文章目录
基础
hello,world
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
return 0;
}
getline
成员函数getline()是从输入流中读取一行字符,读到终止符时会将’\0’存入结果缓冲区中 [4],作为输入的终止。终止符可以是默认的终止符,也可以是定义的终止符。函数的语法结构是:
getline(<字符数组chs>,<读取字符的个数n>,<终止符>)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
string welcomeMessage;
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
cin>>name;
cout << "Hi!" <<name<< endl;
getline(cin,welcomeMessage,'#');
cout<<welcomeMessage<<endl;
return 0;
}
Hello world!
lisi
Hi!lisi
you are good student!
#
you are good student!
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 11.410 s
Press any key to continue.
std::cin
可同时接收多个数据输入,每个数据用空格分隔!
Hello world!
name age
lisi 29
Hi!lisi 29
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 3.817 s
Press any key to continue.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string name;
int age;
int temp;
string welcomeMessage;
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
cout<<"name age"<<endl;
cin>>name>>age;
cout << "Hi!" <<name<<" "<<age<<endl;
return 0;
}
引用与指针
- 标量
100
100
88
99
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 1.819 s
Press any key to continue.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
int &a1=a;
int *a2=&a;
cin>>a;
cout<<a<<endl;
a1=88;
cout<<a<<endl;
*a2=99;
cout<<a<<endl;
return 0;
}
- 数组指针
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int *s=a;
for (int *p=a;p<s+8;p++){
cout<<p<<":"<<*p<<endl;
}
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
for (int *p=a;p<a+8;p++){
cout<<p<<":"<<*p<<endl;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.126 s
Press any key to continue.
- 数组的引用
下面的程序是错误的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
for (int (&p)[8]=a;p<a+7;p++){
cout<<*p<<endl;
}
}
错误如下
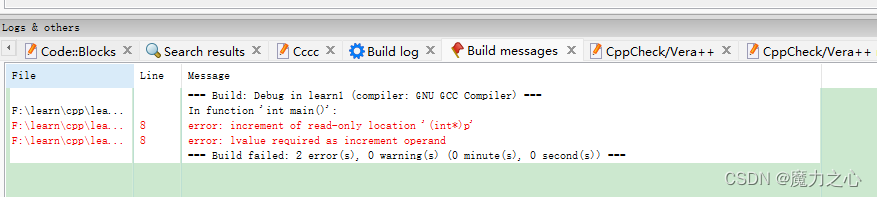
正确的写法只能如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int (&p)[8]=a;
for (int i=0;i<8;i++){
cout<<p[i]<<endl;
}
}
如果一定要用指针,只能考虑另外使用一个指针变量了,因为引用指向的内容可以更改,但引用本身的指向是不能更改,只读的。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int (&p)[8]=a;
for (int *p1=p;p1<a+8;p1++){
cout<<*p1<<endl;
}
}
函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void goThrough(int (&arr)[8]){
for (int *p1=arr;p1<arr+8;p1++){
cout<<*p1<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
goThrough(a);
}
更改数组元素
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void goThrough(int (&arr)[8]){
for (int *p1=arr;p1<arr+8;p1++){
cout<<*p1<<endl;
}
for (int *p1=arr;p1<arr+8;p1++){
*p1*=10;
}
for (int *p1=arr;p1<arr+8;p1++){
cout<<*p1<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
goThrough(a);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.130 s
Press any key to continue.
数据类型
基本数据类型
在C++中,基本数据类型包括整数类型、浮点类型和字符类型。整数类型包括short、int、long和char,浮点类型包括float和double。
以下是各种基本数据类型的大小和范围:
整数类型:
short:2字节
int:通常是4字节
long:在64位系统上是8字节,32位系统是4字节
char:通常是1字节,可能是有符号的,也可能是无符号的
浮点类型:
float:4字节
double:8字节
字符类型:
char:通常是1字节,可以是有符号的也可以是无符号的
short shortVar = 123;
int intVar = 12345678;
long longVar = 123456789012345;
float floatVar = 1.23f;
double doubleVar = 1.23456789;
char charVar = 'A';
以上内容引用自AI生成内容:AI自动生成内容
更多类型
1、bool型(布尔型):true或false
bool isOk=true;
bool isBlue=false;
2、string
C++string 是C++中的字符串。 字符串对象是一种特殊类型的容器,专门设计来操作的字符序列。 不像传统的c-strings,只是在数组中的一个字符序列,我们称之为字符数组,而C + +字符串对象属于一个类,这个类有很多内置的特点,在操作方式,更直观,另外还有很多有用的成员函数。
string 的定义为:typedef basic_string string;
更多内容请见string,百度百科
sizeof
在 C++ 语言中,sizeof() 是一个判断数据类型或者表达式长度的运算符。
cout<<sizeof(int)<<endl;
正则表达式
smatch 对应于 string,wsmatch 对应于 wstring,cmatch 对应于 char 或 wcmatch 对应于 wchar_t*。*
单次匹配
#include <iostream>
#include <regex>
#include <string>
int main() {
using namespace std;
const char *str = "abce12389iiu4645ppp";
const char *first=str;
const char *last=str+strlen(str);
regex strRx(R"(\d+)");
cmatch match;
bool found = regex_search(first, last, match, strRx);
if (found)
cout <<"find the number:"<<match.str() << endl;
return 0;
}
find the number:12389
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.045 s
Press any key to continue.
多次匹配
#include <iostream>
#include <regex>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
const char *str = "abce12389iiu4645ppp";
const char *first=str;
const char *last=str+strlen(str);
typedef regex_iterator<const char *> StrIter;
StrIter::regex_type strRx(R"(\d+)");
StrIter next(first, last, strRx);
StrIter end;
for (; next != end; ++next)
std::cout << "find number: " << next->str() << std::endl;
}
find number: 12389
find number: 4645
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.293 s
Press any key to continue.
组匹配
find the str:12389iiu4645
find the str:12389
find the str:iiu
find the str:4645
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.287 s
Press any key to continue.
#include <iostream>
#include <regex>
#include <string>
int main() {
using namespace std;
const char *str = "abce12389iiu4645ppp";
const char *first=str;
const char *last=str+strlen(str);
regex strRx(R"((\d+)(\D+)(\d+))");
cmatch matchs;
bool found = regex_search(first, last, matchs, strRx);
if (found){
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[0].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[1].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[2].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[3].str() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
字符串的匹配
使用smatch
smatch 对应于 string,wsmatch 对应于 wstring,cmatch 对应于 char 或 wcmatch 对应于 wchar_t*。*
#include <iostream>
#include <regex>
#include <string>
int main() {
using namespace std;
string str = "abce12389iiu4645ppp";
regex strRx(R"((\d+)(\D+)(\d+))");
smatch matchs;
bool found = regex_search(str, matchs, strRx);
if (found){
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[0].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[1].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[2].str() << endl;
cout <<"find the str:"<<matchs[3].str() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
split
c+中没有split,于是需要自己实现这个函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator) {
vector<string> tokens;
stringstream ss(text);
string item;
while (getline(ss, item, separator)) {
if (!item.empty()) {
tokens.push_back(item);
}
}
return tokens;
}
int main() {
string codeStr = "x:long=88;y:float=11.22;z:int=99";
char delimiter = ';';
vector<string> codeTokens=split(codeStr,delimiter);
for (const std::string &codeLineToken : codeTokens) {
cout << codeLineToken << endl;
}
return 0;
}
x:long=88
y:float=11.22
z:int=99
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.041 s
Press any key to continue.
- getline会生成一个包含一串从输入流读入的字符的字符串,直到以下情况发生会导致生成的此字符串结束:1)到文件结束,2)遇到函数的定界符,3)输入达到最大限度。
- 在函数遇到和结束定界符相等的字符时函数结束,同时函数抽出定界符,此种情况下该定界符既不被放回输入流,也不被放入要生成的字符串。所以由此可以理解输入结束后的第一个回车是定界符,被确认后抛弃,而第二个才是程序执行运行时正常需要的。
- 更多 见百度百科
map
用于存储和检索集合中的数据,此集合中的每个元素均为包含数据值和排序键的元素对。 键的值是唯一的,用于自动排序数据。
更多见百度百科
基础
在C++中,map是一个关联容器,用于存储键值对,并且通过键来对数据进行排序。
下面引用自百度百科的自动生成内容:
下面是一个简单的使用map的例子:
#include <map> #include <iostream> int main() { std::map<int, std::string> exampleMap; // 插入元素 exampleMap[1] = "one"; exampleMap[2] = "two"; exampleMap[3] = "three"; // 访问元素 std::cout << "Key 2 corresponds to Value " << exampleMap[2] << std::endl; // 遍历元素 for (const auto& pair : exampleMap) { std::cout << "Key: " << pair.first << " Value: " << pair.second << std::endl; } return 0; } ```这段代码展示了如何创建一个map,如何插入元素,如何通过键访问元素,以及如何遍历map中的所有键值对。
实战
整型变量符号表
//value_type
//存储为 map 中的元素的对象的类型。
typedef pair<const Key, Type> value_type;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef map<string, int> TableIntMap;
int main()
{
TableIntMap intSymbols;
intSymbols.insert(TableIntMap::value_type("a1", 1));
intSymbols.insert(TableIntMap::value_type("a2", 2));
intSymbols.insert(TableIntMap::value_type("a3", 3));
// find and show elements
cout << "intSymbols.at('a1') == " << intSymbols.at("a1") << endl;
cout << "intSymbols.at('a2') == " << intSymbols.at("a2") << endl;
cout << "intSymbols.at('a3') == " << intSymbols.at("a3") << endl;
return (0);
}
intSymbols.at('a1') == 1
intSymbols.at('a2') == 2
intSymbols.at('a3') == 3
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.132 s
Press any key to continue.
简单分析生成整型变量表
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef map<string, int> TableIntMap;
vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator) {
vector<string> tokens;
stringstream ss(text);
string item;
while (getline(ss, item, separator)) {
if (!item.empty()) {
tokens.push_back(item);
}
}
return tokens;
}
string removeSpaces(const string& input) {
string result = input;
result.erase(std::remove(result.begin(), result.end(), ' '), result.end());
return result;
}
int main(){
string codeStr = "x:int=88;y:int=11;z:int=99";
char delimiter = ';';
vector<string> codeTokens=split(codeStr,delimiter);
TableIntMap intSymbols;
vector<string> symbolTokens,sysmbolVarTokens;
for (const std::string &codeLineToken : codeTokens) {
delimiter = '=';
symbolTokens=split(codeLineToken,delimiter);
delimiter = ':';
sysmbolVarTokens=split(symbolTokens[0],delimiter);
if (removeSpaces(sysmbolVarTokens[1])=="int"){
string intSysbol=removeSpaces(sysmbolVarTokens[0]);
int intValue=stoi(removeSpaces(symbolTokens[1]));
intSymbols.insert(TableIntMap::value_type(intSysbol, intValue));
}
}
cout<<"int "<<endl;
for (const auto& elem : intSymbols) {
cout << " [" << elem.first << ": " << elem.second << "]"<<endl;
}
return (0);
}
int
[x: 88]
[y: 11]
[z: 99]
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.037 s
Press any key to continue.























 2888
2888

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








