An ordinary Doubly Linked List requires space for two address fields to store the addresses of previous and next nodes. A memory efficient version of Doubly Linked List can be created using only one space for address field with every node. This memory efficient Doubly Linked List is called XOR Linked List or Memory Efficient as the list uses bitwise XOR operation to save space for one address. In the XOR linked list, instead of storing actual memory addresses, every node stores the XOR of addresses of previous and next nodes.
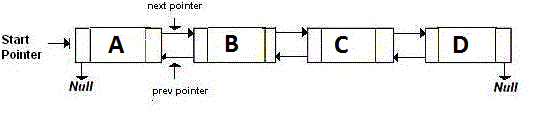
Consider the above Doubly Linked List. Following are the Ordinary and XOR (or Memory Effiecient) representations of the Doubly Linked List.
Ordinary Representation:
Node A:
prev = NULL, next = add(B) // previous is NULL and next is address of B
Node B:
prev = add(A), next = add(C) // previous is address of A and next is address of C
Node C:
prev = add(B), next = add(D) // previous is address of B and next is address of D
Node D:
prev = add(C), next = NULL // previous is address of C and next is NULL
XOR List Representation:
Let us call the address variable in XOR representation npx (XOR of next and previous)
Node A:
npx = 0 XOR add(B) // bitwise XOR of zero and address of B
Node B:
npx = add(A) XOR add(C) // bitwise XOR of address of A and address of C
Node C:
npx = add(B) XOR add(D) // bitwise XOR of address of B and address of D
Node D:
npx = add(C) XOR 0 // bitwise XOR of address of C and 0
Traversal of XOR Linked List:
We can traverse the XOR list in both forward and reverse direction. While traversing the list we need to remember the address of the previously accessed node in order to calculate the next node’s address. For example when we are at node C, we must have address of B. XOR of add(B) and npx of C gives us the add(D). The reason is simple: npx(C) is “add(B) XOR add(D)”. If we do xor of npx(C) with add(B), we get the result as “add(B) XOR add(D) XOR add(B)” which is “add(D) XOR 0″ which is “add(D)”. So we have the address of next node. Similarly we can traverse the list in backward direction.
We have covered more on XOR Linked List in the following post.
XOR Linked List – A Memory Efficient Doubly Linked List | Set 2
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XOR_linked_list
http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/6828?page=0,0






















 234
234











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








