1、递归的概念
递归在计算机科学和数学中是一个很重要的工具,计算机工作者用来定义句法、解决表和树形结构的搜索等问题。数学家在研究组合问题时也经常要用到递归。
在数学上,一个正整数的阶乘可以用以下公式进行定义:
n! = n×(n-1)× ••• ×1,
幂函数运算可以用如下公式进行定义:
xn=x×x×∙∙∙×x
,
这种方法作为阶乘函数和幂函数运算的定义不是很严密。
正规的阶乘定义应为
1 if n = 0
n! =
n ×(n-1)! if n >0幂函数运算的定义
1 if n = 0
xn =
x × xn-1 if n >0- 递归的定义
若一个对象部分地包含它自己,或用它自己给自己下定义,称这
个对象是递归的;若一个过程直接地或间接地调用自己,则称这
个过程是递归的过程。
- 使用递归方法的情况
⑴定义是递归的;
阶乘函数的计算,由于是递归函数,用递归过程来求解。
4! = 4 ×3!
= 4 ×(3 ×2!)
= 4 ×(3 ×(2 ×1!))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×(1×0!)))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×(1×1)))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×1))
= 4 ×(3 ×2)
= 4 ×6
= 24
⑵数据结构是递归的;
单链表:
①一个结点,其指针域为NULL,是一个单链表;
②一个结点,其指针域指向一个单链表,仍是一个单链表。
广义表等。
⑶问题的解法是递归的。
如 Hanoi 塔、 game tree问题等。
2、递归函数的设计
每一个递归过程(recursive process)由两部分组成:
⑴一个最小的基础情况,它不再需用递归来处理;
⑵一个通用的方法(又称递归步骤),它根据某种规律把问题简化成一个或几个较小的问题。这一步骤应该导致过程的最终终止的方向发展。
使用 if– else 语句,if 语句块判断递归结束的条件,处理这个最小的基础情况,else语句块处理递归的情况,或这个通用的方法。
幂函数计算
1 if n = 0
n! =
n ×(n-1)! if n >0int fractorial (int n)
{
if (n = = 0)
return 1
else
return n *fractorial(n-1)
}- 递归函数的设计
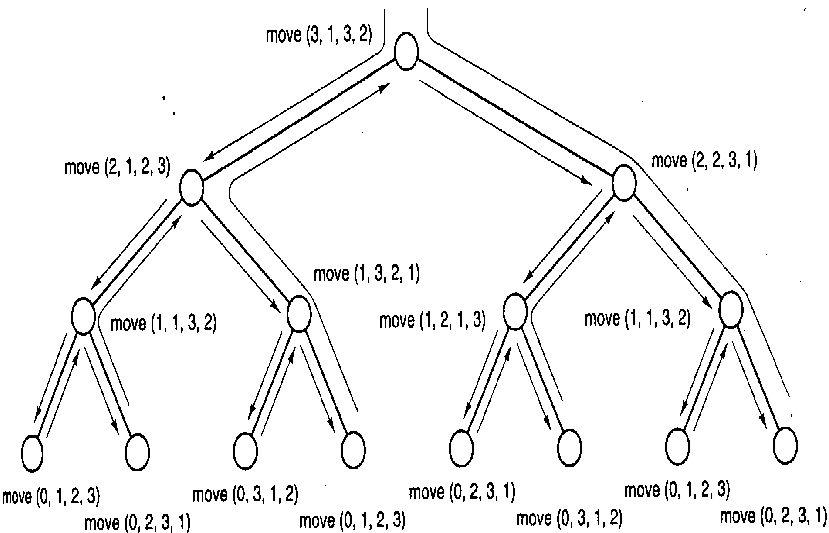
Hanoi塔问题
结束条件:只有一块盘子,将这一盘子直接送到C柱
递归过程:将A柱上上面的 n – 1 个盘子送到B柱,
直接把A柱上最后一个盘子移到C柱,
将B柱上 n – 1 个盘子移到C柱。
void move (int n, int A, int C, int B)
{
if (n = = 1)
cout<<“move”<<A<<“to”<<C<<endl
else{
move( n – 1, A, B, C);
cout<<“move”<<A<<“to”<<C<<endl;
move( n – 1, B, C, A);
}
}注意 if – else 这种形式的变形。
Hanoi塔的算法
Const int disks = 64;
Void move ( int count, int start, int finish, int temp);
/* Pre: None.
Post: The simulation of the Towers of Hanoi has terminated. */
Main ( )
{
move( disks, 1, 3, 2);
}
Void move( int count, int start, int finish, int temp)
{
if (count>0) {
move( count – 1, start, temp, finish);
cout <<“Move disk”<< count << “from” << start << “to”
<< finish << “.” <<endl;
move( count – 1, temp, finish, start,);
}
} 一般过程调用与递归过程
通常,当一个过程在运行期间调用另一个过程时,在运行被调用过程之前,系统需先完成三件事:
⑴将所有的实在参数,返回地址等信息传递给被调用过程保存;
⑵为被调用过程的局部变量分配存储区;
⑶将控制转移到被调用过程的入口。
在从被调用过程返回调用过程之前,系统也应完成三件事:
⑴保存被调用过程的计算结果;
⑵释放被调用过程数据存储区;
⑶按照被调用过程保存的返回地址将控制转移到调用过程。
一般主程序调用一个过程是外部调用,其他调用都属于内部调用,外部调用结束后,将返回调用该过程的主程序,而内部调用结束后,将返回到本次调用语句的后继语句处。
递归过程的运行过程类似于多个过程的嵌套调用,只是调用过程和被调用是同一个过程,这样,“层次”概念就显得十分重要。
3、递归过程与递归工作栈
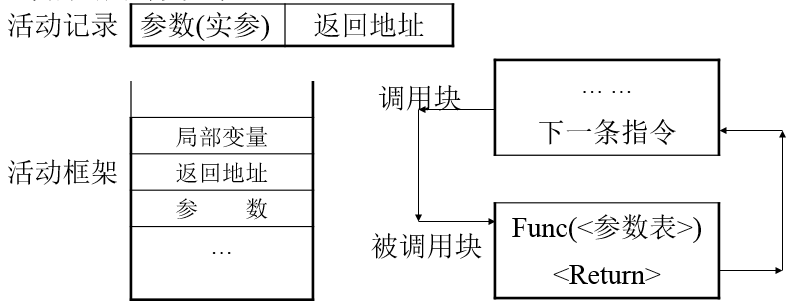
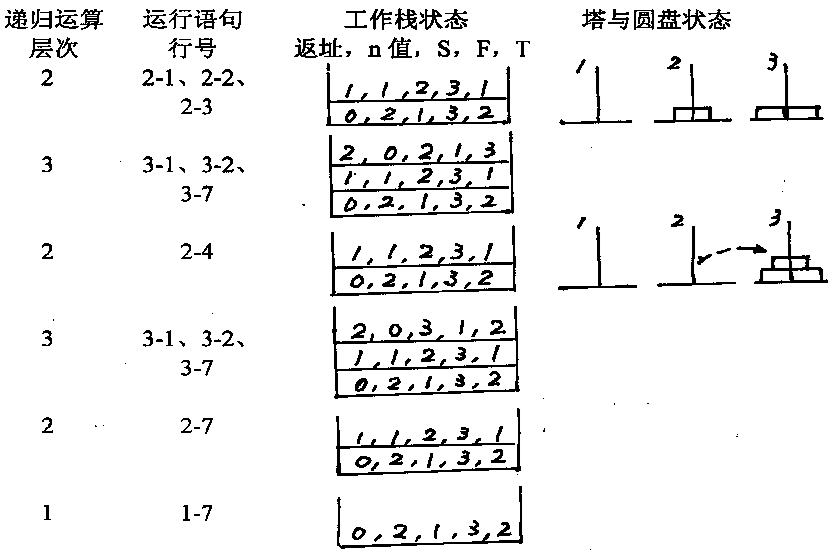
活动记录( activation record )
为确保递归过程的每次调用和返回的正确执行,在每次递归过程调用前,必须做参数保存、参数传递等工作。这一切是通过一个递归工作栈来进行处理的,每一层递归调用所需保存的信息构成一个工作记录,称之为活动记录,包括如下内容:
⑴返回地址:即上一层中本次调用自己的语句的后继语句处;
⑵在本次过程调用时,与形参结合的实参值;
⑶本层的局部变量值。
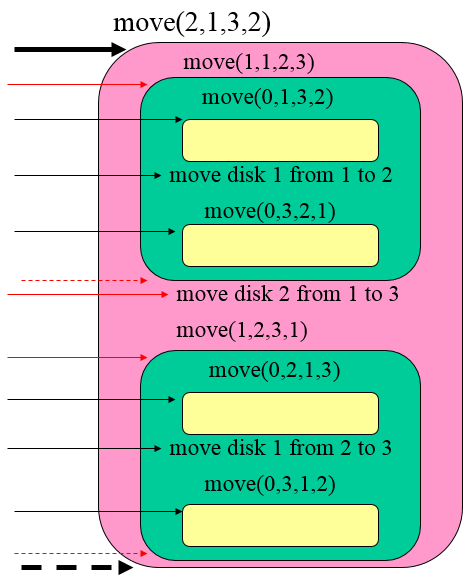
2个盘的Hanoi塔的调用示意图
3、递归过程与递归工作栈(例)
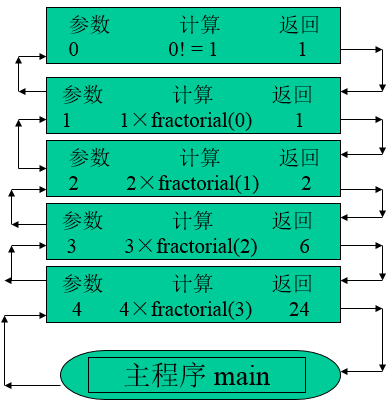
下图反映了阶乘函数计算函数调用过程
4! = 4 ×3!
= 4 ×(3 ×2!)
= 4 ×(3 ×(2 ×1!))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×(1×0!)))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×(1×1)))
= 4 ×(3 ×(2×1))
= 4 ×(3 ×2)
= 4 ×6
= 24递归工作栈的例
2个盘的Hanoi塔的递归工作栈示意图

分析递归过程的工具
递归树
递归算法设计的原则
为了设计一个递归算法,通常,先考虑几个较为简单的例子,待对问题解法有了比较正确的理解后,应规划一个更有通用性的解法,以下几点是应该在设计算法时予以注意的:
⑴确定关键步骤( Find the key step. )
⑵找到终止条件( Find a stopping rule. )
⑶拟订算法大纲( Outline your algorithm. )
⑷确认终止条件(Check termination. )
⑸构画递归树( Draw a recursion tree. )
4、递归过程的非递归化
用单纯的循环方式非递归化
阶乘的非递归算法
int factorial (int n)
/* factorial: iterative version
Pre: n is a nonnegative integer.
Post: Return the value of the factorial of n */
{
int count, product= 1;
for (count = 1; count< = n; count+ +)
product﹡=count;
return product;
}Fibonacci数列
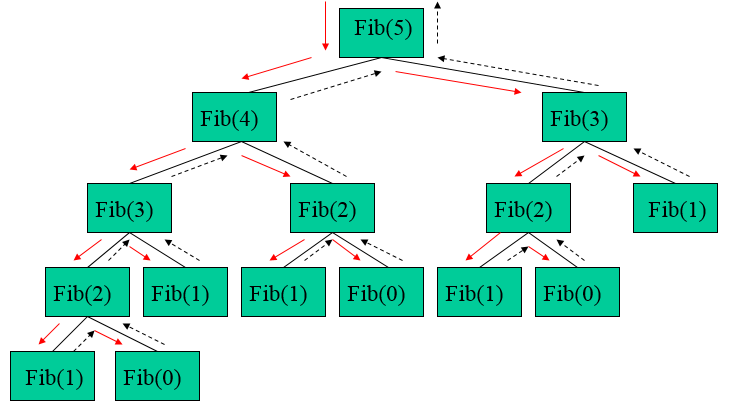
Fibonacci 数列的定义
0 若n = 0
F(n) = 1 若n = 1
F(n –1)+F(n – 2) 若n≧2终止条件:F(0) =0 或 F(1)=1
递归步骤: F(n) = F(n –1)+F(n – 2)
int fibonacci(int n)
/* fibonacci: recursive version
Pre: The parameter n is a nonnegative integer.
Post: The function returns the nth Fibonacci number. */
{
if (n <= 0) return 0;
else if (n = = 1) return 1;
else return fibonacci(n-1)+fibonacci(n – 2)
}递归过程的非递归化
Fibonacci数的递归树
迭代法计算Fibonacci数列
int fibonacci(int n)
/* fibonacci: iterative version
Pre: The parameter n is a nonnegative integer.
Post: The function returns the nth Fibonacci number. */
{
int last_but_one; // second previous Fibonacci number, F i-2
int last_value; // previous Fibonacci number, F i-1
int current; // current Fibonacci number F,
if (n <= 0) return 0;
else if (n == 1) return 1;
else {
last_but_one = 0;
last_value = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
current = last_but_one + last_value;
last_but_one = last_value;
last_value = current;
}
return current;
}
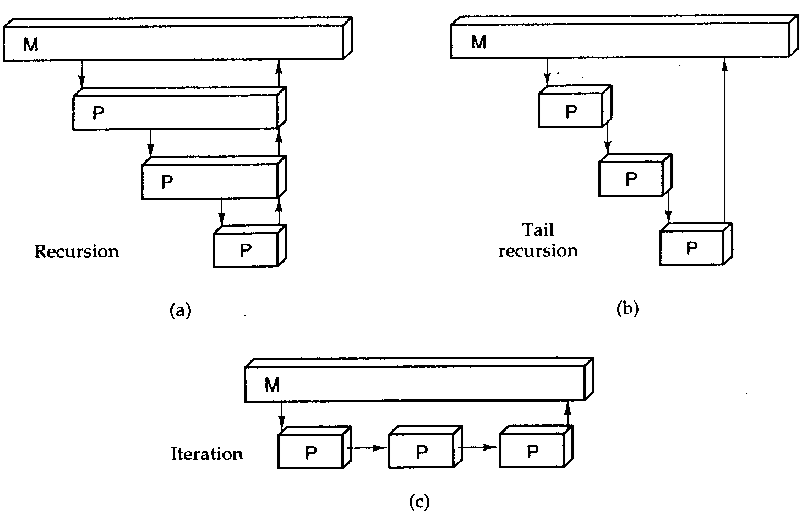
}尾递归
先分析一般的调用的情况
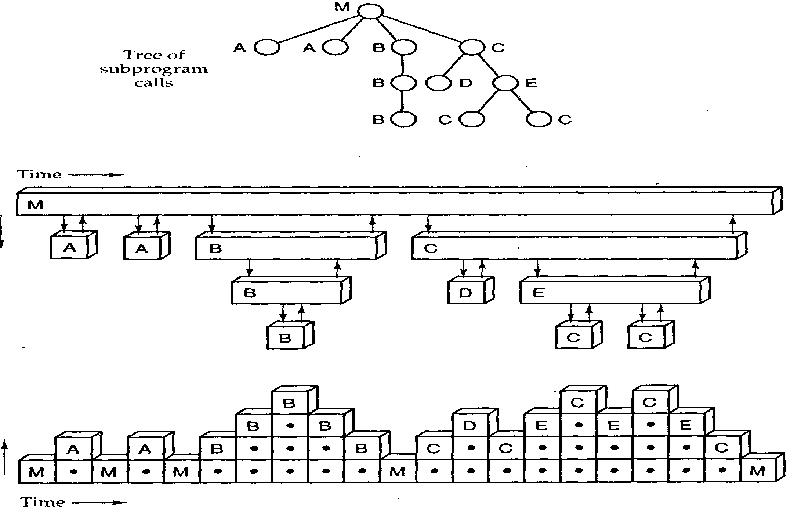
尾递归及其图示意
函数最后一句执行的语句是递归调用,称为尾递归。
消除尾递归的 Hanoi 塔算法
void move (int count, int start, int finish, int temp)
/* move: iterative version.
Pre: Disk count is a valid disk to be moved.
Post: Moves count disks from start to finish using temp for temporary storage. */
{
int swap; // temporary storage to swap towers
while (count > 0 ) { // Replace the if statement with a loop.
move (count-1, start, temp, finish); // first recursive call
cout <<“Move disk”<< count << “from”<< start <<
<<“to”<< finish <<“.”<< endl;
count - -; // Change parameters to mimic the
swap = start; // second recursive call.
start = temp;
temp = swap;
}
}回溯法(Backtracking)
回溯法又称为“通用的解题法”。用它可以系统地搜索一个问题的所有解:构造局部解(partial solutions),并在满足问题要求的前提下,扩大这个局部解,直至问题得到解决;如果在扩大过程中,局部解与问题要求一致性得不到保证,就应该返回,称之为回溯( backtracks ),并要删除所有得最近构造的局部解,然后寻找另外的可能解。
如果把每一个解(包括局部解)视作结点,按照形成的过程,组成一个树状的解空间,称为解空间树。回溯法就是以这棵解空间树为基础,根结点为开始结点,用深度优先的方式搜索的过程。搜索开始时,这个开始结点成为一个活结点,同时也成为当前的扩展结点。在当前的扩展结点处,搜索向纵深方向移至一个新结点。这个新结点成为一个新的活结点,并成为当前扩展结点。如果在当前扩展结点处不能再向纵深方向移动,则当前的扩展结点就成为死结点。此时,应往回移动(回溯)至最近的一个活结点处,并使这个活结点成为当前的扩展结点。回溯法就是以这种工作方式递归地再解空间树中搜索,直至找到所要求的解或解空间中已无活结点时为止。
回溯法的算法框架
由于回溯法是对解空间的深度优先搜索,一般情况可用递归函数来实现回溯法。
void Backtrack( int t) {
/* 本算法是对递归回溯方法框架式的描述(或抽象算法)
if ( t > n ) Output(x);
else
for (int i = f( n, t); i <= g( n, t ); i + +) {
x[t] = h (i);
if (Constraint(t) && Bound(t)) Backtrack(t + 1);
}
}形式参数 t 表示递归深度,即当前扩展结点在解空间树中的深度;
n 是解空间树的高度;x 表示得到的一个可行解;
f( n, t) 和 g( n, t ) 分别表示在当前扩展结点处未搜索过的子树的起始编号和终止编号。 h (i)表示在当前扩展结点处x[t]的第i个可选值。
Constraint(t) 和 Bound(t) 分别表示在当前扩展结点处的约束函数和限界函数。
八皇后问题的算法框架
solve_from (Queens configuration)
if Queens configuration already contains eight queens
print configuration
else
for every chessboard square p that is unguarded by configuration
{
add a queen on square p to configuration;
solve_from(configuration);
remove the queen from square p of configuration;
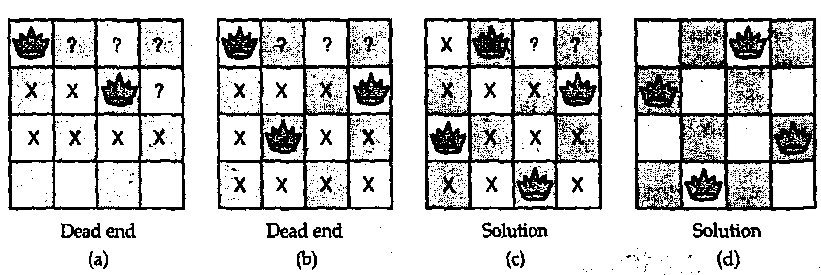
};四皇后的解法示意
Queens 类 二个数据成员:board_size,count 前者表示问题的规模,后者不仅表示已有的皇后数,而且表示第一个未被盘上皇后占用的行的行号。主要的方法有unguarded、insert、remove、is_solved。
变量configuration 表示了问题的部分解,初始化时为空。
八皇后问题的总体算法
int main( )
/* Pre: The user enters a valid board size.
Post: All solutions to the n-queens puzzle for the selected board size are printed.
Uses:The class Queens and the recursive function solve_from.*/
{
int board_size;
print_information( );
cout <<“What is the size of the board?”<< flush;
cin >> board_size;
if (board_size<0 ‖board_size > max_board)
cout<< “The number must be between 0 and “<<max_board<<endl;
else{
Queens configuration(board_size); // 初始化configuration
solve_from(configuration); // 从configuration 扩展所有解
}
}八皇后问题的抽象算法
void solve_from(Queens &configuration)
/* Pre: The Queens configuration represents a partially completed arrangement of nonattacking queens on a chessboard.
Post: All n-queens solutions that extend the given configuration are printed. The configuration is restored to its initial state.
Uses: The class Queens and the function solve_from, recursively. */
{
if (configuration.is_solved( )) configuration.print( );
else
for (int col = 0; col < configuration. board_size; col+ +)
if (configuration.unguarded(col)) {
Configuration.insert(col);
solve_from(configuration); // 递归调用增加新的皇后
configuration. remove(col);
}
}八皇后问题(以二维数组为存储结构)
const int max_board = 30; !
class Queens {
public:
Queens(int size);
bool is_solved( ) const;
void print( ) const;
bool unguarded(int col) const;
void insert(int col);
void remove(int col);
int board_size; // dimension of board = maximum number of queens.
private:
int count; // current number of queens = first unoccupied row.
bool queen_square[max_board] [max_board];
};八皇后的构造函数与插入运算
初始化一个configuration 和 插入运算
Queens:: Queens(int size)
/* Post: The Queens object is set up as an empty configuration on a chessboard with size squares in each row and column. “ */
{
board_size = size;
count = 0;
for ( int row = 0; row < board_size; row+ +)
for (int col = 0; col < board_size; col+ +)
queen_square[row] [col] = false;
}
void Queens:: insert(int col)
/* Pre: The square in the first unoccupied row (row count) and column col is not guarded by any queen.
Post: A queen has been inserted into the square at row count and column col; count has been incremented by 1. */
{
queen_square [count + +] [col] = true;
}互相攻击的判断
按行、列、对角线判断
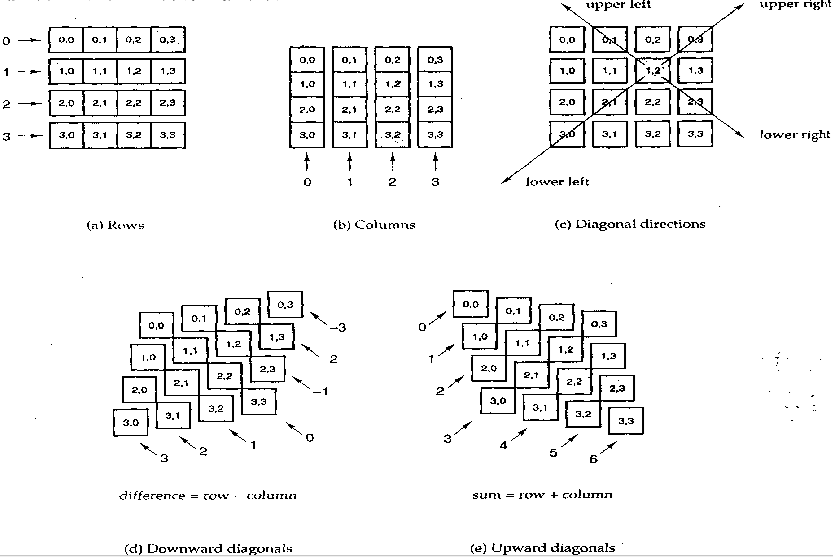
互相攻击的判断(算法)
boil Queens:: unguarded(int col) const
/* Post: Returns true or false according as the square in the first unoccupied row(row count,) and column col is not guarded by any queen. */
{
int i;
bool ok = true; // 若在列或对角线上发现皇后返回 false
for (i = 0; ok && i < count; i + +)
ok = ! queen_square [i] [col]; // 检查列的上部
// queen_square的初值为false,对ok赋值要求反
for(i = 1; ok && count - i >=0&&col - i >= 0; i+ +)
ok = !queen_square [count - i] [col - i]; // 检查左上部分对角线
for (i = 1; ok && count - i >= 0&&col + i < board_size; i+ +)
ok = !queen_square [count - i] [col + i]; // 检查右上部分对角线
return ok;
} 修改后的八皇后问题
class Queens {
public:
Queens(int size);
bool is_solved( ) const;
void print( ) const;
bool unguarded(int col) const;
void insert(int col);
void remove(int col);
int board_size;
private: '
int count;
bool col_free[max_board]; ;
bool upward_free [2 * max_board - 1];
bool downward_free[2 * max_board - 1];
int queen_in_row[max_board]; // 每行中皇后的列号
};修改后的八皇后构造函数
Queens:: Queens(int size)
/* Post: The Queens object is set up as an empty configuration on a chessboard with size squares in each row and column. */
{
board_size = size;
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; i+ +) col_free[i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < (2 * board_size - 1); j+ +) upward_free[j] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < (2 * board_size - 1); k+ +)
downward_free[k] = true;
}修改后的八皇后部分算法
void Queens:: insert(int col)
/* Pre: The square in the first unoccupied row (row count) and column col is not
guarded by any queen.
Post: A queen has been inserted into the square at row count and column col;
count has been incremented by 1. */
{
queen_in_row [count] = col;
col_f ree [col] = false;
upward_free [count + col] = false;
downward_free [count - col + board_size - 1] = false;
count + +;
}修改后的八皇后部分算法
相互攻击的判断
bool Queens:: unguarded(int col) const
{
return col_free(col)
&& upward_free[count + col]
&& downward_free[count - col + board_size - 1];
}八皇后的递归树
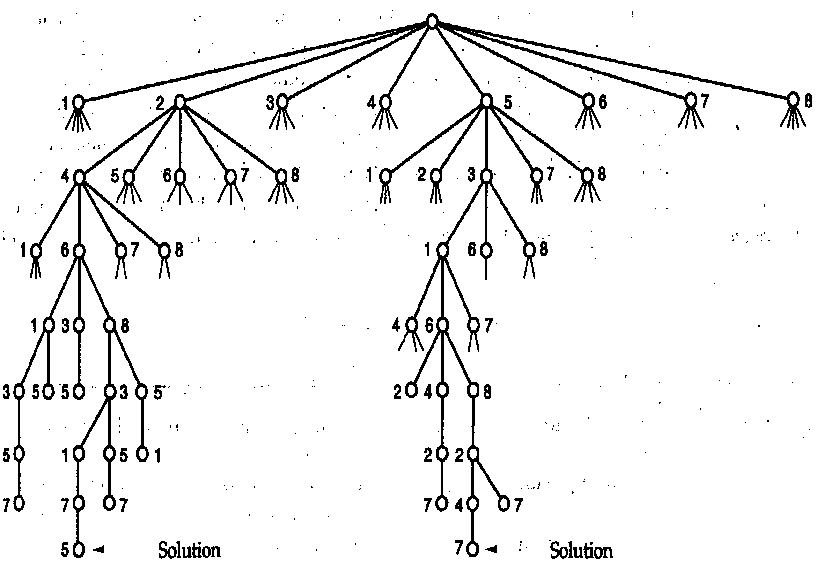
竞赛树
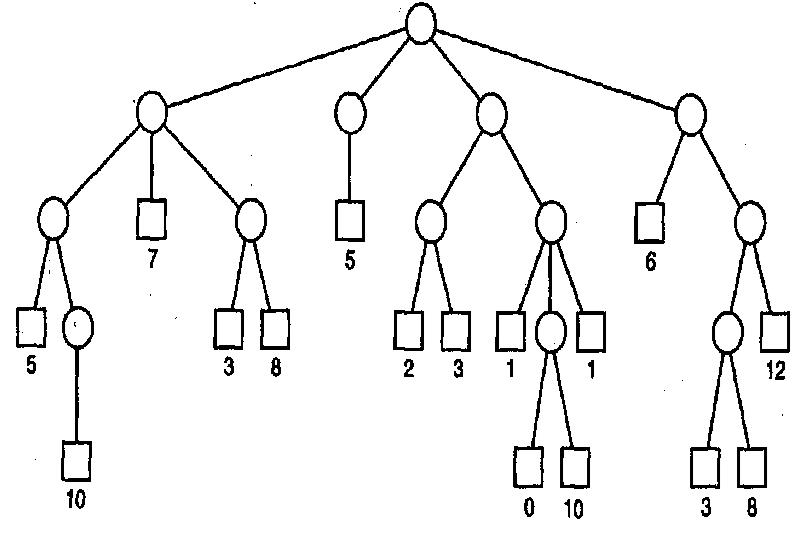
竞赛树
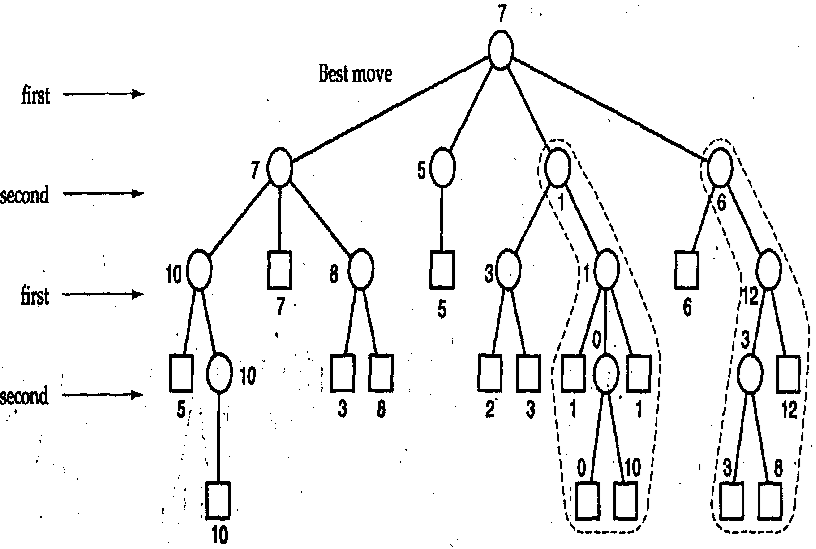
竞赛树
class Board {
public:
Board( ); // constructor for initialization
int done( ) const; // Test whether the game is over.
void play(Move try_it);
int evaluate( ) const;
int legal_moves(Stack &moves) const;
int worst_case( ) const;
int better(int value, int old_value) const;
// Which parameter does the mover pre
void print( ) const;
void instructions( ) const;
/* Additional methods, functions, and data will depend on the game l
sideration. */
};
int look_ahead(const Board &game, int depth,Move &recommended)
/* Pre: Board game represents a legal game position.
Post: An evaluation of the game, based on looking ahead depth moves, is returned. The best move that can be found for the mover is recorded as Move recommended.
Uses: The classes Stack, Board, and Move, together with function look_ahead recursively. */
{
If (game.done( ) || depth == 0)
return game.evaluated( );
else{
Stack moves;
game.legal_moves(moves);
int value, best_value = game.worst_case( );
while (!moves.empty( )) {
Move try_it, reply;
moves.top(try_it);
Board new_game = game;
new_game.play(try_it);
value = look_ahead(new_game, depth - 1, reply);
if (game.better (value, best_value)) { // try_it is the best move yet
best_value = value; // found
recommended = try_it;
}
moves. pop( );
}
return best_value;
}
}
持续更新中。。。
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (一) 绪论
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (二) 栈
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (三) 队列
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (四) 链式栈和队列
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (五) 递归
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (六) 表与串
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (七) 查找
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (八) 排序
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (九) 表与信息检索
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十) 二叉树
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十一) 多路数
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十二) 集合及其表示
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十三) 图
数据结构C++语言描述专题系列 (十四) 波兰表达式























 577
577

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








