傅里叶光学基础总结
傅里叶光学傅里叶变换的本质:将光场分解为不同空间频率的光的相干叠加。
关键问题:空间频率的理解,透镜如何实现傅里叶变换的,光学傅里叶变换里面的相位是什么。本人也是在不断学习中,下面的理解有问题的地方欢迎批评指正,非常感谢。
基础
傅里叶变换的本质:将原信号分解为不同频率复指数信号的叠加,并求取这些不同频率信号的加权强度。
光学傅里叶变换的导出:衍射。
不懂微分方程也没关系,因为我也不太擅长。但是基于前人的结果,大概能看懂就行,利用他们的结果就好。这里面主要涉及到用微分方程求解衍射光场,而我们的重点在于傅里叶变换及其应用。
光的相干叠加:同相相长,反相相消
平面单色光波:


注意平面波已经是复指数信号了。
空间频率
空间频率,就是在每单位长度上,出现几个同样的几何结构。如果同样的几何结构重复的距离为λ,那空间频率就是λ的倒数。不同的空间频率代表图像中不同的讯息,高空间频率出现在空间剧烈变化的位置



光的衍射
求一个闭合曲面光场传播到某处一点p的光场->基尔霍夫积分定力->菲涅尔近似/夫郎和费近似。夫郎和费衍射是p点距离光场曲面很远的时候成立。一般在光场后面增加一个透镜,来满足此条件。因为后焦面对应无限远。


光学傅里叶变换





4f系统
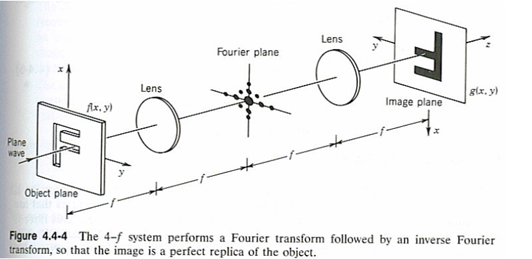
输入面在前焦面,后焦面为输入面的傅里叶变换。再放置一组透镜,对前面透镜的傅里叶变换再进行一次傅里叶变换。注意是傅里叶变换的变换,而不是反变换。这使得最终为输入的倒像。

傅里叶光学应用略
不同于常规的图像处理,输入图像是纯实数,比较少对相位进行操作。而傅里叶光学输入本身就是既有强度,又有相位。而且光学傅里叶变换应用中尤其注重对相位的操纵。
空间光调制器Spatial Light Modulator (SLM)
二维液晶像素阵列,通过每个像素上的电压对对输入光的相位进行0-2π或者更大相位范围进行调制。
数字微镜Digital Micromirror Device (DMD)/数字光处理器Digital Light Processing (DLP)/ Deformable Mirror等等
同样为二维像素阵列,但每个像素由可以翻转的微镜构成,加电压和不加电压微镜偏转角度不同。
具体的应用后面再继续总结添加,列如自适应光学,波前整形,散射介质成像等。
常用激光作为照明光源,但激光为高斯光束,幅度和相位都是高斯的,但是平面波更好处理,怎么办?可以把高斯光束扩束,再截取中间部分近似平面波。
几个问题
为什么角度越大,空间频率越大?
数值上,x,y方向上的空间频率为f_x=x/λf,f_y=y/λf,x,y为傅里叶平面上的坐标,因此x,y越大,空间频率越大。
另一方面,参考维基百科上的空间频率描述,空间频率是空间上正弦波的振荡频率,正如一维电信号傅里叶变换后分解为一维空间上不同频率正弦波的叠加。而这里的空间频率是方向,如何把两者结合起来?

如下图,垂直于平面波的红色线为等相面,因此幅度是不变的。当有一定空间频率的光入射是,在衍射平面(蓝色线部分)上投影不是等相的,因此会产生一个有一定振荡频率的正弦波。当没有空间频率(水平方向平面波入射)时,蓝色部分变成等相面,幅度和相位都一样,没有振荡,因此是常数信号。空间频率越大的光,在衍射平面等距离相位变换越大,因此蓝色正弦波振荡越快,因此确实是空间频率越大了。

可以参考下面部分进行理解

参考书籍
物理光学与应用光学,西安电子科技大学,石顺祥
Diffraction, Fourier Optics and Imaging,OKAN K. ERSOY
Luchang Li
20170824
HUST


























 1303
1303

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










