C# 委托各种用法, 委托就相当于 一个变量类型, 类似INT ,INT用来装整数, 委托用来装 函数, 按照 返回值,参数 规定的格式来装
基本原理:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Action ac1 = fun1;//无返回值无参数
ac1();
Action<int> ac2 = fun2;//无返回值,有1参数
ac2(1);
Action<int, int> ac3 = fun3;//无返回值,有2参数
ac3(2,3);
Func<int> f1 = fun4;//有1个返回值, 无参数
f1();
Func<int,int> f2 = fun5;//有1个返回值, 1个参数
f2(1);
Func<int, int,int> f3 = fun6;//有1个返回值, 2个参数
f3(1,1);
}
static void fun1()
{
}
static void fun2(int a)
{
}
static void fun3(int a, int b)
{
}
static int fun4()
{
return 1;
}
static int fun5(int a)
{
return 1;
}
static int fun6(int a,int b)
{
return 1;
}
}
}
实际项目用法: 怪物死亡后委托更新人物经验和UI界面显示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 怪物死亡委托
{
class Monster
{
public Action<int> deadDoSomthing;
public void Dead()
{
int xp = 1000;
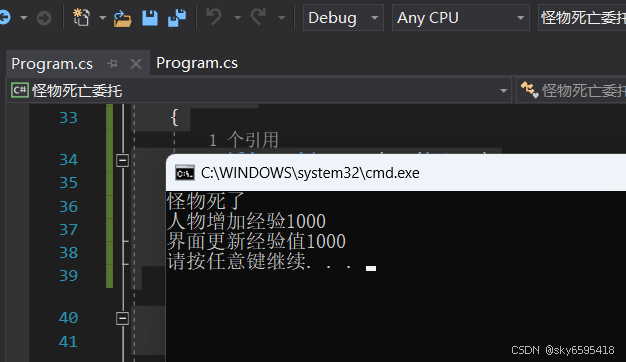
Console.WriteLine("怪物死了");
if (deadDoSomthing != null)
{
deadDoSomthing(xp);
}
}
}
class Player
{
public void AddXp(int xp)
{
Console.WriteLine("人物增加经验{0}",xp);
}
}
class UI
{
public void UpgradeUI(int xp)
{
Console.WriteLine("界面更新经验值{0}", xp);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Monster m = new Monster();
Player p = new Player();
UI u = new UI();
m.deadDoSomthing += p.AddXp;
m.deadDoSomthing += u.UpgradeUI;
m.Dead();
}
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










