocation(
ambientState.getFractionToShade(), ambientState.isOnKeyguard());
algorithmState.mCurrentYPosition += expansionFraction * gap;
algorithmState.mCurrentExpandedYPosition += gap;
}
// Must set viewState.yTranslation _before_ use.
// Incoming views have yTranslation=0 by default.
//记录每个view的开始Y值偏移量,即上个view的结束位置加上padding
viewState.setYTranslation(algorithmState.mCurrentYPosition);
float stackTop = SceneContainerFlag.isEnabled()
? ambientState.getStackTop()
: ambientState.getStackY();
float viewEnd = stackTop + viewState.getYTranslation() + viewState.height;
maybeUpdateHeadsUpIsVisible(viewState, ambientState.isShadeExpanded(),
view.mustStayOnScreen(),
// TODO(b/332574413) use the position from the HeadsUpNotificationPlaceholder
/* topVisible= */ viewState.getYTranslation() >= mNotificationScrimPadding,
viewEnd, /* hunMax */ ambientState.getMaxHeadsUpTranslation()
);
if (view instanceof FooterView) {
if (FooterViewRefactor.isEnabled()) {
if (SceneContainerFlag.isEnabled()) {
final float footerEnd =
stackTop + viewState.getYTranslation() + view.getIntrinsicHeight();
final boolean noSpaceForFooter = footerEnd > ambientState.getStackCutoff();
((FooterView.FooterViewState) viewState).hideContent =
noSpaceForFooter || (ambientState.isClearAllInProgress()
&& !hasNonClearableNotifs(algorithmState));
} else {
// TODO(b/333445519): shouldBeHidden should reflect whether the shade is closed
// already, so we shouldn't need to use ambientState here. However,
// currently it doesn't get updated quickly enough and can cause the footer to
// flash when closing the shade. As such, we temporarily also check the
// ambientState directly.
if (((FooterView) view).shouldBeHidden() || !ambientState.isShadeExpanded()) {
viewState.hidden = true;
} else {
final float footerEnd = algorithmState.mCurrentExpandedYPosition
+ view.getIntrinsicHeight();
final boolean noSpaceForFooter =
footerEnd > ambientState.getStackEndHeight();
((FooterView.FooterViewState) viewState).hideContent =
noSpaceForFooter || (ambientState.isClearAllInProgress()
&& !hasNonClearableNotifs(algorithmState));
}
}
} else {
final boolean shadeClosed = !ambientState.isShadeExpanded();
final boolean isShelfShowing = algorithmState.firstViewInShelf != null;
if (shadeClosed) {
viewState.hidden = true;
} else {
final float footerEnd = algorithmState.mCurrentExpandedYPosition
+ view.getIntrinsicHeight();
final boolean noSpaceForFooter = footerEnd > ambientState.getStackEndHeight();
((FooterView.FooterViewState) viewState).hideContent =
isShelfShowing || noSpaceForFooter
|| (ambientState.isClearAllInProgress()
&& !hasNonClearableNotifs(algorithmState));
}
}
} else {
if (view instanceof EmptyShadeView) {
float fullHeight = SceneContainerFlag.isEnabled()
? ambientState.getStackCutoff() - ambientState.getStackTop()
: ambientState.getLayoutMaxHeight() + mMarginBottom
- ambientState.getStackY();
viewState.setYTranslation((fullHeight - getMaxAllowedChildHeight(view)) / 2f);
} else if (view != ambientState.getTrackedHeadsUpRow()) {
if (ambientState.isExpansionChanging()) {
// We later update shelf state, then hide views below the shelf.
viewState.hidden = false;
viewState.inShelf = algorithmState.firstViewInShelf != null
&& i >= algorithmState.visibleChildren.indexOf(
algorithmState.firstViewInShelf);
} else if (ambientState.getShelf() != null) {
// When pulsing (incoming notification on AOD), innerHeight is 0; clamp all
// to shelf start, thereby hiding all notifications (except the first one, which
// we later unhide in updatePulsingState)
// TODO(b/192348384): merge InnerHeight with StackHeight
// Note: Bypass pulse looks different, but when it is not expanding, we need
// to use the innerHeight which doesn't update continuously, otherwise we show
// more notifications than we should during this special transitional states.
boolean bypassPulseNotExpanding = ambientState.isBypassEnabled()
&& ambientState.isOnKeyguard() && !ambientState.isPulseExpanding();
final float stackBottom = !ambientState.isShadeExpanded()
|| ambientState.getDozeAmount() == 1f
|| bypassPulseNotExpanding
? ambientState.getInnerHeight()
: ambientState.getInterpolatedStackHeight();
final float shelfStart = stackBottom
- ambientState.getShelf().getIntrinsicHeight()
- mPaddingBetweenElements;
//当Y值大于shelfStart时,把view添加到NotificationShelf
updateViewWithShelf(view, viewState, shelfStart);
}
}
viewState.height = getMaxAllowedChildHeight(view);
if (!view.isPinned() && !view.isHeadsUpAnimatingAway()
&& !ambientState.isPulsingRow(view)) {
// The expansion fraction should not affect HUNs or pulsing notifications.
viewState.height *= expansionFraction;
}
}
//记录当前的Y值偏移量,供给下个view使用,其中getMaxAllowedChildHeight(view)是view的高度
algorithmState.mCurrentYPosition +=
expansionFraction * (getMaxAllowedChildHeight(view) + mPaddingBetweenElements);
algorithmState.mCurrentExpandedYPosition += view.getIntrinsicHeight()
+ mPaddingBetweenElements;
setLocation(view.getViewState(), algorithmState.mCurrentYPosition, i);
//记录当前view最终的偏移量
viewState.setYTranslation(viewState.getYTranslation() + stackTop);
}
- 在计算好位置参数后,真正起作用是上面说到的applyCurrentState方法
#frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/NotificationStackScrollLayout.java
private void applyCurrentState() {
int numChildren = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < numChildren; i++) {
ExpandableView child = getChildAtIndex(i);
child.applyViewState();
}
if (NotificationsLiveDataStoreRefactor.isEnabled()) {
if (mLocationsChangedListener != null) {
mLocationsChangedListener.onChildLocationsChanged(collectVisibleLocationsCallable);
}
} else {
if (mLegacyLocationsChangedListener != null) {
mLegacyLocationsChangedListener.onChildLocationsChanged();
}
}
runAnimationFinishedRunnables();
setAnimationRunning(false);
updateViewShadows();
}
- 最终所有View都是通过applyToView更新xTranslation,yTranslation,zTranslation,scaleX,scaleY,layer type,alpha,visibility
#fframeworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/notification/stack/ViewState.java
public void applyToView(View view) {
if (this.gone) {
// don't do anything with it
return;
}
// apply xTranslation
boolean animatingX = isAnimating(view, TAG_ANIMATOR_TRANSLATION_X);
if (animatingX) {
updateAnimationX(view);
} else if (view.getTranslationX() != this.mXTranslation) {
view.setTranslationX(this.mXTranslation);
}
// apply yTranslation
boolean animatingY = isAnimating(view, TAG_ANIMATOR_TRANSLATION_Y);
if (animatingY) {
updateAnimationY(view);
} else if (view.getTranslationY() != this.mYTranslation) {
view.setTranslationY(this.mYTranslation);
}
// apply zTranslation
boolean animatingZ = isAnimating(view, TAG_ANIMATOR_TRANSLATION_Z);
if (animatingZ) {
updateAnimationZ(view);
} else if (view.getTranslationZ() != this.mZTranslation) {
view.setTranslationZ(this.mZTranslation);
}
// apply scaleX
boolean animatingScaleX = isAnimating(view, SCALE_X_PROPERTY);
if (animatingScaleX) {
updateAnimation(view, SCALE_X_PROPERTY, mScaleX);
} else if (view.getScaleX() != mScaleX) {
view.setScaleX(mScaleX);
}
// apply scaleY
boolean animatingScaleY = isAnimating(view, SCALE_Y_PROPERTY);
if (animatingScaleY) {
updateAnimation(view, SCALE_Y_PROPERTY, mScaleY);
} else if (view.getScaleY() != mScaleY) {
view.setScaleY(mScaleY);
}
int oldVisibility = view.getVisibility();
boolean becomesInvisible = this.mAlpha == 0.0f
|| (this.hidden && (!isAnimating(view) || oldVisibility != View.VISIBLE));
boolean animatingAlpha = isAnimating(view, TAG_ANIMATOR_ALPHA);
if (animatingAlpha) {
updateAlphaAnimation(view);
} else if (view.getAlpha() != this.mAlpha) {
// apply layer type
boolean becomesFullyVisible = this.mAlpha == 1.0f;
boolean becomesFaded = !becomesInvisible && !becomesFullyVisible;
if (FadeOptimizedNotification.FADE_LAYER_OPTIMIZATION_ENABLED
&& view instanceof FadeOptimizedNotification) {
// NOTE: A view that's going to utilize this interface to avoid having a hardware
// layer will have to return false from hasOverlappingRendering(), so we
// intentionally do not check that value in this if, even though we do in the else.
FadeOptimizedNotification fadeOptimizedView = (FadeOptimizedNotification) view;
boolean isFaded = fadeOptimizedView.isNotificationFaded();
if (isFaded != becomesFaded) {
fadeOptimizedView.setNotificationFaded(becomesFaded);
}
} else {
boolean newLayerTypeIsHardware = becomesFaded && view.hasOverlappingRendering();
int layerType = view.getLayerType();
int newLayerType = newLayerTypeIsHardware
? View.LAYER_TYPE_HARDWARE
: View.LAYER_TYPE_NONE;
if (layerType != newLayerType) {
view.setLayerType(newLayerType, null);
}
}
// apply alpha
view.setAlpha(this.mAlpha);
}
// apply visibility
int newVisibility = becomesInvisible ? View.INVISIBLE : View.VISIBLE;
if (newVisibility != oldVisibility) {
if (!(view instanceof ExpandableView) || !((ExpandableView) view).willBeGone()) {
// We don't want views to change visibility when they are animating to GONE
view.setVisibility(newVisibility);
}
}
}
小结
简单的说通知就是从上到下把每张卡片叠起来,同时通过一定的计算展示部分视图,当向下展开动画时,把整个卡片往下推,最终通过applyToView对每张卡片进行偏移量和透明度等操作。
思考
通知的堆叠展示视图大多数都是使用visible和invisible的方式进行,当通知较多的时候,这种视图的堆叠就会影响一定的性能,那为何谷歌还使用这种方式,而不是对view进行gone的操作?
























 1062
1062

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








