目录
上一篇博客我们介绍了mybatis中关于数据源的配置原理,本篇博客介绍mybatis的事务管理。
对于事务,我们是在mybatis-configuration.xml 文件中配置的:

关于解析 <environments />标签在上一篇数据源的配置我们已经介绍了,不了解的可以参考上篇博客。
1、mybatis 支持的事务类图
mybatis 支持的所有事务的所有类都在如下包中:

下面通过类图来理解该包中所有类的关系:

2、mybatis 支持的两种事务类型管理器
通过配置文件中的 type 属性:
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />我们可以配置不同的事务管理器来管理事务。在mybatis中支持两种事务类型管理器,分别是:
①、type = "JDBC":这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
②、type="MANAGED":这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。例如:
1 <transactionManager type="MANAGED">
2 <property name="closeConnection" value="false"/>
3 </transactionManager>注意:和数据源配置一样,通常项目中我们不会单独使用 mybatis 来管理事务。比如选择框架 Spring +mybatis,这时候没有必要配置事务管理器, 因为 Spring 模块会使用自带的管理器来覆盖前面的配置。
再回头看看在 mybatis 的 org.apache.ibatis.transaction 包下的所有类,也就是上面的类图。mybatis的事务首先会定义一个事务接口 Transaction,
3、初始化事务管理器
我们说事务(Transaction),一般是指要做的或所做的事情。在数据库中,事务具有如下四个属性:
①、原子性(atomicity):一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么都做,要么都不做。
②、一致性(consistency):事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。
③、隔离性(isolation):一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
④、持久性(durability):持久性也称永久性(permanence),指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响。
这也就是常说的事务 ACID 特性。而在程序中,对于事务的操作通常是:
1、创建事务(create)
2、提交事务(commit)
3、回滚事务(rollback)
4、关闭事务(close)
在mybatis的 org.apache.ibatis.transaction 包下的 Transaction 接口便为我们定义了这一套操作:

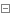

1 /**
2 * Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors.
3 *
4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7 *
8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9 *
10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14 * limitations under the License.
15 */
16 package org.apache.ibatis.transaction;
17
18 import java.sql.Connection;
19 import java.sql.SQLException;
20
21 /**
22 * Wraps a database connection.
23 * Handles the connection lifecycle that comprises: its creation, preparation, commit/rollback and close.
24 *
25 * @author Clinton Begin
26 */
27 public interface Transaction {
28
29 /**
30 * Retrieve inner database connection
31 * @return DataBase connection
32 * @throws SQLException
33 */
34 Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
35
36 /**
37 * Commit inner database connection.
38 * @throws SQLException
39 */
40 void commit() throws SQLException;
41
42 /**
43 * Rollback inner database connection.
44 * @throws SQLException
45 */
46 void rollback() throws SQLException;
47
48 /**
49 * Close inner database connection.
50 * @throws SQLException
51 */
52 void close() throws SQLException;
53
54 /**
55 * Get transaction timeout if set
56 * @throws SQLException
57 */
58 Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
59
60 }
同时,mybatis为了获取事务采用了工厂模式,定义了一个工厂接口:TransactionFactory

通过实现该工厂接口,mybatis提供了两种不同的事务管理器:

这两种事务管理器的获取也是采用了工厂模式。下面我们来分别看看这两种事务管理器。
4、JdbcTransaction
当在配置文件中配置:type = "JDBC"时,就是用 JdbcTransaction 来管理事务。使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
代码如下:

1 public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
2
3 private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
4 //数据库连接
5 protected Connection connection;
6 //数据源
7 protected DataSource dataSource;
8 //隔离级别
9 protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
10 //是否自动提交
11 protected boolean autoCommmit;
12
13 public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
14 dataSource = ds;
15 level = desiredLevel;
16 autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
17 }
18
19 public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
20 this.connection = connection;
21 }
22
23 @Override
24 public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
25 if (connection == null) {
26 openConnection();
27 }
28 return connection;
29 }
30
31 //调用connection.commit()来实现
32 @Override
33 public void commit() throws SQLException {
34 if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
35 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
36 log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
37 }
38 connection.commit();
39 }
40 }
41
42 //调用connection.rollback()来实现
43 @Override
44 public void rollback() throws SQLException {
45 if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
46 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
47 log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
48 }
49 connection.rollback();
50 }
51 }
52
53 //调用connection.close()来实现
54 @Override
55 public void close() throws SQLException {
56 if (connection != null) {
57 resetAutoCommit();
58 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
59 log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
60 }
61 connection.close();
62 }
63 }
64
65 protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
66 try {
67 //事务提交状态不一致
68 if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
69 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
70 log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
71 }
72 connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
73 }
74 } catch (SQLException e) {
75 // Only a very poorly implemented driver would fail here,
76 // and there's not much we can do about that.
77 throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
78 + "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
79 + "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
80 }
81 }
82
83 protected void resetAutoCommit() {
84 try {
85 if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
86 // MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed.
87 // Some databases start transactions with select statements
88 // and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection.
89 // A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection.
90 // Sybase throws an exception here.
91 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
92 log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
93 }
94 connection.setAutoCommit(true);
95 }
96 } catch (SQLException e) {
97 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
98 log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
99 + "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
100 }
101 }
102 }
103
104 protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
105 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
106 log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
107 }
108 connection = dataSource.getConnection();
109 if (level != null) {
110 connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
111 }
112 setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
113 }
114
115 @Override
116 public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
117 return null;
118 }
119
120 }
5、ManagedTransaction
ManagedTransaction的代码实现几乎都是一个空的方法,它选择让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。

1 /**
2 * Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors.
3 *
4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7 *
8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9 *
10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14 * limitations under the License.
15 */
16 package org.apache.ibatis.transaction.managed;
17
18 import java.sql.Connection;
19 import java.sql.SQLException;
20 import javax.sql.DataSource;
21
22 import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log;
23 import org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory;
24 import org.apache.ibatis.session.TransactionIsolationLevel;
25 import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction;
26
27 /**
28 * {@link Transaction} that lets the container manage the full lifecycle of the transaction.
29 * Delays connection retrieval until getConnection() is called.
30 * Ignores all commit or rollback requests.
31 * By default, it closes the connection but can be configured not to do it.
32 *
33 * @author Clinton Begin
34 *
35 * @see ManagedTransactionFactory
36 */
37 public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
38
39 private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class);
40
41 private DataSource dataSource;
42 private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
43 private Connection connection;
44 private boolean closeConnection;
45
46 public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
47 this.connection = connection;
48 this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
49 }
50
51 public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
52 this.dataSource = ds;
53 this.level = level;
54 this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
55 }
56
57 @Override
58 public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
59 if (this.connection == null) {
60 openConnection();
61 }
62 return this.connection;
63 }
64
65 @Override
66 public void commit() throws SQLException {
67 // Does nothing
68 }
69
70 @Override
71 public void rollback() throws SQLException {
72 // Does nothing
73 }
74
75 @Override
76 public void close() throws SQLException {
77 if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
78 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
79 log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
80 }
81 this.connection.close();
82 }
83 }
84
85 protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
86 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
87 log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
88 }
89 this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
90 if (this.level != null) {
91 this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
92 }
93 }
94
95 @Override
96 public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
97 return null;
98 }
99
100 }







 本文深入探讨mybatis的事务管理,包括mybatis支持的事务类图、JDBC和Managed两种事务类型管理器的配置与工作原理。重点讲解JdbcTransaction如何依赖JDBC处理事务,以及ManagedTransaction如何让容器管理事务生命周期。
本文深入探讨mybatis的事务管理,包括mybatis支持的事务类图、JDBC和Managed两种事务类型管理器的配置与工作原理。重点讲解JdbcTransaction如何依赖JDBC处理事务,以及ManagedTransaction如何让容器管理事务生命周期。














 352
352

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








