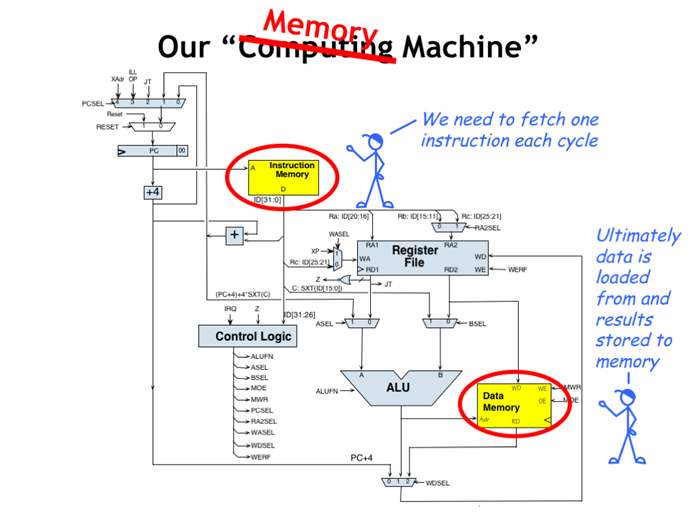
1. 我们的内存机器
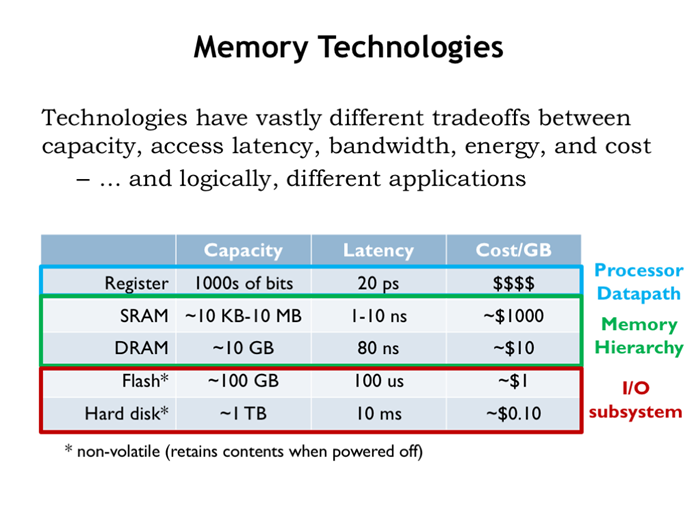
2. 内存技术
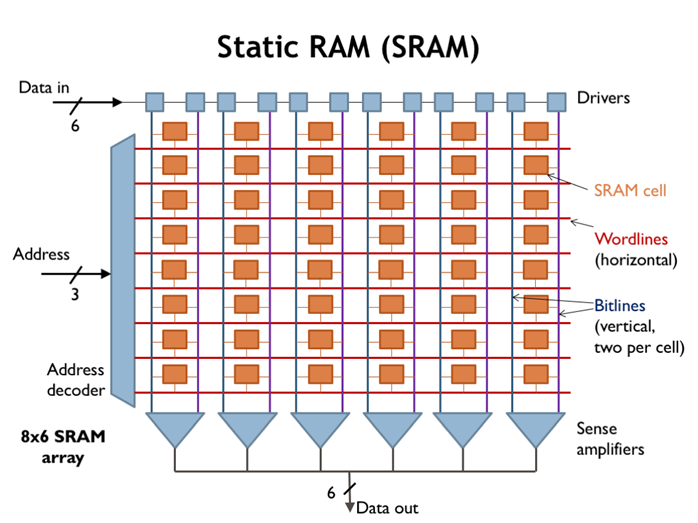
3. SRAM
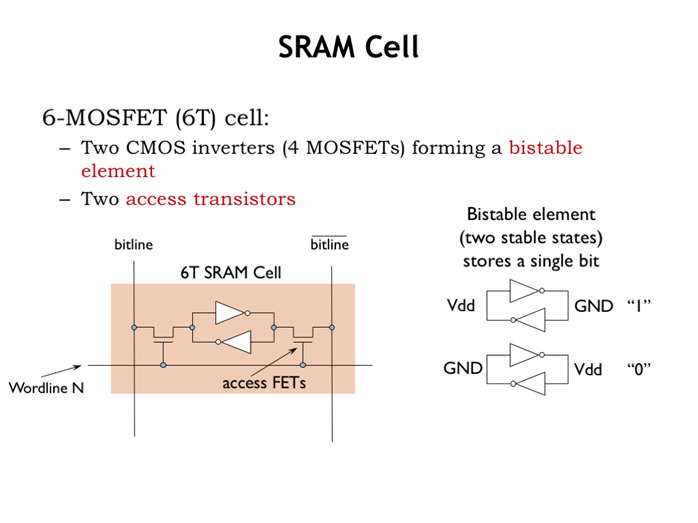
4. SRAM单元
5. SRAM读
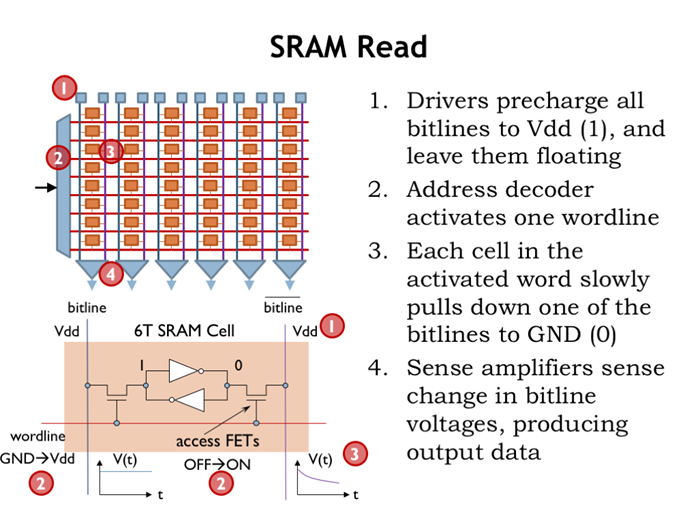
1、所有bitline电压都设置为1
2、某个wordline电压设为高电平,让对应cell的两个mos管接通
3、cell两边bitline中的某一个肯定会主键降为低电平
4、无需等到某个bitline降低到gnd,感应放大器感应到变化即可有相应输出
6. SRAM写
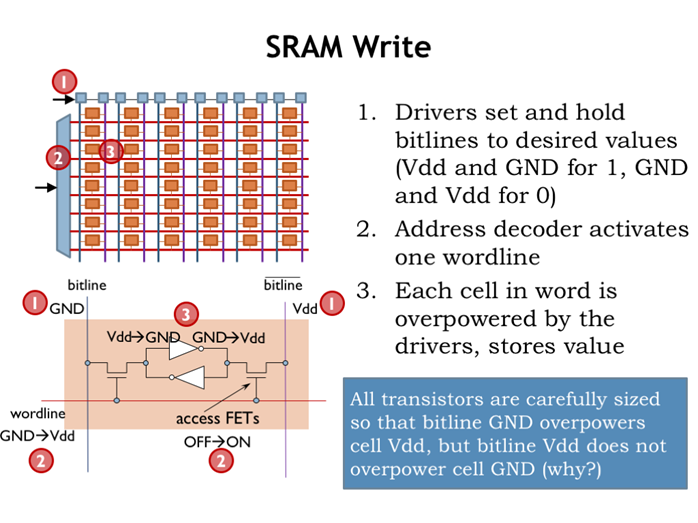
1、驱动将bitline设置为要写入的电压
2、地址解码器选中某一wordline
3、bitline中的值覆盖掉cell中的值
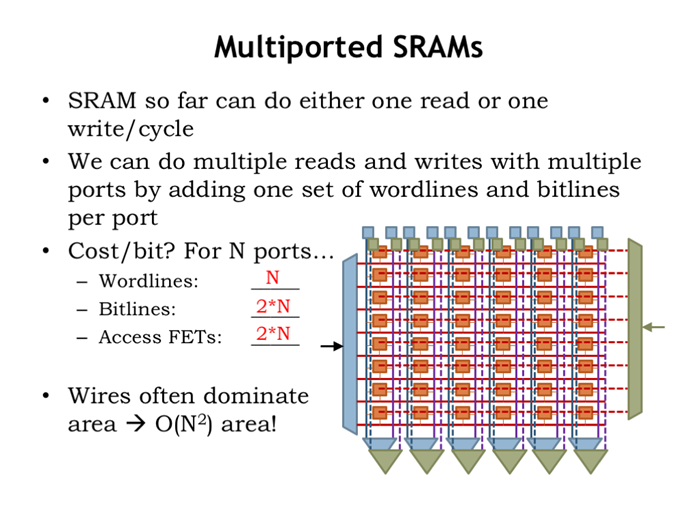
7. 多端口SRAM
8. SRAM总结
9. DRAM Cell
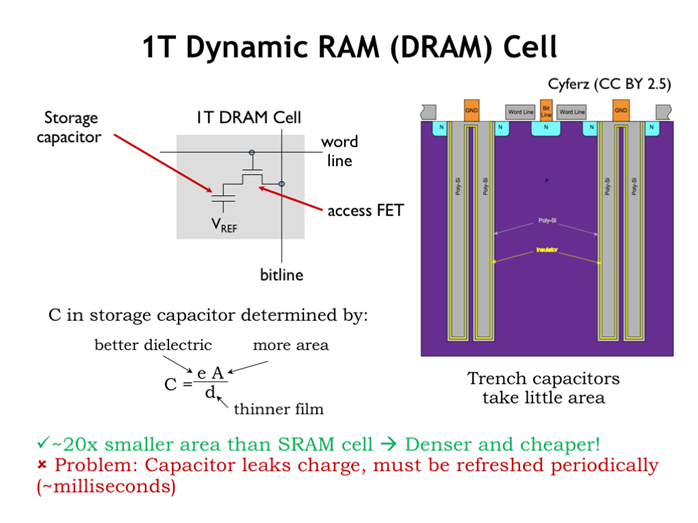
因为电容器、mos管漏电,不能稳定保持一定的电荷量,所以需要周期性地读取、重写cell的值,保证cell中的值有效
10. DRAM写和读
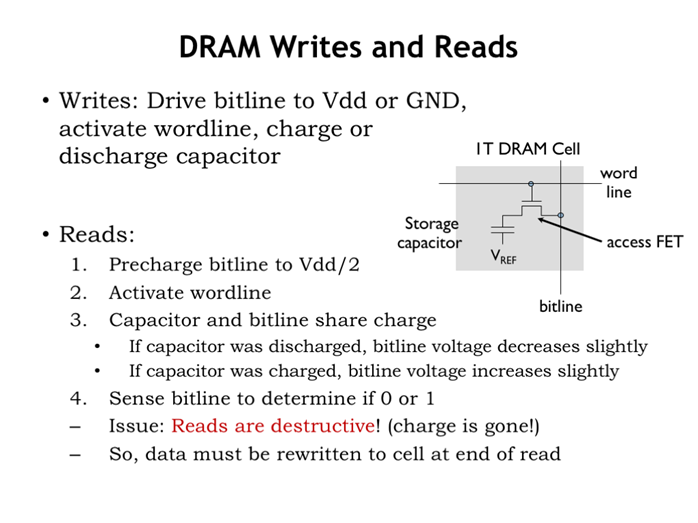
电容存放电荷用来代表0、1,wordline选中某行,读时,bitline电压设为Vdd/2,根据bitline的充放电判断cell的值,若cell为高电平,那么每次读会导致cell电荷量减少,需要重写;
写时,bitline设高低电平,来对电容充放电。
行地址选中(延时较大)后,同一行内,选择不同列时延迟较低
11. DRAM总结
12. 稳定存储:Flash
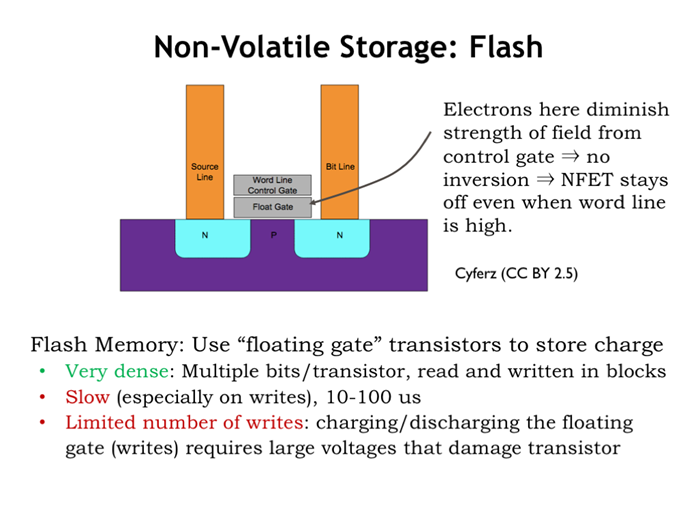
floating gate无电荷时:wordline施加V1,即可让NMOS导通。
floating gate有电荷时:wordline施加V2(一个大于V1的电压),才可以让NMOS导通。
那么施加一个V1到V2之间的电压,通过观测NMOS是否导通,得知floating gate处于哪种状态。
写有次数限制。
13. 稳定存储:硬盘
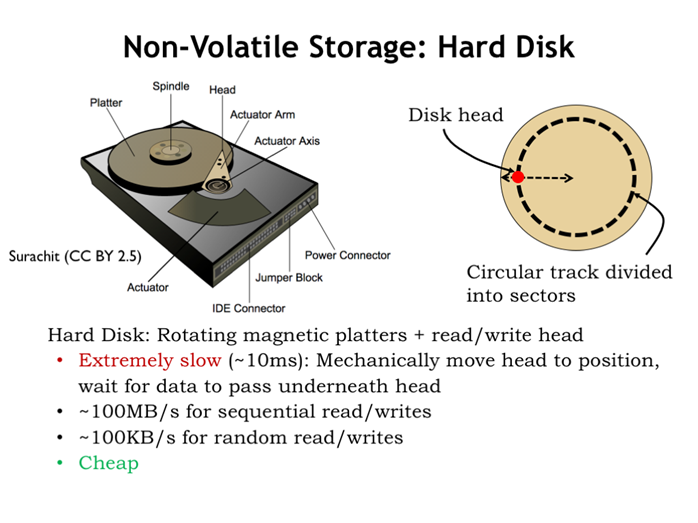
确定哪个扇面,再确定哪个圆圈,再确定圆圈哪一段。
串行读/写100MB/s,随机读写100KB/s
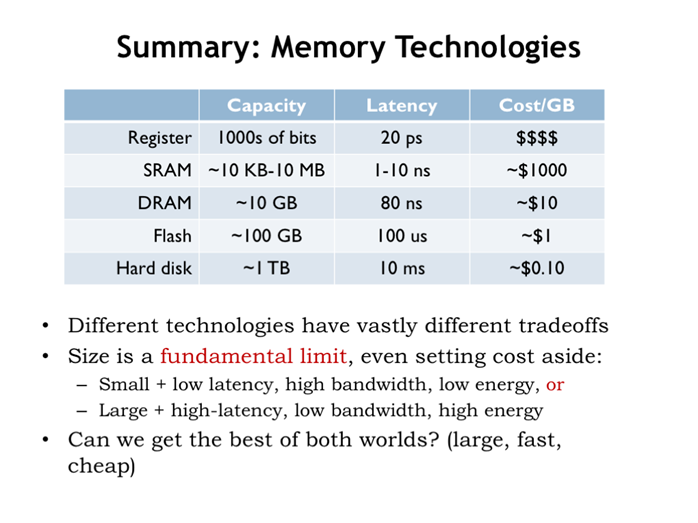
14. 总结:内存技术
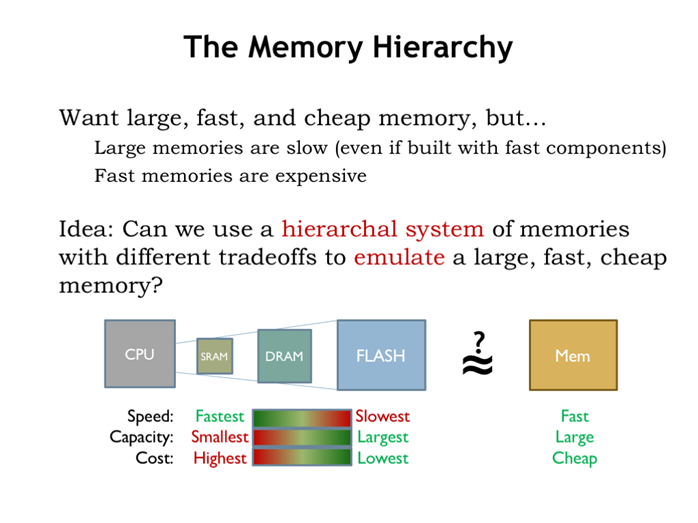
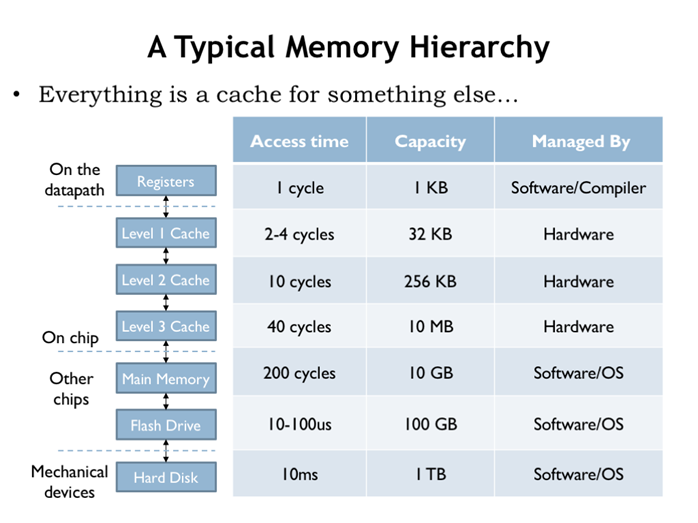
15. 内存分级
16. 内存层级连接
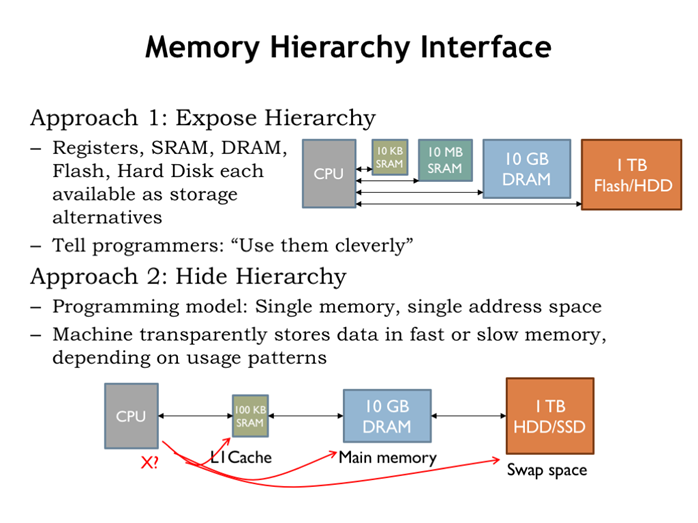
程序直接管理各个层级内存:超级计算机Seymour Cray就是个典型例子。
计算机内存系统管理各级内存:程序员只知道有一个大内存,有统一的地址可以访问。
17. 局部原则

局部性访问,空间局部性:访问地址a后,地址a附近的其他内存也更可能被访问;时间局部性:访问地址a后,接下来的时间里,a也很可能再次被访问。
访问DRAM中的数据后,内存系统会把DRAM中该数据附近的一块数据,放到SRAM中缓存。
18. 内存引用模式
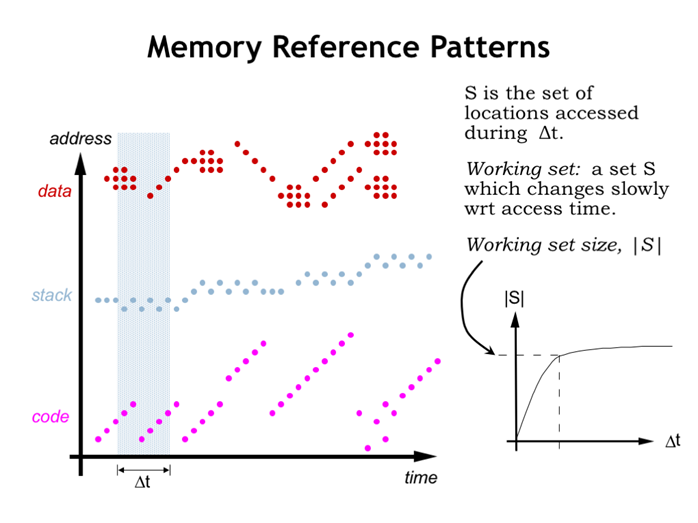
19. 缓存
20. 一个典型的内存分级
21. 缓存访问
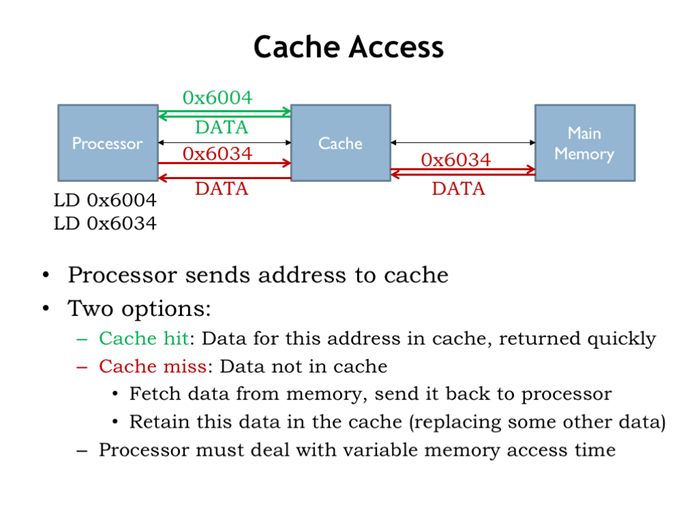
cpu从cache拿数据4ns,从主存拿数据44ns,cpu如何应对不同的内存访问时间。要么等着,现代处理器超线程技术可以在这段时间执行其他程序的指令。
22. 缓存指标
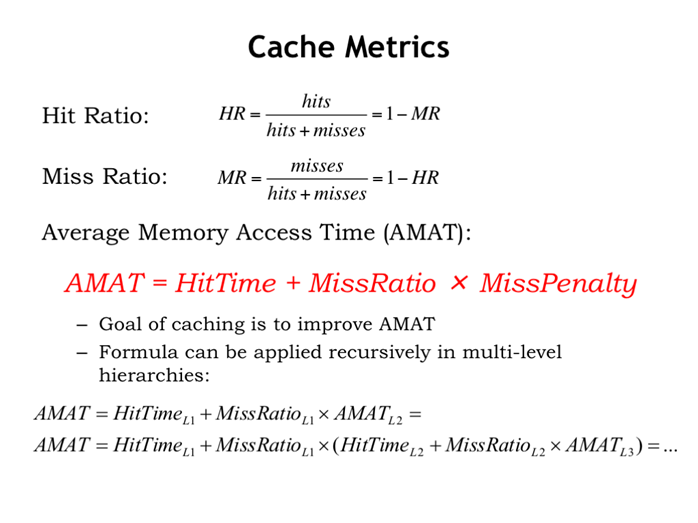
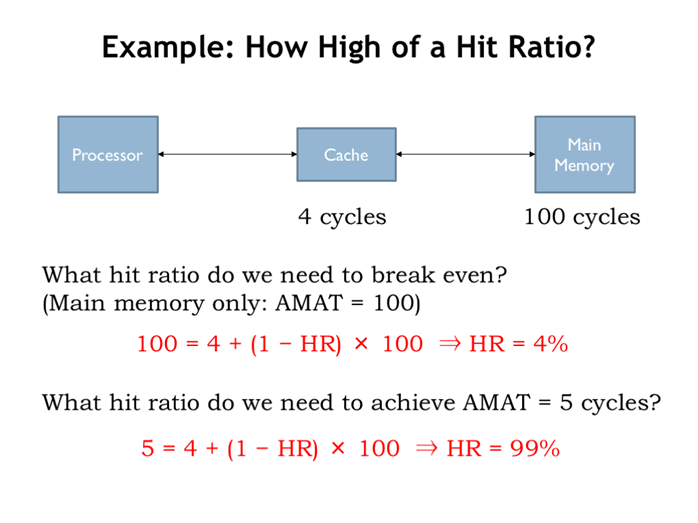
23. 例子:命中率要有多高
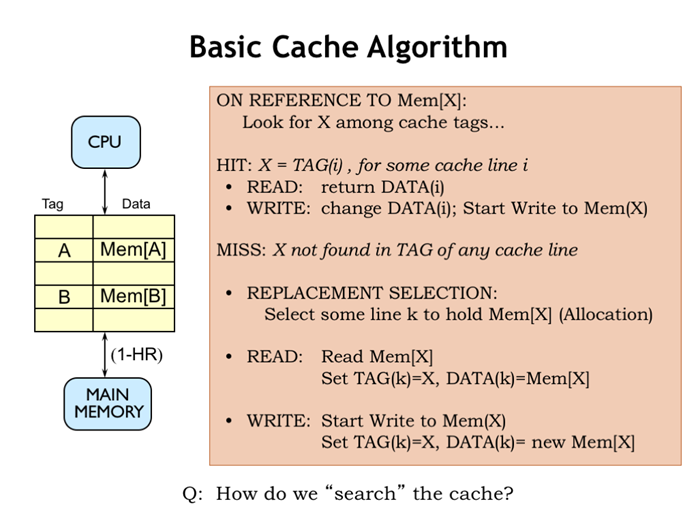
24. 基本缓存算法
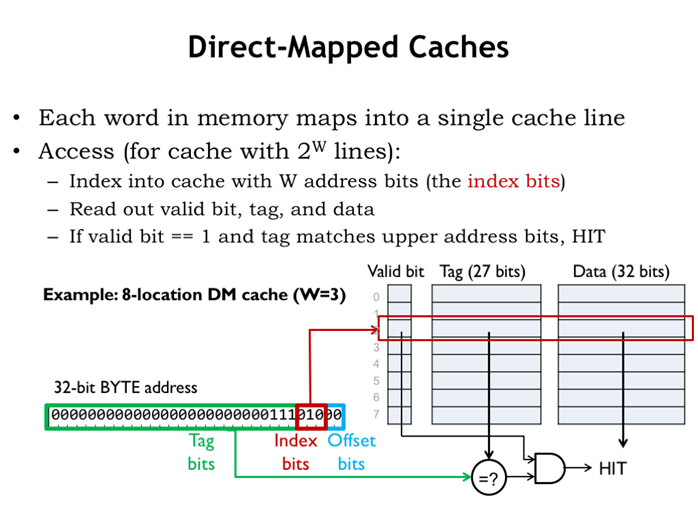
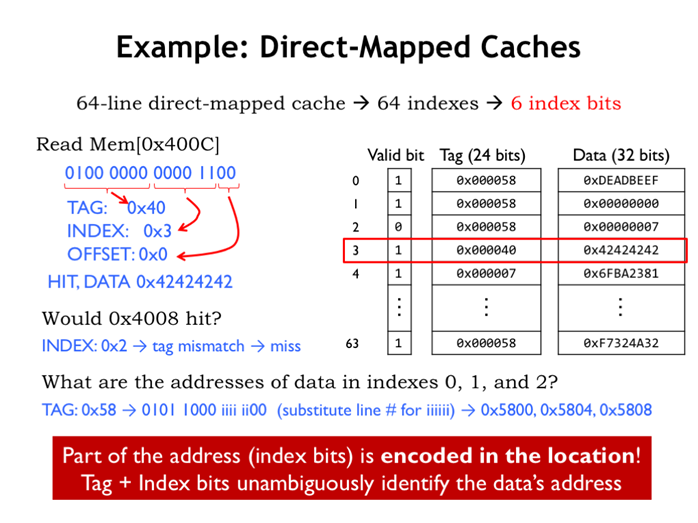
25. 直接映射缓存
26. 例子:直接映射缓存
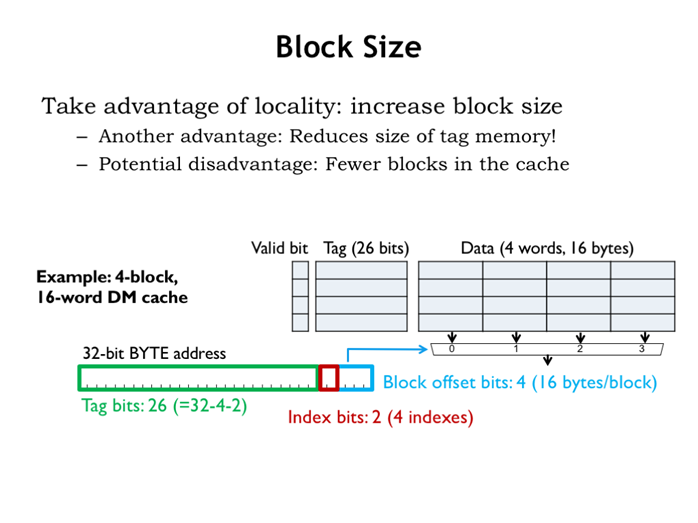
27. 块尺寸
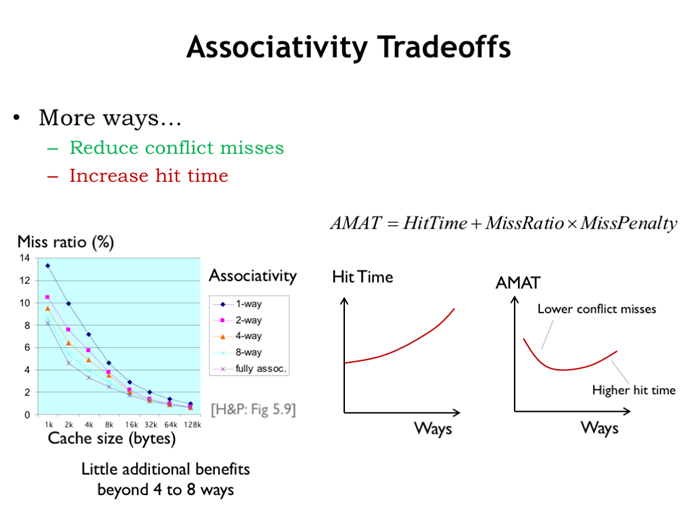
28. 块尺寸权衡
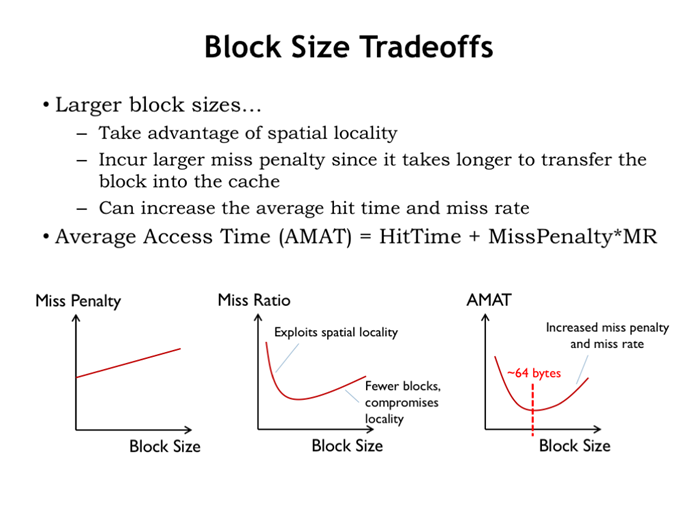
miss处罚:随着块尺寸增大而增大;
miss比率:随着块尺寸增大先降低、后升高;
amat:随着块尺寸增大先降低、后升高;
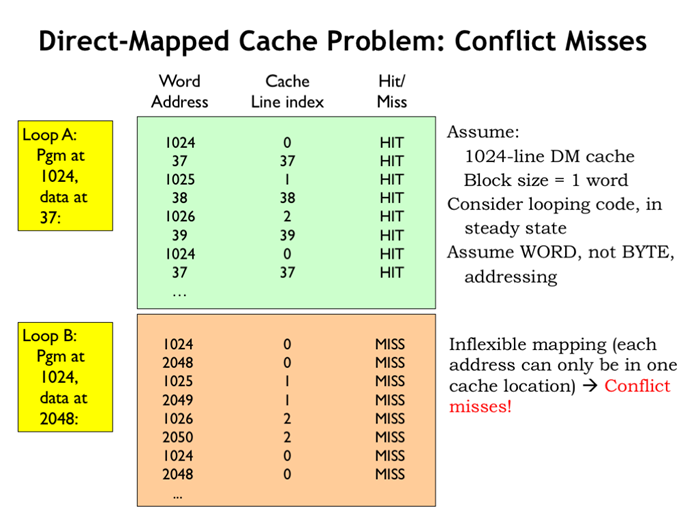
29. 直接映射缓存问题:conflict miss
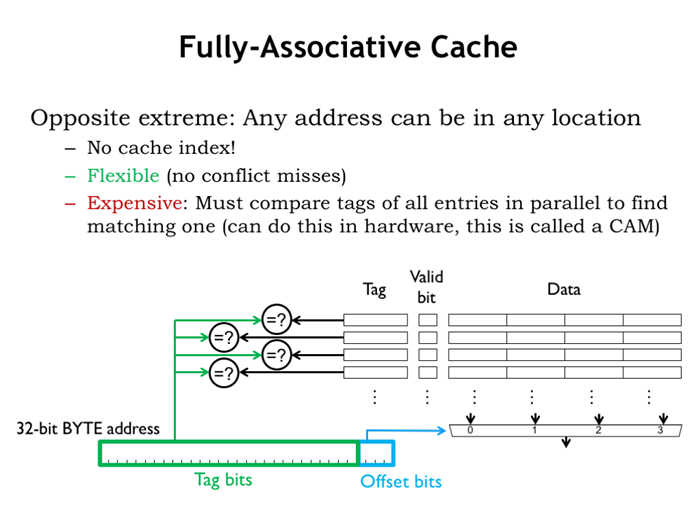
30. 全相联缓存
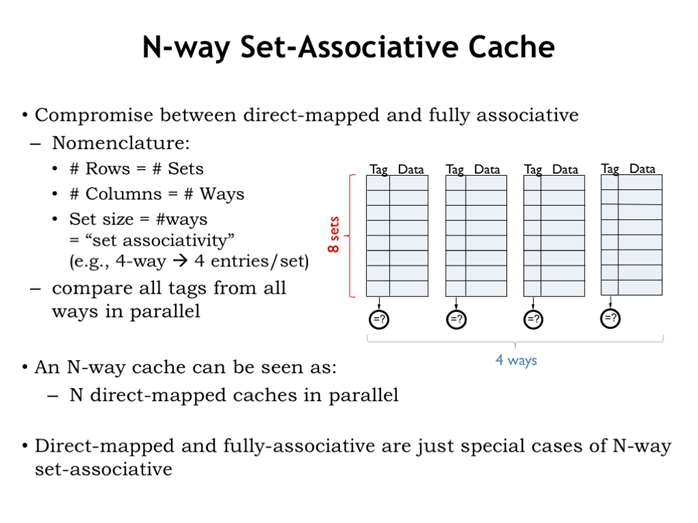
31. N路组相联缓存1
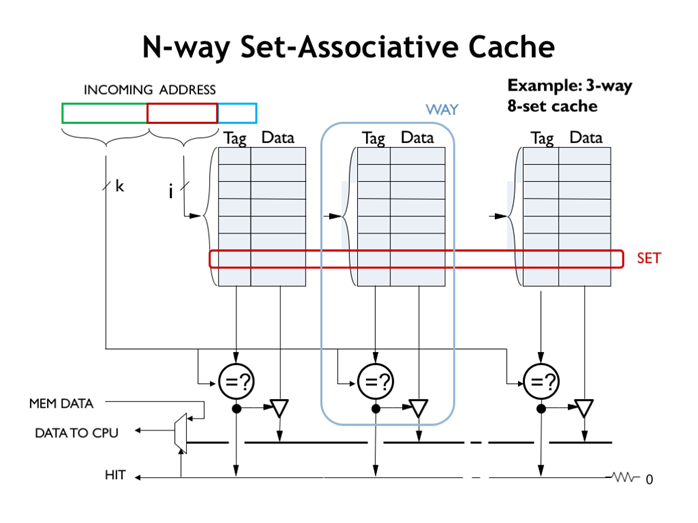
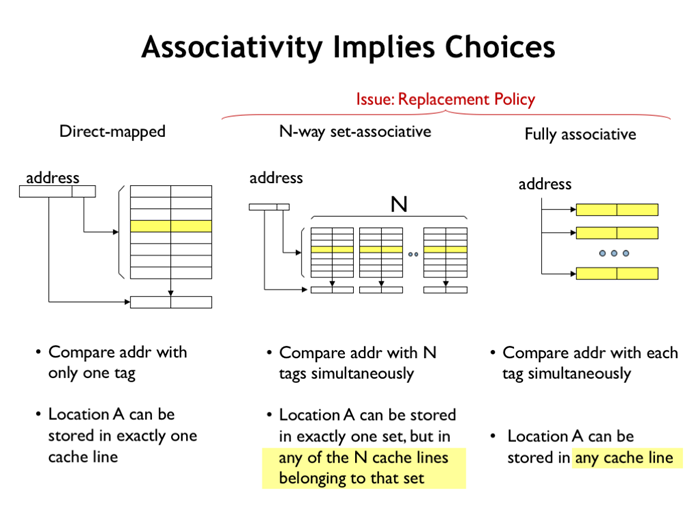
地址的index位定位到某个set(某行),再通过N个比较器,比较N个tag和地址的tag位。
32. N路组相联缓存2
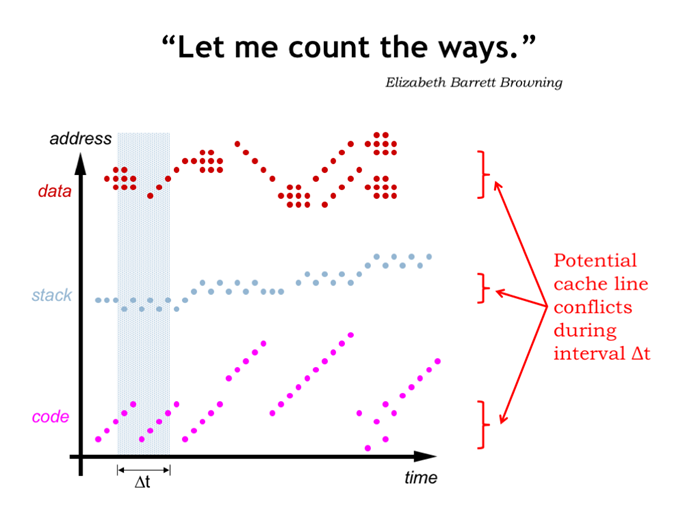
33. 让我们算下路数?
34. 相联权衡
35. associativity implies choices
36. 取代策略

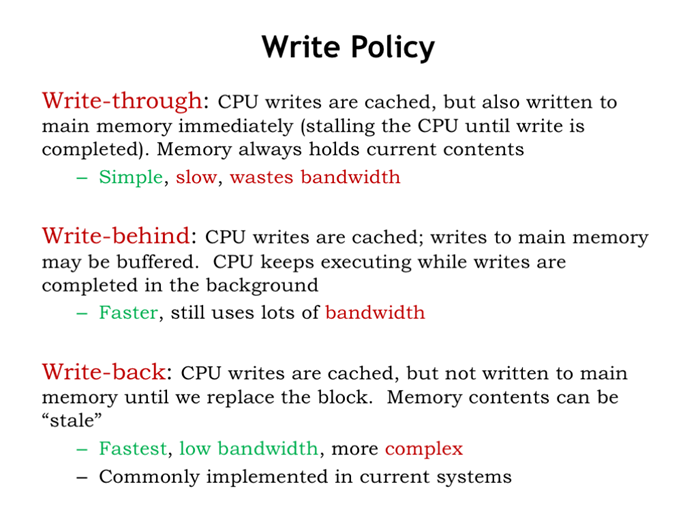
37. 写策略
38. 回写

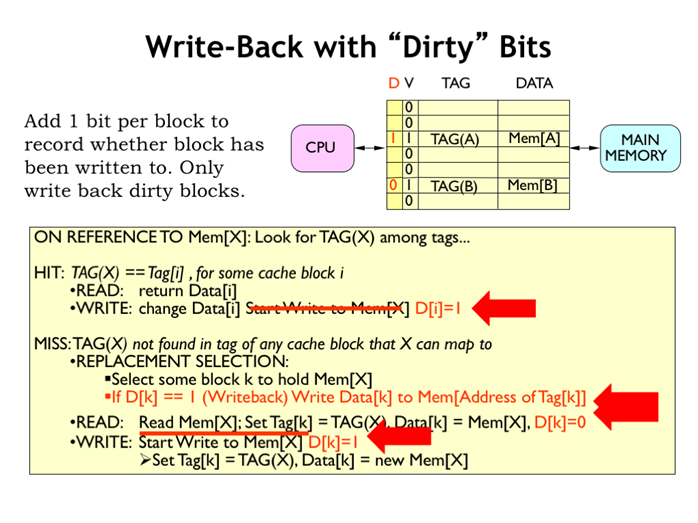
39. 带“脏”位的写回
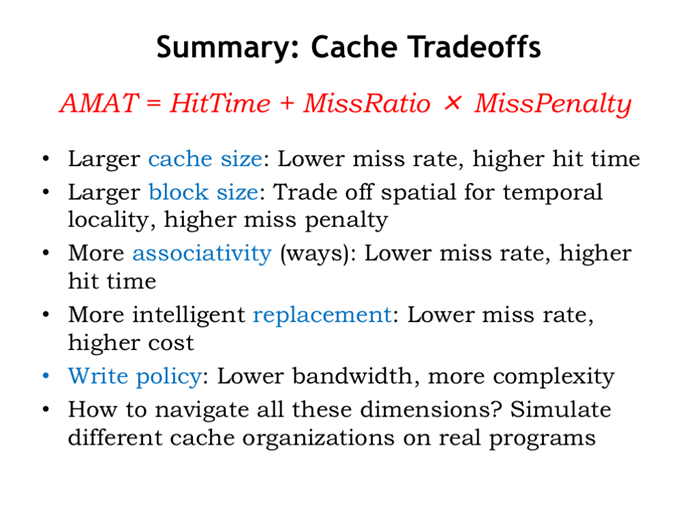
40. 总结:缓存权衡





















 1046
1046











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








