前言
在计算几何中,我们经常需要寻找一个2D多边形(Polygon)的极值点。例如通过x\y的极值点,我们可以定义一个多边形的包围盒。更一般的情况下,我们可能会需要寻找一个多边形在任意方向上的极值点。对于n个点的点集,很容易找到一个O(n)的算法,只需要依次测试每个点即可。然而对于凸多边形,可以利用二分搜索的思想在时间内找到极值点。首先,定义一个任意的方向向量u,接下来我们详细讲解该算法的思路。
平面点集和简单多边形的凸包在这两篇博文中已经介绍过了:平面点集的凸包算法、多边形快速凸包算法。因此,对于平面点集和任意简单多边形只需要先计算凸包,然后再计算凸包极值点即可。其算法复杂度由凸包算法决定。
凸包极值点算法
首先,定义2D凸多边形S由n个点构成V0,V1,...,Vn-1,Vn=V0,并且沿着逆时针方向给定。
定义为第i条边(从Vi到Vi+1),
为边向量。
目标:找到S中的所有点在u方向上的极值点。也就是将点投影在u说定义的直线上,极值点就是投影点的极值点,如下图所示:
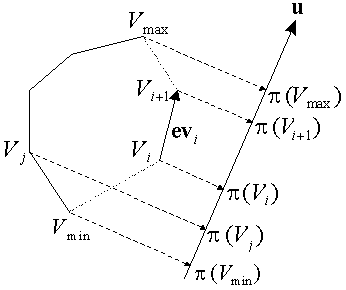
可以看到,相对于u,Vi在Vj之上。也就是(Vi-Vj)与u之间形成一个锐角,相当于下面的几何条件:
这个条件可以帮助我们判断,一条边相对于u的投影是在增加还是减少。
暴力算法
最直接的办法就是暴力搜索每个点,每一步与当前保存的极值点比较。该算法的伪代码如下:
Input: W = {V0,V1,...,Vn-1} n个点的点集
u = 给定的方向向量
记 max = min = 0。
for each point Vi in {V1,...,Vn-1} (i=1,n-1)
{
if (u · (Vi - Vmax) > 0) { // Viis above the prior max
max = i; // new max index = i
continue; // a new max can't be a new min
}
if (u · (Vi - Vmin) < 0) // Vi is below the prior min
min = i; // new min index = i
}
return max = 最大值点的Index
min = 最小值点的Index尽管算法是线性的,但还可以通过二分搜索加快。
二分搜索
对于一个凸多边形的点集,我们可以通过二分搜索,在时间内找到极值点。
首先,假设极大值点在顶点Va和Vb之间,Vc为Va和Vb的中间点,为了实现二分搜索,我们需要将下一步的搜索范围缩小到[a, c]或者[c, b]。由于多边形是凸的,我们可以通过比较A、C处的边向量、
来做到这一点。下面详细说明:
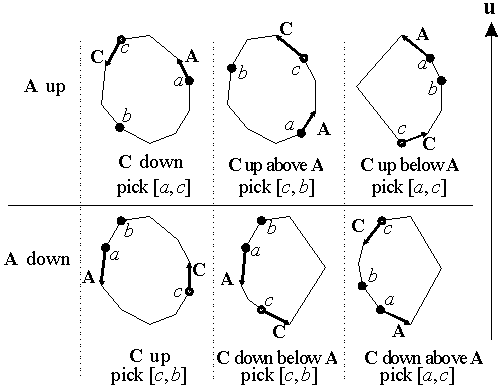
如上图所示。假定u向上,A、B、C的相对位置可能有6种情况。对于每种情况,要么[a, c],要么[c, b]包含最大值点。这是因为,多边形S在u方向上是单调的,它由两个单调链组成,从最小值点开始,到最大值点单调递增,然后再单调递减回到最小值点。而且无论u的方向如何,这个结论都是成立的。
接下来,我们就能构造二分搜索了。从开始,
,在每一步,我们需要确定是将a增加到c,还是b减小到c,将包含最大值的区间缩小一半。当然,我们需要检查,是否已经找到了一个局部极大值点Vc,这只需要检查
和
的符号是否一致即可。如果两者的符号不一致,说明Vc是局部极大值点,同时也是多边形的全局最大值点。
于是,我们得到,寻找相对于u的最大值点的伪代码如下:
Input: OMEGA = {V0,V1,...,Vn-1,Vn=V0} is a 2D proper convex polygon
u = a 2D direction vector
if V0 is a local maximum, then return 0;
Put a=0; b=n;
Put A = the edge vector at V0;
forever {
Put c = the midpoint of [a,b] = int((a+b)/2);
if Vc is a local maximum, then it is the global maximum
return c;
// no max yet, so continue with the binary search
// pick one of the two subchains [a,c] or [c,b]
Put C = the edge vector at Vc;
if (A points up) {
if (C points down) {
b = c; select [a,c]
}
else C points up {
if Va is above Vc {
b = c; select [a,c]
}
else Va is below Vc {
a = c; select [c,b]
A = C;
}
}
}
else A points down {
if (C points up) {
a = c; select [c,b]
A = C;
}
else C points down {
if Va is below Vc {
b = c; select [a,c]
}
else Va is above Vc {
a = c; select [c,b]
A = C;
}
}
}
if (b <= a+1) then the chain is impossibly small
return an error; since something's wrong
}
下面是二分搜索算法的一个C++实现:
// Assume that classes are already given for the objects:
// Point and Vector (2D) with:
// coordinates {float x, y;}
// operators for:
// == to test equality
// != to test inequality
// = for assignment
// -Vector for unary minus
// Point = Point ± Vector
// Vector = Point - Point
// Vector = Vector ± Vector
// Line with defining points {Point P0, P1;}
//===================================================================
// dot product (2D) which allows vector operations in arguments
#define dot(u,v) ((u).x * (v).x + (u).y * (v).y)
// tests for vector orientation relative to a direction vector u
#define up(u,v) (dot(u,v) > 0)
#define down(u,v) (dot(u,v) < 0)
#define dr(u,Vi,Vj) (dot(u, (Vi)-(Vj))) // direction sign of (Vi-Vj)
#define above(u,Vi,Vj) (dr(u,Vi,Vj) > 0) // true if Vi is above Vj
#define below(u,Vi,Vj) (dr(u,Vi,Vj) < 0) // true if Vi is below Vj
// polyMax_2D(): find a polygon's max vertex in a specified direction
// Input: U = a 2D direction vector
// V[] = array vertices of a proper convex polygon
// n = number of polygon vertices, with V[n]=V[0]
// Return: index (>=0) of the maximum vertex, or
// (-1) = an error [Note: should be impossible, but...]
int
polyMax_2D( Vector U, Point* V, int n )
{
if (n < 10) { // use brute force search for small polygons
int max = 0;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++) // for each point in {V1,...,Vn-1}
if (above(U, V[i], V[max])) // if V[i] is above prior V[max]
max = i; // new max index = i
return max;
}
// use binary search for large polygons
int a, b, c; // indices for edge chain endpoints
Vector A, C; // edge vectors at V[a] and V[c]
int upA, upC; // test for "up" direction of A and C
a=0; b=n; // start chain = [0,n] with V[n]=V[0]
A = V[1] - V[0];
upA = up(U,A);
// test if V[0] is a local maximum
if (!upA && !above(U, V[n-1], V[0])) // V[0] is the maximum
return 0;
for(;;) {
c = (a + b) / 2; // midpoint of [a,b], and 0<c<n
C = V[c+1] - V[c];
upC = up(U,C);
if (!upC && !above(U, V[c-1], V[c])) // V[c] is a local maximum
return c; // thus it is the maximum
// no max yet, so continue with the binary search
// pick one of the two subchains [a,c] or [c,b]
if (upA) { // A points up
if (!upC) { // C points down
b = c; // select [a,c]
}
else { // C points up
if (above(U, V[a], V[c])) { // V[a] above V[c]
b = c; // select [a,c]
}
else { // V[a] below V[c]
a = c; // select [c,b]
A = C;
upA = upC;
}
}
}
else { // A points down
if (upC) { // C points up
a = c; // select [c,b]
A = C;
upA = upC;
}
else { // C points down
if (below(U, V[a], V[c])) { // V[a] below V[c]
b = c; // select [a,c]
}
else { // V[a] above V[c]
a = c; // select [c,b]
A = C;
upA = upC;
}
}
}
// have a new (reduced) chain [a,b]
if (b <= a+1) // the chain is impossibly small
return (-1); // return an error: something's wrong
}
}
//===================================================================






















 2499
2499











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








