原题:
Quadtrees
A quadtree is a representation format used to encode images. The fundamental idea behind the quadtree is that any image can be split into four quadrants. Each quadrant may again be split in four sub quadrants, etc. In the quadtree, the image is represented by a parent node, while the four quadrants are represented by four child nodes, in a predetermined order.
Of course, if the whole image is a single color, it can be represented by a quadtree consisting of a single node. In general, a quadrant needs only to be subdivided if it consists of pixels of different colors. As a result, the quadtree need not be of uniform depth.
A modern computer artist works with black-and-white images of tex2html_wrap_inline34 units, for a total of 1024 pixels per image. One of the operations he performs is adding two images together, to form a new image. In the resulting image a pixel is black if it was black in at least one of the component images, otherwise it is white.
This particular artist believes in what he calls the preferred fullness: for an image to be interesting (i.e. to sell for big bucks) the most important property is the number of filled (black) pixels in the image. So, before adding two images together, he would like to know how many pixels will be black in the resulting image. Your job is to write a program that, given the quadtree representation of two images, calculates the number of pixels that are black in the image, which is the result of adding the two images together.
In the figure, the first example is shown (from top to bottom) as image, quadtree, pre-order string (defined below) and number of pixels. The quadrant numbering is shown at the top of the figure.
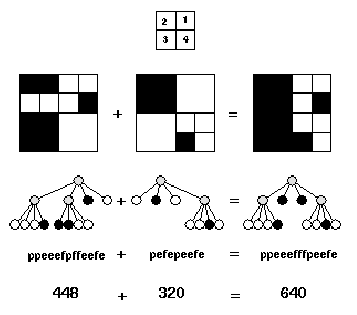
Input Specification
The first line of input specifies the number of test cases (N) your program has to process.
The input for each test case is two strings, each string on its own line. The string is the pre-order representation of a quadtree, in which the letter ‘p’ indicates a parent node, the letter ‘f’ (full) a black quadrant and the letter ‘e’ (empty) a white quadrant. It is guaranteed that each string represents a valid quadtree, while the depth of the tree is not more than 5 (because each pixel has only one color).
Output Specification
For each test case, print on one line the text ‘There are X black pixels.’, where X is the number of black pixels in the resulting image.
Example Input
3
ppeeefpffeefe
pefepeefe
peeef
peefe
peeef
peepefefe
Example Output
There are 640 black pixels.
There are 512 black pixels.
There are 384 black pixels.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>
#include<set>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
//fstream output,input;
struct Qtree
{
char c;
Qtree *child[4];
};
int inde,ans;
string s,s1,s2;
Qtree *t1,*t2;
Qtree *build(Qtree *T)//建立树
{
inde++;
if(inde==s.size())//设置全局变量用来遍历字符串
return NULL;
T= new Qtree;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
T->child[i]=NULL;
T->c=s[inde];
if(s[inde]=='p')
{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
if(T->child[i]==NULL)
T->child[i]=build(T->child[i]);//如果是字母p说明还有子节点
}
return T;//返回对应的节点
}
void dfs(Qtree *T1,Qtree *T2,int dep)//遍历两颗四分树
{
if(T1==NULL&&T2==NULL)//如果两个树都是空就返回
return;
if(T1!=NULL&&T2!=NULL)//两个都不空的话进行如下操作
{
if(T1->c=='p'&&T2->c=='p')//如果当前且对应的节点都有子节点
{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)//说明两个节点都是黑白相间的,继续查找子节点
dfs(T1->child[i],T2->child[i],dep+1);
}
if(T1->c=='f'||T2->c=='f')//如果两个节点当中有一个是f那就是说明两个树的节点中
{//有一个是纯黑的,计算后返回
ans+=1024>>(dep*2);
return;
}
if(T1->c=='e'&&T2->c=='p')
{//有一个是空的,另外一个是混色的,那么递归那个混色的
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
dfs(T1,T2->child[i],dep+1);
}
if(T1->c=='p'&&T2->c=='e')
{//同上
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
dfs(T1->child[i],T2,dep+1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
cin>>s1>>s2;
ans=0;
inde=-1;
s=s1;
t1=build(t1);
inde=-1;
s=s2;
t2=build(t2);
dfs(t1,t2,0);
cout<<"There are "<<ans<<" black pixels."<<endl;
}
// input.close();
// output.close();
return 0;
}
思路:
我对递归理解的很烂,这道题晃悠了很久才弄出来。主要就了解递归和搜索的过程,具体思路在代码中。
这里注意,for(int i=0;i<4;i++)递归完成后,如果回溯,那么回溯到上一个栈帧保存的i值就是你递归当前的i值,不会因为int重新定义而刷新。另外,不用释放空间。
本来没想用递归做,自己不熟练是一个原因,另外怕超时。没想到速度还挺快的,0秒就过了。























 999
999











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








