R语言里面的data.frame就是数据库里面的table,R语言的分析,建模大部分都是基于data.frame数据结构,由rows和columns组成。data.frame每一个column会存储同样的数据类型,可以是numeric, factor, character.
- 创建一个data.frame
R用data.frame() function创建一个data.frame
data.frame(..., row.names = NULL, check.rows = FALSE,
check.names = TRUE, fix.empty.names = TRUE,
stringsAsFactors = default.stringsAsFactors())
# create data.frame
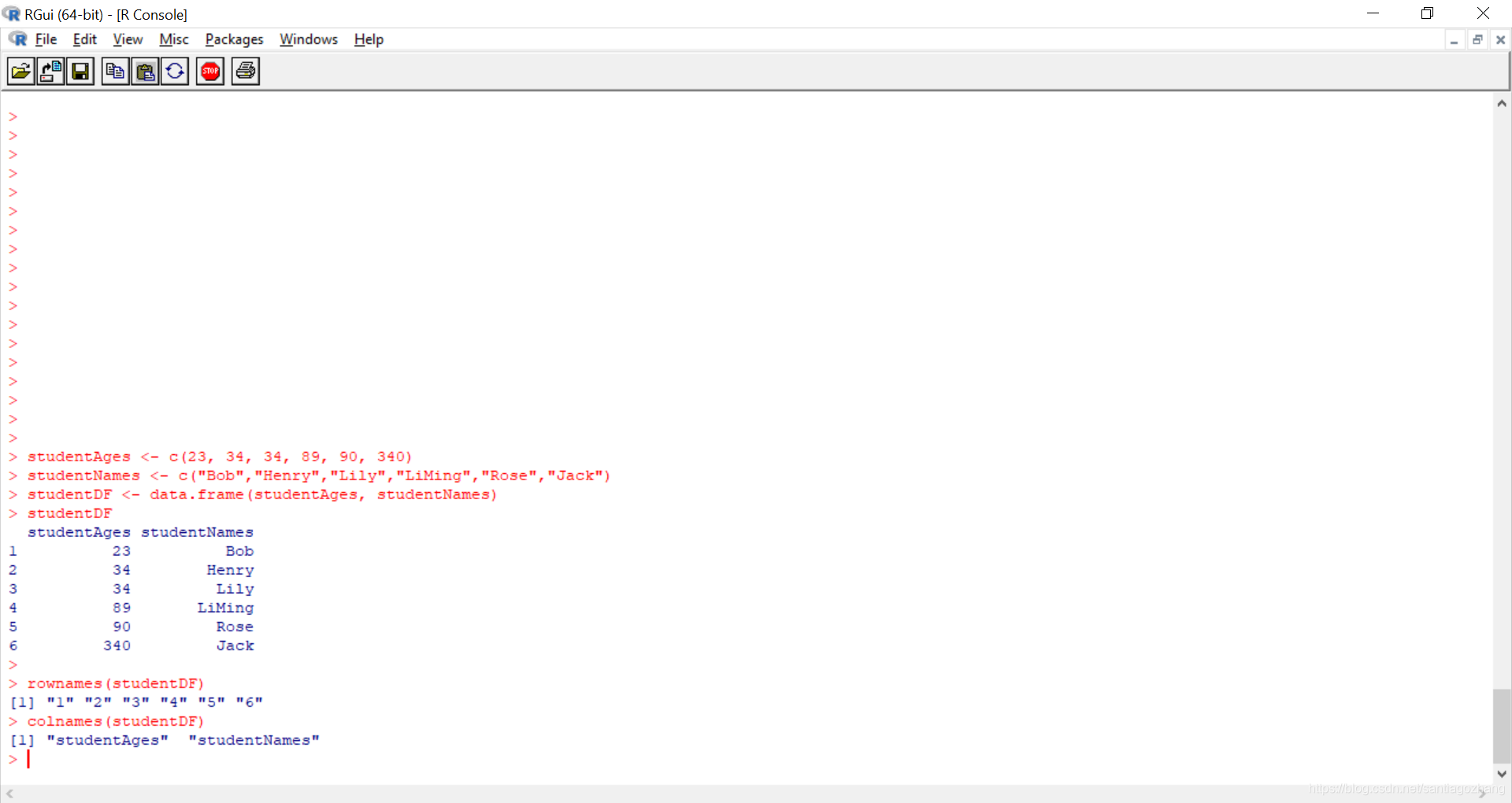
studentAges <- c(23, 34, 34, 89, 90, 340)
studentNames <- c("Bob","Henry","Lily","LiMing","Rose","Jack")
studentDF <- data.frame(studentAges, studentNames)
studentDF
rownames(studentDF)
colnames(studentDF)
rownames和colnames可以用来看行名和列名。
- data.frame 增加一列
# add a column to data.frame
studentHeight <- c(150, 165, 180, 155, 167, 186)
studentDF <- cbind(studentDF, studentHeight)
studentDF
- data.frame 增加一行
# add a row to data.frame
newStudent <- list(34, "Winters", "190")
studentDF <- rbind(studentDF, newStudent)
studentDF
- 查看data.frame的结构,str
# check data.frame structure with str
str(studentDF)

5. 获取data.frame部分数据,subset
# this will get the row 1 and column 2 element
studentDF[1,2]
# this will get the whole firt row
studentDF[1,]
# this will get the whole second column
studentDF[,2]
# you also can get several rows or columns together
studentDF[2:4,]
- data.frame里面查找符合条件的rows
# find a row in data.frame, in this, to find height>170
# studentDF[,3] > 170 this will give a true, false vector
validStudentDF <- studentDF[studentDF[,3] > 170,]























 215
215

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








