1 概述
递归神经网络是时间递归神经网络(recurrent neural network)和结构递归神经网络(recursive neural network)的总称。RNN一般指代时间递归神经网络。
RNN早先被提到的可以追溯到1989年Axel Cleeremans的论文。
详情查看:http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.160.2979&rep=rep1&type=pdf
RNN被提出的初衷是用来处理序列数据的。
RNN相对于传统神经网络最大的不同是神经元的输入的改变。RNN隐藏层神经元的输入不止是上一层神经元的输出,还包括了本层的输出。
但是鉴于RNN误差反向传播时候梯度消失的问题。1997年Sepp Hochreiter等人提出了典型的LSTM网络。
详情查看:http://www.bioinf.jku.at/publications/older/2604.pdf
LMST是RNN的升级版,它的隐藏层神经元的输入和输出会在RNN的基础上做进一步的处理,在本文末有提到。
RNN背后的思想是利用顺序信息。它包含循环的网络,允许信息的持久化。
2 优缺点
优点:时间递归神经网络可以描述动态时间行为,因为和前馈神经网络接受较特定结构的输入不同,RNN将状态在自身网络中循环传递,因此可以接受更广泛的时间序列结构输入。
缺点:简单递归神经网络无法处理随着递归,梯度爆炸或者梯度消失的问题,并且难以捕捉长期时间关联;有效的处理方法是忘掉错误的信息,记住正确的信息。LSTM能够比较好的解决这个问题。
3 应用
RNN已经被在实践中证明对NLP是非常成功的。如词向量表达,语句合法性检查,词性标注等。在RNN中,目前使用最广泛最成功的模型是LSTM模型。
基于LSTM的系统可以学习翻译语言、控制机器人、图像分析、文档摘要、语音识别图像识别、手写识别、控制聊天机器人、预测疾病、点击率和股票、合成音乐等等任务。举个例子,在2015年,谷歌通过基于CTC训练的LSTM程序大幅提升了安卓手机和其他设备中语音识别的能力,使用了我的实验室在2006年发表的方法。百度也使用了CTC;苹果的iPhone在QucikType和Siri中使用了LSTM;微软不仅将LSTM用于语音识别,还将这一技术用于虚拟对话形象生成和编写程序代码等等。亚马逊Alexa通过双向LSTM在家中与你交流,而谷歌使用LSTM的范围更加广泛,它可以生成图像字幕,自动回复电子邮件,它包含在新的智能助手Allo中,也显著地提高了谷歌翻译的质量(从2016年开始)。事实上,谷歌数据中心的很大一部分计算资源现在都在执行LSTM任务。
内容链接地址:https://www.zhihu.com/question/37082800/answer/173870605
4 相关概念
序列: 序列是被排成一列的对象(或事件)。可以是一句话,一串数字等。RNN训练数据时,会以序列为单位训练数据。同一序列中的每次训练代表一个时刻t。
5 RNN网路结构
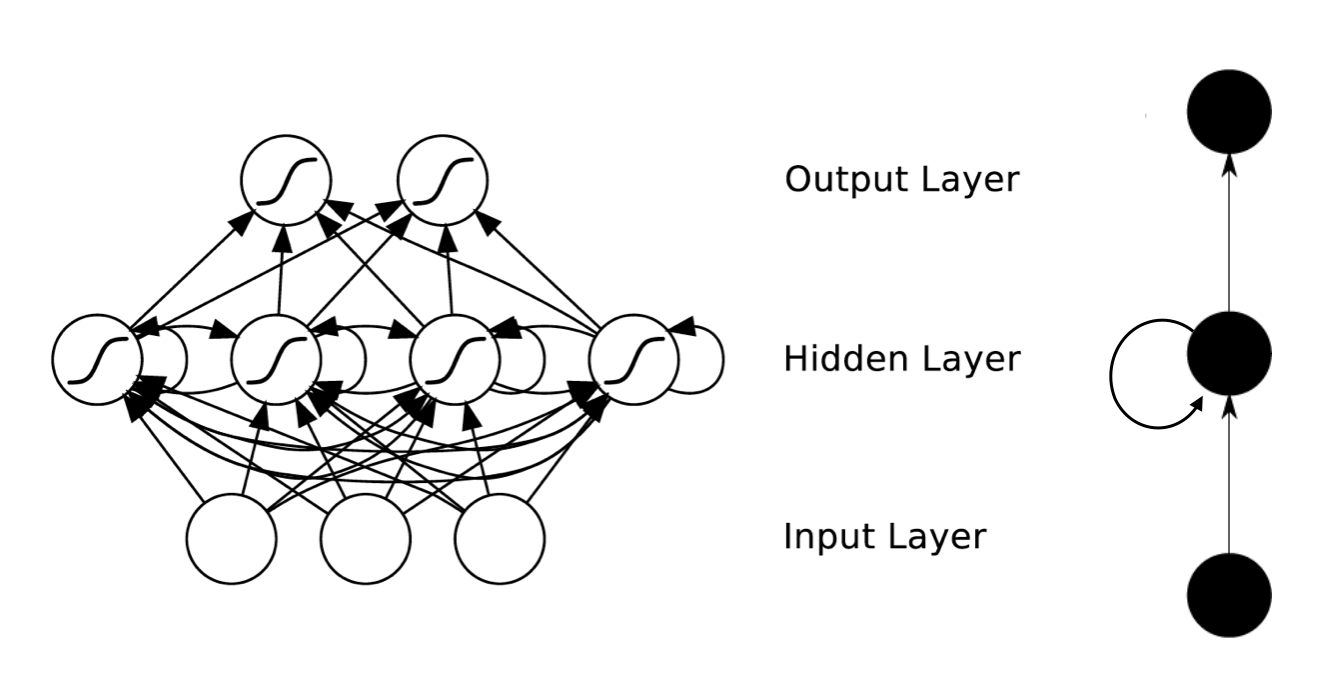
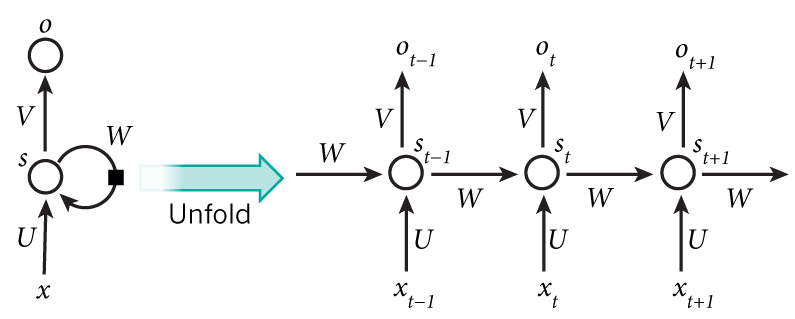
从上图我们可以看出,RNN隐藏层神经元的连接方式和普通神经网路的连接方式有一个非常明显的区别,就是同一层的神经元的输出也成为了这一层神经元的输入。当然同一时刻的输出是不可能作为这个时刻的输入的。所以是前一个时刻(t-1)的输出作为这个时刻(t)的输入。
上图就是一个序列的结构展开示意图。
6 公式推导
设输入层到隐层的权重矩阵为V;隐层自循环的权重矩阵为U;隐层到输出层的权重矩阵为W;对应的偏置为 bh








 本文介绍了递归神经网络RNN的基本概念、优缺点、应用场景和相关概念,重点阐述了RNN的网络结构和公式推导。通过一个Python代码示例展示了RNN如何实现八位二进制数加法,同时提到了为解决RNN梯度消失问题的LSTM网络。
本文介绍了递归神经网络RNN的基本概念、优缺点、应用场景和相关概念,重点阐述了RNN的网络结构和公式推导。通过一个Python代码示例展示了RNN如何实现八位二进制数加法,同时提到了为解决RNN梯度消失问题的LSTM网络。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 85
85

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








