一.概念
消息队列提供了一种从一个进程向另一个进程发送一个数据块的方法。 每个数据块都被认为是有一个类型,接收者进程接收的数据块可以有不同的类型值。我们可以通过发送消息 来避免命名管道的同步和阻塞问题。消息队列与管道不同的是,消息队列是基于消息的, 而管道是基于字节流的,且消息队列的读取不⼀定是先入先出。消息队列与命名管道有一样的不足,就是每个消息的最大长度是有上限的(MSGMAX),每个消息队列的总的字节数是有上限的(MSGMNB),系统上消息队列的总数也有⼀个上限(MSGMNI)。
查看机器的三个上限值:
二. IPC对象数据结构
内核为每个IPC对象维护⼀一个数据结构(/usr/include/linux/ipc.h)
struct ipc_perm
{
key_t __key; /* Key supplied to xxxget(2) */
uid_t uid; /* Effective UID of owner */
gid_t gid; /* Effective GID of owner */
uid_t cuid; /* Effective UID of creator */
gid_t cgid; /* Effective GID of creator */
unsigned short mode; /* Permissions */
unsigned short __seq; /* Sequence number */ }; 消息队列,共享内存和信号量都有这样⼀一个共同的数据结构。
三、消息队列结构(/usr/include/linux/msg.h)
/* Obsolete, used only for backwards compatibility and libc5 compiles */
struct msqid_ds {
<span style="color:#FF0000;">struct ipc_perm msg_perm;</span>
struct msg *msg_first; /* first message on queue,unused */
struct msg *msg_last; /* last message in queue,unused */
__kernel_time_t msg_stime; /* last msgsnd time */
__kernel_time_t msg_rtime; /* last msgrcv time */
__kernel_time_t msg_ctime; /* last change time */
unsigned long msg_lcbytes; /* Reuse junk fields for 32 bit */
unsigned long msg_lqbytes; /* ditto */
unsigned short msg_cbytes; /* current number of bytes on queue */
unsigned short msg_qnum; /* number of messages in queue */
unsigned short msg_qbytes; /* max number of bytes on queue */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t msg_lspid; /* pid of last msgsnd */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t msg_lrpid; /* last receive pid */
};
可以看到第⼀个 红色条目就是IPC结构体,即是共有的,后面的都是消息队列所私有的成员。
消息队列是用链表实现的。
四.消息队列的函数
实现消息队列的相关函数:
1.生成新消息队列或者取得已存在的消息队列
int msgget(ket_t key,int msgflg);参数: msgflg:
IPC_CREAT:如果IPC不存在,则创建一个IPC资源,否则打开操作。
IPC_EXCL:只有在共享内存不存在的时候,新的共享内存才建立,否则就产生错误。 如果单独使用IPC_CREAT XXXget()函数要么返回一个已经存在的共享内存的操作符,要 么返回一个新建的共享内存的标识符。 如果将IPC_CREAT和IPC_EXCL标志一起使用,XXXget()将返回一个新建的IPC标识符 ;如果该IPC资源已存在,或者返回-1。 IPC_EXEL标志本身并没有太大的意义,但是和IPC_CREAT标志一起使用可以用来保证所得的对象是新建的,而不是打开已有的对象。
返回值:返回msgid。
2.向队列读/写消息msgrcv取消息:
ssize_t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_t msgsz, long msgtyp, int msgflg); msgsnd读消息:
int msgsnd(int msqid, const void *msgp, size_t msgsz, int msgflg);msqid:消息队列的标识码。
msgp:指向消息缓冲区的指针,此位置用来暂时存储发送和接收的消息,是一个用户可定义的通用结构,形态如下:
struct msgstru
{
long mtype;//大于0
char mtext[_SIZE_]; //_SIZE_ 用户指定大小
}msgsz:消息的大小。
msgtyp:从消息队列内读取的消息形态。如果值为零,则表示消息队列中的所有消息都会被读取。
msgflg:用来指明核心程序在队列没有数据的情况下所应采取的行动。如果msgflg和常数IPC_NOWAIT合用,则在msgsnd()执行时若是消息队列已满,则msgsnd()将不会阻塞,而会立即返回-1,如果执行的是msgrcv(),则在消息队列呈空时,不做等待马上返回-1,并设定 错误码为ENOMSG。当msgflg为0时,msgsnd()及msgrcv()在队列呈满或呈空的情形时,采取 阻塞等待的处理模式。
五 .应用
———使用消息队列实现一个简单的客户端--服务端的通信
实现代码如下给出:
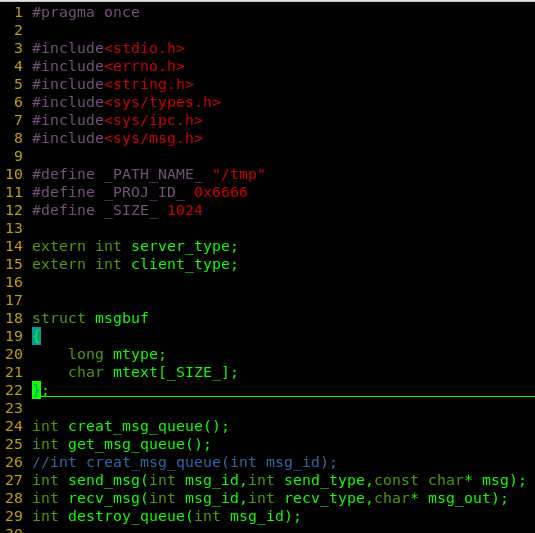
comm.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/msg.h>
#define _PATH_NAME_ "/tmp"
#define _PROJ_ID_ 0x6666
#define _SIZE_ 1024
extern int server_type;
extern int client_type;
struct msgbuf
{
long mtype;
char mtext[_SIZE_];
};
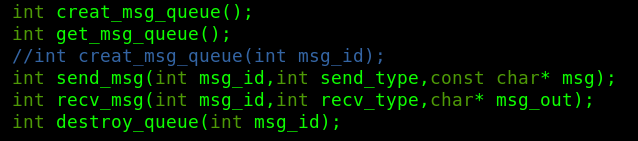
int creat_msg_queue();
int get_msg_queue();
//int creat_msg_queue(int msg_id);
int send_msg(int msg_id,int send_type,const char* msg);
int recv_msg(int msg_id,int recv_type,char* msg_out);
int destroy_queue(int msg_id);
comm.c:
#include"comm.h"
int server_type = 1;
int client_type = 2;
static int comm_msg_queue(int flags)
{
key_t _key = ftok(_PATH_NAME_,_PROJ_ID_);
if(_key < 0)
{
printf("%d : %s",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
int msg_id = msgget(_key,flags);
//int msg_id = msgget(_key,IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666);
return msg_id;
}
int creat_msg_queue()
{
int flags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666;
return comm_msg_queue(flags);
}
int get_msg_queue()
{
int flags = IPC_CREAT;
return comm_msg_queue(flags);
}
int destroy_queue(int msg_id)
{
if(msgctl(msg_id,IPC_RMID,NULL) != 0)
{
printf("%d : %s",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int send_msg(int msg_id,int send_type,const char* msg)
{
struct msgbuf _buf;
_buf.mtype = send_type;
strncpy(_buf.mtext,msg,strlen(msg)+1);
if(msgsnd(msg_id,&_buf,sizeof(_buf.mtext),0) < 0)
{
printf("%d : %s",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int recv_msg(int msg_id,int recv_type,char* msg_out)
{
struct msgbuf _buf;
_buf.mtype = 0;
memset(_buf.mtext,'\0',sizeof(_buf.mtext));
if(msgrcv(msg_id,&_buf,sizeof(_buf.mtext),recv_type,0) < 0)
{
printf("%d : %s",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
strcpy(msg_out,_buf.mtext);
return 0;
}
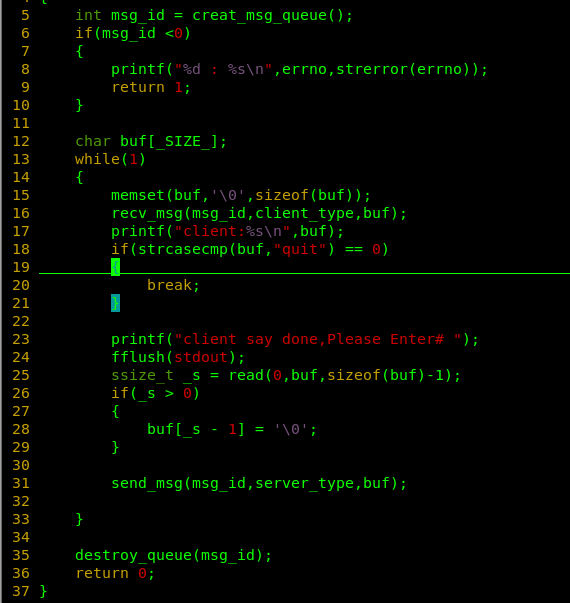
server.c:
#include"comm.h"
int main()
{
int msg_id = creat_msg_queue();
if(msg_id <0)
{
printf("%d : %s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
char buf[_SIZE_];
while(1)
{
memset(buf,'\0',sizeof(buf));
recv_msg(msg_id,client_type,buf);
printf("client:%s\n",buf);
if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
printf("client say done,Please Enter# ");
fflush(stdout);
ssize_t _s = read(0,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(_s > 0)
{
buf[_s - 1] = '\0';
}
send_msg(msg_id,server_type,buf);
}
destroy_queue(msg_id);
return 0;
}client.c:
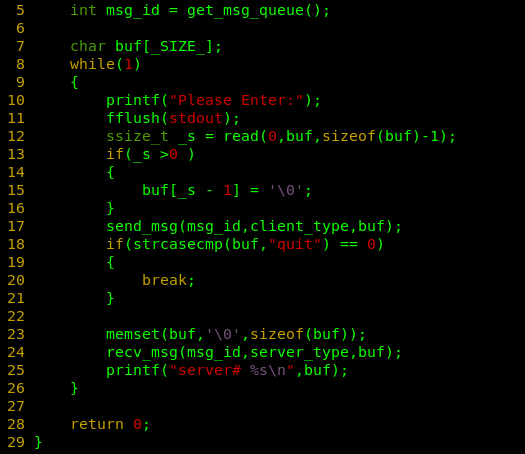
#include"comm.h"
int main()
{
//int msg_id = creat_msg_queue();
//if(msg_id <0)
//{
// printf("%d : %s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
// return 1;
//}
//
//
int msg_id = get_msg_queue();
char buf[_SIZE_];
while(1)
{
printf("Please Enter:");
fflush(stdout);
ssize_t _s = read(0,buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(_s >0 )
{
buf[_s - 1] = '\0';
}
send_msg(msg_id,client_type,buf);
if(strcasecmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
memset(buf,'\0',sizeof(buf));
recv_msg(msg_id,server_type,buf);
printf("server# %s\n",buf);
}
return 0;
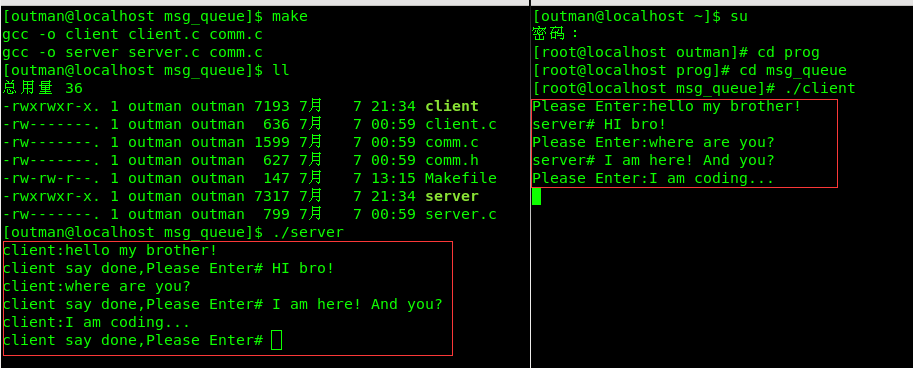
}六.测试过程及结果
头文件:
各个接口:
int creat_msg_queue(); //创建一个消息队列
int get_msg_queue(); //获得消息队列的msg_id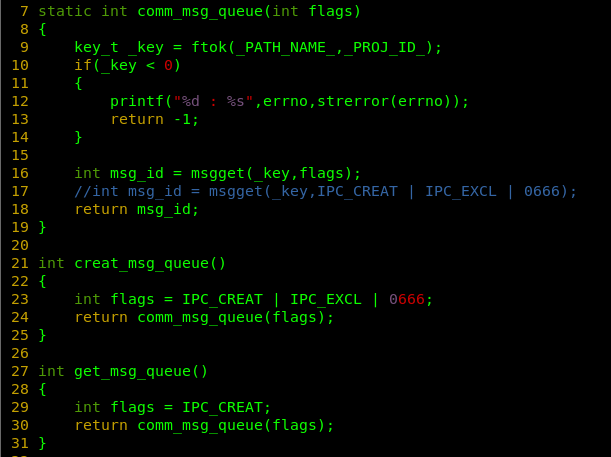
int send_msg(int msg_id,int send_type,const char* msg); //发送消息
int recv_msg(int msg_id,int recv_type,char* msg_out); //接收消息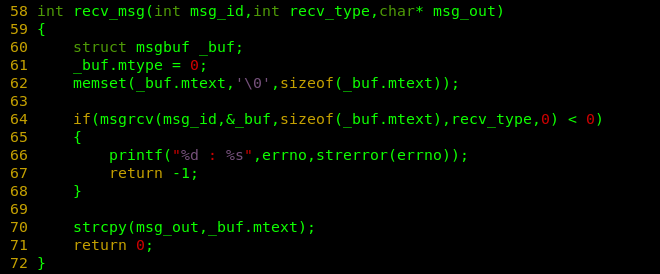
int destroy_queue(int msg_id); //销毁队列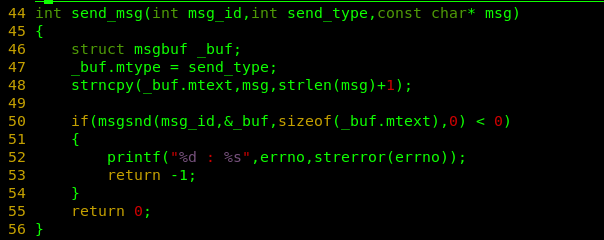
server.c:创建消息队列,接收客户端发送的消息,同时给客户端发送消息
client.c:获取msg_id,接收服务端发送的消息,同时给客户端反馈
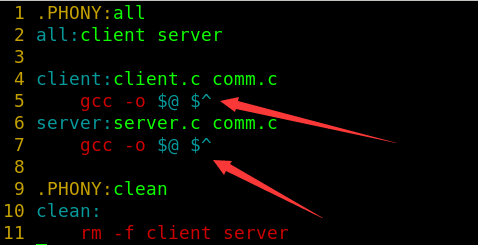
Makefile:
要生成两个可执行程序,所以使用伪目标all。
$@(依赖关系中代表目标文件) $^(依赖关系中:右边的所有内容)
测试结果:
如有纰漏,欢迎指正。























 4038
4038

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








