看了下网上的gui教程都没有什么比较好的,不管是java、安卓还是ios,设计UI都应该先从布局上来考虑,而不是看一点写一点。如果你一来就想着用绝对布局,我只能说这种思想很危险,砖慢慢搬吧。
这个是中期考试的时候边学边做的一个东西,做一个eclipse的搜索gui,类似下图,其实也就是个苦力活。
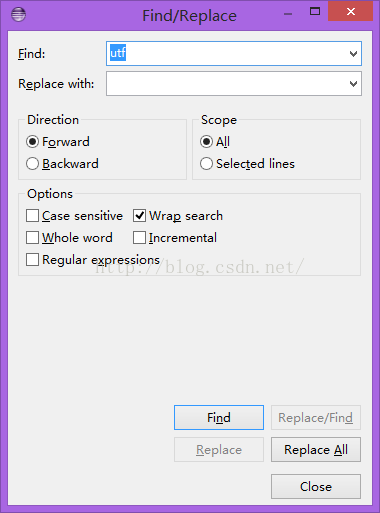
原图:
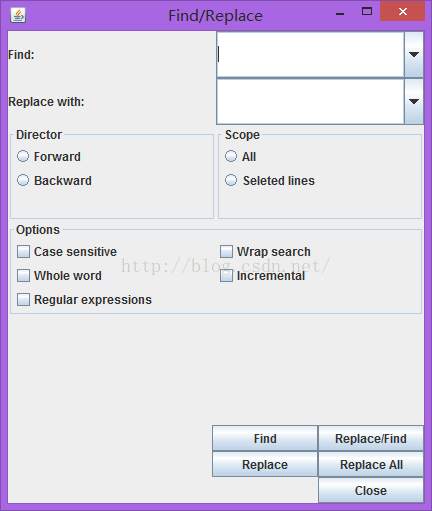
我的代码跑出来的图:
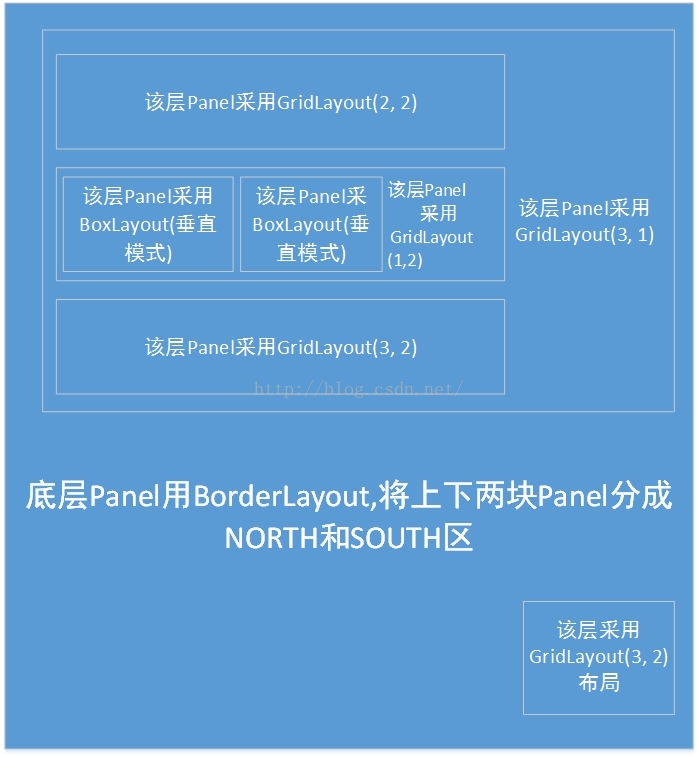
先说布局,我直接给张图:
设计到的控件(从上到下、从左到右的顺序):
North区:
JLabel、JComboBox
JRadioButton
JCheckBox
South区:
JButton
值得一提的是panel的titleBorder,就是这个玩意儿:
这是我花时间最长的地方,因为我一直以为那是个控件,其实是panel的Border,像这样设置一下panel的Border属性就可以了:
JPanel panelDirector = new JPanel();
panelDirector .setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Director"));
package org.echo.project2;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.BorderFactory;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.ButtonGroup;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JCheckBox;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JRadioButton;
/**
* echo 邮箱756451227@qq.com
*
*/
public class MainView extends JFrame{
public MainView() {
this.setTitle("Find/Replace");
this.setSize(600, 600);
this.setLocation(500, 500);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// find
JPanel panelFind = new JPanel();
JLabel findLabel = new JLabel("Find:");
JComboBox findBox = new JComboBox();
findBox.setEditable(true);
panelFind.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
panelFind.add(findLabel);
panelFind.add(findBox);
// replace
JPanel panelReplace = new JPanel();
panelReplace.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
JLabel replaceLabel = new JLabel("Replace with:");;
JComboBox replaceBox = new JComboBox();
replaceBox.setEditable(true);
panelReplace.add(replaceLabel);
panelReplace.add(replaceBox);
// find and replace
JPanel panelArea1 = new JPanel();
panelArea1.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelArea1, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
panelArea1.add(panelFind);
panelArea1.add(panelReplace);
// direction
JPanel panelDirection = new JPanel();
panelDirection.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelDirection, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
JRadioButton forButton = new JRadioButton("Forward");
JRadioButton backButton = new JRadioButton("Backward");
ButtonGroup directionGroup = new ButtonGroup();
directionGroup.add(forButton);
directionGroup.add(backButton);
panelDirection.add(forButton);
panelDirection.add(backButton);
panelDirection.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Director"));
// scope
JPanel panelScope = new JPanel();
panelScope.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelScope, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
JRadioButton allButton = new JRadioButton("All");
JRadioButton selectedButton = new JRadioButton("Seleted lines");
ButtonGroup scopeGroup = new ButtonGroup();
scopeGroup.add(allButton);
scopeGroup.add(selectedButton);
panelScope.add(allButton);
panelScope.add(selectedButton);
panelScope.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Scope"));
// direction and scope
JPanel panelDireAndScope = new JPanel();
panelDireAndScope.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,2));
panelDireAndScope.add(panelDirection);
panelDireAndScope.add(panelScope);
// options
JPanel panelOptions = new JPanel();
panelOptions.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2));
JCheckBox checkBox1 = new JCheckBox("Case sensitive");
JCheckBox checkBox2 = new JCheckBox("Wrap search");
JCheckBox checkBox3 = new JCheckBox("Whole word");
JCheckBox checkBox4 = new JCheckBox("Incremental");
JCheckBox checkBox5 = new JCheckBox("Regular expressions");
ButtonGroup optionsGroup = new ButtonGroup();
optionsGroup.add(checkBox1);
optionsGroup.add(checkBox2);
optionsGroup.add(checkBox3);
optionsGroup.add(checkBox4);
optionsGroup.add(checkBox5);
panelOptions.add(checkBox1);
panelOptions.add(checkBox2);
panelOptions.add(checkBox3);
panelOptions.add(checkBox4);
panelOptions.add(checkBox5);
panelOptions.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Options"));
// choose buttons
JPanel panelButtons = new JPanel();
panelButtons.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2));
JButton btnFind = new JButton("Find");
JButton btnReOrFind = new JButton("Replace/Find");
JButton btnReplace = new JButton("Replace");
JButton btnReplaceAll = new JButton("Replace All");
JLabel lblNull = new JLabel("");
JButton btnClose = new JButton("Close");
panelButtons.add(btnFind);
panelButtons.add(btnReOrFind);
panelButtons.add(btnReplace);
panelButtons.add(btnReplaceAll);
panelButtons.add(lblNull);
panelButtons.add(btnClose);
// panel south
JPanel southPanel = new JPanel();
southPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
southPanel.add(panelButtons, BorderLayout.EAST);
// panel north
JPanel northPanel = new JPanel();
northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1));
northPanel.add(panelArea1);
northPanel.add(panelDireAndScope);
northPanel.add(panelOptions);
this.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
this.add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.add(southPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
this.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Single mode
MainView mainView = new MainView();
}
}






















 1396
1396

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








