注:本文第一篇为 Cisco 配置 IS-IS 邻接和区域类型的文档,增加一处讨论。
第二篇作者提到了 GNS3 仿真环境中 Cisco IOS 镜像的注意事项。
第三篇 串一下 Huawei 基配。
简介
本文档介绍中间系统到中间系统 (IS-IS) 协议邻接关系和区域类型。
先决条件
要求
- 对中间系统到中间系统 (IS-IS) 的基本了解
- 开放最短路径优先 (OSPF) 协议的基础知识
使用的组件
本文档不限于特定的软件和硬件版本。
本文档中的信息都是基于特定实验室环境中的设备编写的。本文档中使用的所有设备最初均采用原始(默认)配置。如果您的网络处于活动状态,请确保您了解所有命令的潜在影响。
背景信息
IS-IS 协议被广泛用作互联网服务提供商 (ISP) 环境中的内部网关协议 (IGP)。本文档的范围是提供有关 IS-IS 区域类型、配置和故障排除的信息。它显示了一个示例网络场景及其配置,以及一些调试、捕获和输出,以便更好地理解。
在本文中,IS-IS 表示集成 IS-IS。集成 IS-IS 已部署,这意味着 IS-IS 是路由互联网协议 (IP)。 IS-IS 的真正力量在于它使用类型长度值 (TLV) 使得 IS-IS 协议具有高度可扩展性。 随着新功能的引入,它们可以与 TLV 一起添加到协议中。
IS-IS 区域
在 OSPF 协议中,路由器的任何接口都可以分配给特定区域。但是,IS-IS 中的区域概念不同。一般而言,这里的每台路由器属于一个区域。
这种想法源于最初创建 IS-IS 以路由无连接网络协议 (CLNP),其中地址属于设备(路由器),而在 Internet 协议 (IP) 中,地址属于特定接口。
IS-IS 协议有两个级别或层次结构,即级别 1 和级别 2。
级别 1 对应于 OSPF 区域内路由,而级别 2 对应于 OSPF 主干区域 0 路由。
2 级区域将所有区域与主干区域连接起来。
默认情况下,每台 Cisco 路由器都作为 1-2 级 (L1/L2) 路由器提供。
1 级路由器可以与 1 级和 1-2 级 (L1/L2) 路由器邻接。
2 级路由器可以与 2 级或 1-2 级 (L1/L2) 路由器邻接。
仅 L1 路由器和仅 L2 路由器之间没有邻接关系。
IS-IS 第 1 级 (L1) 路由器
对于所有区域内拓扑,IS-IS 第 1 级路由器具有其自己区域的链路状态信息。为了将数据包路由到其他区域,它使用最近的第 2 级路由器 (L1/L2)。 第 1 级区域的行为与 OSPF 完全末节区域大致相同。L1 是发送 L1 Hello 的唯一路由器。
IS-IS 级别 1-2 (L1/L2) 路由器
IS-IS L1/L2 路由器维护两个链路状态数据库信息。
一个用于级别 1,另一个用于级别 2。
将运行两个不同的最短路径优先 (SPF) 计算;一个在第 1 级链路状态数据库中,另一个在第 2 级链路状态数据库中。
IS-IS 级别 1-2 路由器的行为非常接近 OSPF 区域边界路由器 (ABR)。L1/L2 路由器发送 L1 和 L2 Hello 数据包。
默认情况下,L1/L2 路由器允许前缀从 L1 区域到 L2 区域单向通过,但不允许反向通过。
但是,如果需要将前缀从 L2 区域移动到 L1 区域,则需要在 IS-IS 配置下执行 redistribute 命令。
IS-IS 2 级 (L2) 路由器
IS-IS 第 2 级路由器具有区域内和区域间路由的链路状态信息。
L2 路由器仅发送 L2 Hello 数据包。IS-IS 第 2 级区域可与 OSPF 主干区域 0 进行比较。
IS-IS 邻接表
| 路由器类型 | L1 | L1/L2 | L2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L1 邻接(如果区域 ID 匹配),否则无邻接 | L1 邻接(如果区域 ID 匹配),否则无邻接 | 无邻接 |
| L1/L2 | L1 邻接(如果区域 ID 匹配),否则无邻接 | L1 和 L2 邻接(如果区域 ID 匹配),否则仅 L2 邻接 | L2 邻接,区域 ID 不重要 |
| L2 | 无邻接 | L2 邻接,区域 ID 不重要 | L2 邻接,区域 ID 不重要 |
Cisco 社区讨论: L1/L2 之间邻接关系
even if routers and links are L1/L2 capable the type of adjacency between two routers in different areas can only be L2 because the net-id (the CLNS address) is different.
即使路由器和链路支持 L1/L2,不同区域中的两个路由器之间的邻接类型也只能是 L2,因为 net-id(CLNS 地址)不同。
- routing table - all routers IS-IS L1/L2 - Cisco Community
https://community.cisco.com/t5/routing/routing-table-all-routers-is-is-l1-l2/td-p/1041538
| MTU | 如果一个 IS-IS 路由器收到的 ISIS hello 数据包的 MTU 高于其可支持的 MTU(在接口上),则它会丢弃 hello,因此不会出现邻接关系。在最佳实践中,两端的 MTU 必须相同。 |
|---|---|
| 电路类型 | 此属性在接口上配置并定义哪种 hello 类型,即 L1 或 L2 在特定接口上发送。 L1/L2 路由器可以选择性地在一个接口上只发送 L1 hello 数据包,而在另一个接口上只发送 L2 hello 数据包。 如果 L1/L2 路由器尝试与 L1 专用路由器对等,并且 L1/L2 接口配置了 isis circuit-type level-2,则它仅向接口发送 L2 hello 数据包,且与 L1 路由器的邻接关系未建立。路由器必须发送兼容类型的 hello 数据包。 |
| 身份验证 | IS-IS 可以分别对 Hello 和链路状态协议数据单元 (LSP) 进行身份验证。 如果 Hello 数据包的身份验证正确,并且 LSP 身份验证失败,则邻接关系会建立,但更新不会交换。 如果为 IS-IS hello 或 PDU(协议数据单元)配置了身份验证,则两端必须匹配。 |
| 功能 TLV | 如果某个 IS-IS 路由器不支持来自另一个 IS-IS 路由器的功能 TLV,则会静默忽略 TLV。但是,当一台路由器到达 INIT 状态时,由于功能不匹配,会发生一些事件,而另一台路由器会丢弃数据包且无法形成邻接关系。 作为一般建议,功能 TLV 必须匹配才能成功形成邻接关系。 |
| 网络类型 | IS-IS 中有两种网络类型:广播和点对点。广播是默认网络类型。 如果一端配置了 isis network point-to-point,而另一端是默认网络类型,则 hello 数据包将被丢弃,并且不会建立邻接关系。两端的网络类型必须匹配。 |
| Hello | Hello 计时器无需匹配即可建立邻接关系。 |
IS-IS 邻接状态
IS-IS 中只有三种邻接状态。
- Down:这是初始状态。这意味着未收到来自邻居的 hello 消息。
- 正在初始化:此状态意味着本地路由器已成功收到来自邻居路由器的 hello 数据包,但是,不确定邻居路由器是否也成功收到了本地 hello 数据包。
- Up:现在,已确认邻居路由器接收本地路由器的 hello 数据包。
配置
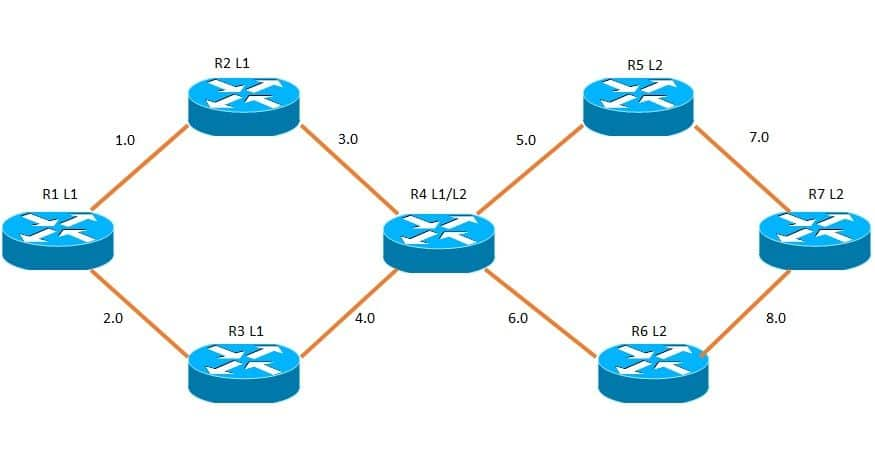
网络图
子网属于 192.168.X.0 类型,其中 X 显示在图中的接口之间。
环回接口的类型为 192.168.YY.YY,其中 Y 为 1(当路由器为 R1 时)。因此,R1 的环回 IP 是 192.168.11.11。
L1、L1/L2 和 L2 分别是 1 级、1-2 级和 2 级路由器。
配置
IS-IS 协议需要在接口级别和全局级别进行配置。
R1
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.11.11 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 49.0000.0000.0001.00
is-type level-1
!
R2
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.22.22 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 49.0000.0000.0002.00
is-type level-1
!
R3
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.33.33 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.2.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.4.3 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 49.0000.0000.0003.00
is-type level-1
!
R4
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.44.44 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.3.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet1/1
ip address 192.168.5.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet2/0
ip address 192.168.6.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 49.0000.0000.0004.00
!
R5
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.55.55 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.5.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.7.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 50.0000.0000.0005.00
is-type level-2-only
!
R6
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.66.66 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.6.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.8.6 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 50.0000.0000.0006.00
is-type level-2-only
!
R7
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 192.168.77.77 255.255.255.255
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.7.7 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
ip address 192.168.8.7 255.255.255.0
ip router isis 1
!
router isis 1
net 50.0000.0000.0007.00
is-type level-2-only
!
验证
R1 和 R2 之间的邻接关系
R1 和 R2 中的区域 ID 相同。两者都是 1 级路由器。 它们之间存在 L1 邻接。
R1#show isis neighbors
Tag 1:
System Id Type Interface IP Address State Holdtime Circuit Id
R2 L1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.2 UP 7 R2.01
由于 R1 和 R2 都是 L1 路由器并且属于同一区域,因此只有第 1 层类型 IS-IS hello 源于 R1 和 R2 之间的 LAN 网段。
R1#debug isis adj-packets fastEthernet 0/0
*Nov 25 19:25:53.995: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on FastEthernet0/0, length 1497
*Nov 25 19:25:54.071: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from ca02.1c80.0000 (FastEthernet0/0), cir type L1, cir id 0000.0000.0002.01, length 1497
-- The highlighted portion shows the Mac Address and the circuit id of R2, it also shows that L1 IS-IS hello packet was received from R2 --
*Nov 25 19:25:54.075: ISIS-Adj: New adjacency, level 1 for ca02.1c80.0000
-- The above line shows that R1 has discovered a new neighbour capable of L1 adjacency, having the mac address ca02.1c80.0000 R2 --
*Nov 25 19:25:54.991: ISIS-Adj: Sending L1 LAN IIH on FastEthernet0/0, length 1497
*Nov 25 19:25:55.047: ISIS-Adj: Rec L1 IIH from ca02.1c80.0000 (FastEthernet0/0), cir type L1, cir id 0000.0000.0002.01, length 1497
*Nov 25 19:25:55.051: ISIS-Adj: L1 adj count 1
*Nov 25 19:25:55.055: ISIS-Adj: L1 adjacency state goes to Up
-- Once both the routers mutually agree on interface settings and other global parameters (e.g. authentication, circuit-type, mtu etc.) the L1 adjacency finally comes up --
数据包捕获
捕获从 R2 发送到 R1 的 IS-IS Hello 数据包
ISIS HELLO
.... ..01 = Circuit type: Level 1 only (0x01) >>> Circuit type is Level 1
0000 00.. = Reserved: 0x00
SystemID {Sender of PDU}: 0000.0000.0002 >>> Identification of R2
Holding timer: 10 >>> Hold timer for hellos
PDU length: 1497 >>> Entire PDU in bytes
.100 0000 = Priority: 64 >>> Default Priority for DR election
0... .... = Reserved: 0
SystemID {Designated IS}: 0000.0000.0002.01 >>> SystemID + Pseudonode ID
Protocols Supported (1)
NLPID (s): IP (0xcc) >>> IS-IS is routing IP
Area address (es) (2)
Area address (1): 49 >>> Area id of R2
IP Interface address (es) (4)
IPv4 interface address: 192.168.1.2 (192.168.1.2) >>> IP of R2’s fa0/0
Restart Signaling (3)
Restart Signaling Flags: 0x00
.... .0.. = Suppress Adjacency: False
.... ..0. = Restart Acknowledgment: False
.... ...0 = Restart Request: False
IS Neighbor (s) (6)
IS Neighbor: ca:01:1d:a4:00:00 (ca:01:1d:a4:00:00) >>> Mac of R2 ( fa0/0 )
Padding (255)
Padding (255)
Padding (255)
Padding (255)








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1502
1502

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








