The (Euclidean a.k.a.  ) squared norm of a vector can be obtained squaredNorm() . It is equal to the dot product of the vector by itself, and equivalently to the sum of squared absolute values of its coefficients.
) squared norm of a vector can be obtained squaredNorm() . It is equal to the dot product of the vector by itself, and equivalently to the sum of squared absolute values of its coefficients.
Eigen also provides the norm() method, which returns the square root of squaredNorm() .
These operations can also operate on matrices; in that case, a n-by-p matrix is seen as a vector of size (n*p), so for example the norm() method returns the "Frobenius" or "Hilbert-Schmidt" norm. We refrain from speaking of the  norm of a matrix because that can mean different things.
norm of a matrix because that can mean different things.
If you want other  norms, use the lpNnorm<p>() method. The template parameter p can take the special value Infinityif you want the
norms, use the lpNnorm<p>() method. The template parameter p can take the special value Infinityif you want the  norm, which is the maximum of the absolute values of the coefficients.
norm, which is the maximum of the absolute values of the coefficients.
The following example demonstrates these methods.
| Example: | Output: |
|---|---|
|
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
VectorXf v(2);
MatrixXf m(2,2), n(2,2);
v << -1,
2;
m << 1,-2,
-3,4;
cout <<
"v.squaredNorm() = " << v.
squaredNorm() << endl;
cout <<
"v.norm() = " << v.norm() << endl;
cout <<
"v.lpNorm<1>() = " << v.lpNorm<1>() << endl;
cout <<
"v.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << v.lpNorm<
Infinity>() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout <<
"m.squaredNorm() = " << m.
squaredNorm() << endl;
cout <<
"m.norm() = " << m.
norm() << endl;
cout <<
"m.lpNorm<1>() = " << m.lpNorm<1>() << endl;
cout <<
"m.lpNorm<Infinity>() = " << m.lpNorm<
Infinity>() << endl;
}
| v.squaredNorm() = 5 v.norm() = 2.23607 v.lpNorm<1>() = 3 v.lpNorm<Infinity>() = 2 m.squaredNorm() = 30 m.norm() = 5.47723 m.lpNorm<1>() = 10 m.lpNorm<Infinity>() = 4 |
1、向量范数
1-范数: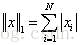
2-范数: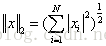
∞-范数: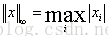
-∞-范数: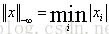
p-范数: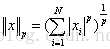
2、矩阵范数
1-范数: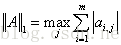
2-范数: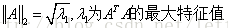
∞-范数: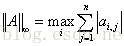
F-范数: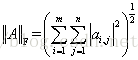
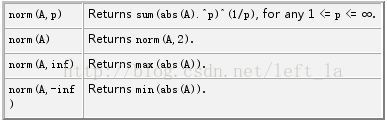
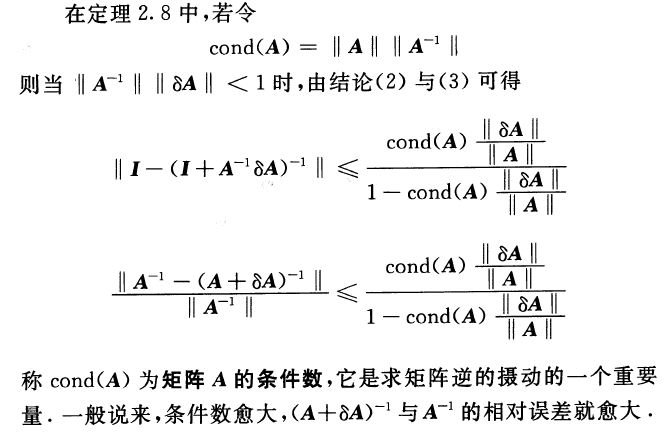
附matlab中norm函数说明
The norm of a matrix is a scalar that gives some measure of the magnitude of the elements of the matrix. The norm function calculates several different types of matrix norms:
n = norm(A) returns the largest singular value of A, max(svd(A)).
n = norm(A,p) returns a different kind of norm, depending on the value of p.
When A is a vector:













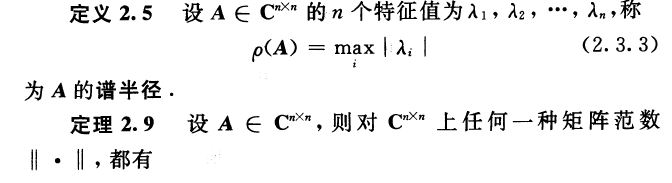
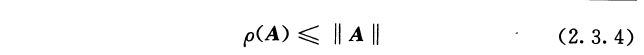














 795
795

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








