全自动驾驶论文
意见 (Opinion)
It’s unquestionable that full self-driving technology (or level 5 autonomy) will be part of our future. The question is — when it will arrive? Next decade? Next 5 years? Next year? Tomorrow? Let’s look at the current state-of-the-art and make a prediction.
毫无疑问,完整的自动驾驶技术( 或5级自动驾驶技术)将成为我们未来的一部分。 问题是-什么时候到达? 下个十年? 未来五年? 明年? 明天? 让我们看一下当前的最新技术并做出预测。
Spoiler: Probably no later than 2025.
剧透:可能不迟于2025年。
哪个公司先到达那里? (Which company will get there first?)
If anyone can solve full self-driving (level 5 autonomy) by 2025, it will be Tesla. You may have heard about Waymo robot taxis but those operate in very restricted regions and require a high-resolution mapping and preparation of the routes (level 4 autonomy). It’s a good attempt but the current approach is not scalable.
如果有人能在2025年之前解决完全的自动驾驶( 5级自动驾驶),那就是特斯拉。 您可能听说过Waymo机器人出租车,但这些出租车在非常受限的区域内运行,需要高分辨率的地图绘制和路线准备( 4级自治 )。 这是一个很好的尝试,但是当前的方法不可扩展。
The main reasons Tesla will be the first to solve full self-driving are:
特斯拉将成为第一个解决全自动驾驶问题的主要原因是:
Data: They have the largest real-world dataset with billions of driven miles.
数据:他们拥有最大的现实世界数据集,拥有数十亿的行驶里程。
Efficient hardware: A smart set of sensors and an in-house designed deep learning chip.
高效的硬件:一套智能传感器和一个内部设计的深度学习芯片。
Advanced software: The neural network driving Teslas is a very complex multi-task problem.
先进的软件:驱动特斯拉的神经网络是一个非常复杂的多任务问题。
Over the next sections, I will develop on each of these three topics and then I will construct my prediction timeline — let’s dive in.
在接下来的部分中,我将研究这三个主题中的每一个,然后构建我的预测时间表-让我们深入研究。
数据 (Data)
With more than a million cars collecting data, Tesla is orders of magnitude ahead of the competition. Furthermore, the size of the Tesla fleet will steeply increase over the next years, as they increase production. Look at this chart showing the estimated number of autopilot driven miles.
特斯拉拥有超过一百万辆汽车在收集数据,比竞争对手领先几个数量级。 此外,随着产量的增加,特斯拉车队的规模将在未来几年急剧增加。 查看此图表,其中显示了自动驾驶行驶里程的估计数量。
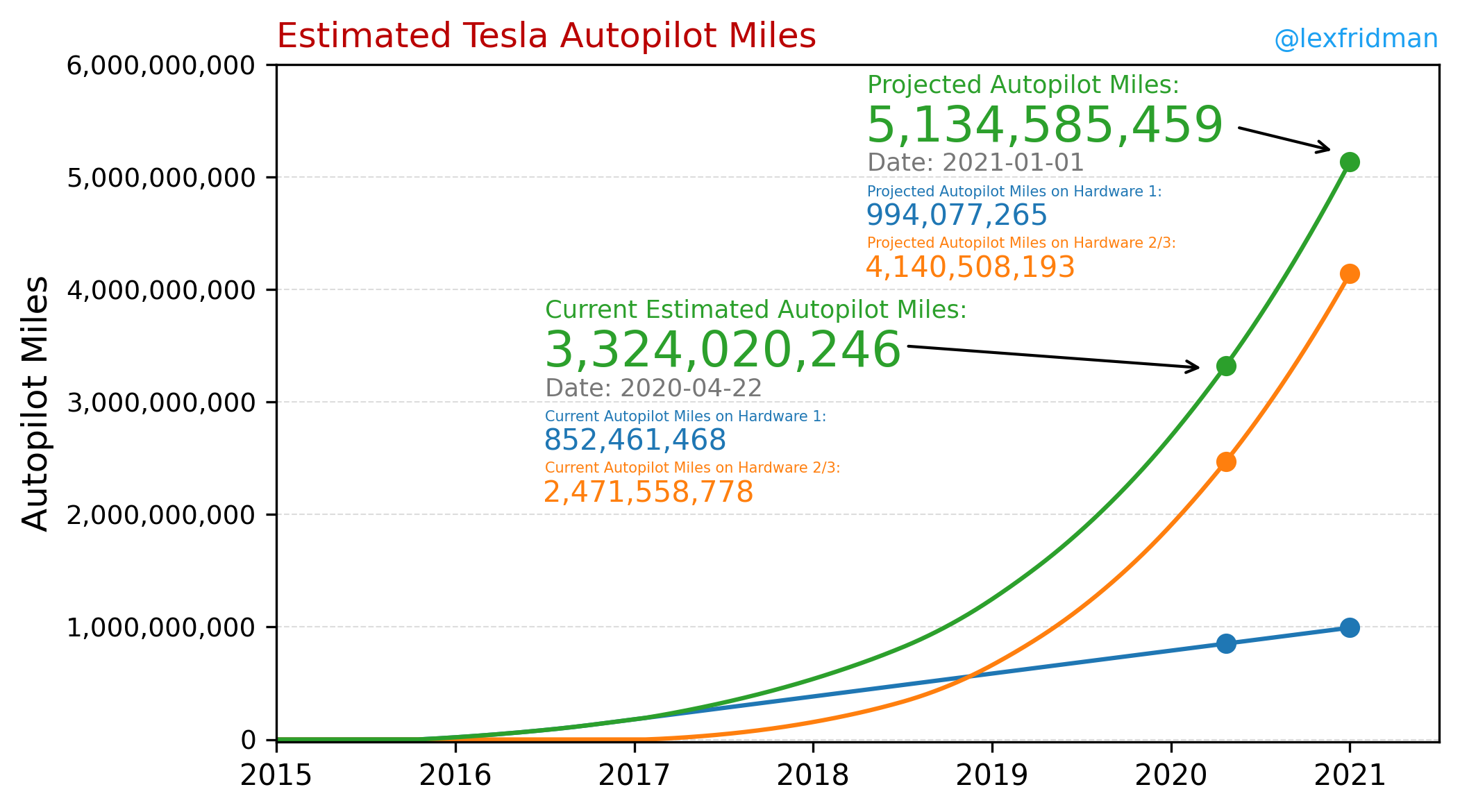
In Deep Learning applications having high volumes of data is a game-changer. Particularly for such a complex problem as self-driving that requires analysing data of multiple sensors in a multi-task problem.
在深度学习应用程序中,具有大量数据的游戏规则改变了。 特别是对于像自动驾驶这样的复杂问题,它需要分析多任务问题中的多个传感器的数据。
Usually, in the real world, the distribution of possible scenarios has a very long tail — meaning that the number of rare situations that the car may face is almost unlimited. Having a large fleet of cars collecting data allows to sample the edge cases needed for gradual improvements. The goal is to make the model more and more robust over time.
通常,在现实世界中,可能场景的分布具有很长的尾巴-这意味着汽车可能会遇到的罕见情况的数量几乎是无限的。 拥有大量的汽车收集数据可以对逐步改进所需的边缘情况进行采样。 目标是使模型随着时间的推移变得越来越强大。
To collect real data, a set of sensors is needed. And that leads me to the next topic — the hardware.
为了收集真实数据,需要一组传感器。 这就引出了下一个主题-硬件。
硬体 (The hardware)
The set of hardware used for full self-driving usually consists of several cameras, LIDAR sensors, RADAR sensors and ultrasonic sensors.
全自动驾驶所使用的一组硬件通常包括几个摄像头,LIDAR传感器,RADAR传感器和超声波传感器。
The cameras are used to collect images all around the vehicle;
摄像机用于收集车辆周围的图像;
The LIDAR sends rapid laser pulses that are reflected on objects allowing to make 3-dimensional maps of the surroundings with high resolution;
LIDAR发送快速的激光脉冲,反射到物体上,从而可以高分辨率地绘制周围环境的3维地图;
RADAR is similar to LIDAR but it works on radio wavelength allowing for better performance in fog and dust conditions trading off with a lower image resolution;
RADAR与LIDAR相似,但它在无线电波长上工作,可以在雾气和灰尘条件下以较低的图像分辨率实现更好的性能。
Ultrasonic sensors are used on a close range to detect the distance to close objects very accurately.
超声波传感器在近距离上使用,可以非常精确地检测到接近物体的距离。
Most people in this field rely heavily on LIDAR enhanced with some cameras and ultrasonic sensors. Tesla, however, is approaching the problem in a different way — without making use of any LIDAR. This makes the problem harder for Tesla! Why are they following this approach?
该领域的大多数人严重依赖配有某些摄像头和超声波传感器的增强型激光雷达。 但是,特斯拉却以不同的方式解决了这个问题,而没有利用任何激光雷达。 这使特斯拉的问题更加棘手! 他们为什么要遵循这种方法?
We know for sure that a vision-based approach can navigate a car reliably —we do that every day when we drive using our two camera sensors (also known as eyes). Another important consideration is that LIDAR sensors are expensive. Prices may get lower over time but until then cars would be significantly more expensive. And again, if we can drive with our eyes then it is feasible that an AI can learn to do it even better by having more eyes all around working all the time without distraction. The RADAR sensor is important mainly to have an enhanced forward vision even in fog and dust conditions. It can also be important to double-check the distance of objects in front. This sensor is also cheaper compared with LIDAR.
我们肯定知道基于视觉的方法可以可靠地驾驶汽车-我们每天使用两个摄像头传感器(也称为眼睛)进行驾驶。 另一个重要的考虑因素是激光雷达传感器价格昂贵。 价格可能会随着时间的流逝而降低,但在那之前,汽车将变得更加昂贵。 再说一次,如果我们可以用眼睛驾驶,那么人工智能可以通过使更多的眼睛一直在工作而不分散注意力的方式学会做得更好。 即使在有雾和多尘的情况下,RADAR传感器也很重要,主要是要具有增强的前视力。 仔细检查前方物体的距离也很重要。 与LIDAR相比,该传感器也更便宜。
The following video gives a clear explanation of Tesla approach for the sensor suite and why in Elon Musk words: “Anyone relying on LIDAR [for full self-driving] is doomed”. I find particularly interesting the talk about using RADAR to auto-label data for depth estimation with cameras. They also mention that depth estimation can be achieved without labels using self-supervision — a very promising technique that is gaining momentum in several Deep Learning applications.
以下视频清晰地解释了特斯拉用于传感器套件的方法,以及为什么用埃隆·马斯克(Elon Musk)的话说: “注定要依靠LIDAR(实现全自动驾驶)的人注定要失败” 。 我发现使用RADAR自动标记数据以进行相机深度估计的话题特别有趣。 他们还提到深度估计无需标签即可使用自我监督来实现,自我监督是一种非常有前途的技术,在一些深度学习应用中正逐渐获得发展。
Overall we see that Tesla is solving a harder problem by not relying on LIDAR and working directly on a vision-based approach. This is the right approach because it is scalable and results in lower-cost cars that ultimately will be able to provide the lowest prices as robot taxis and accelerate the transition to electric vehicles.
总体而言,我们看到特斯拉不依靠激光雷达,而是直接采用基于视觉的方法来解决更棘手的问题。 这是正确的方法,因为它具有可伸缩性,可以生产出成本更低的汽车 ,这些汽车最终将能够以最低的价格提供机器人出租车服务,并加速向电动汽车的过渡。
Another important aspect regarding hardware is that Tesla developed a Deep Learning chip (Hardware 3.0) that has the power to enable full self-driving in an energy-efficient way. Now it’s just a matter of getting the software up to the point and deploy it by over the air updates.
关于硬件的另一个重要方面是,特斯拉开发了深度学习芯片( 硬件3.0 ),该芯片具有以节能方式实现完全自动驾驶的能力。 现在只需要更新软件并通过无线更新进行部署即可。
Talking about the software, let’s move to the next topic and take a look at the neural network behind Tesla autopilot.
在谈论软件时,让我们进入下一个主题,看看特斯拉自动驾驶仪背后的神经网络。
驾驶特斯拉汽车的神经网络 (The neural network driving Tesla cars)
Over the past few years, the autopilot software has improved gradually. Some exciting news is that Tesla has been working on a major update to the neural network structure to make it work with 4D data instead of a combination of 2D images. As a result, the rate of progress will likely be faster over the next months as Tesla AI team further explore the potentiality of the system that they aim to deploy at the end of 2020.
在过去的几年中,自动驾驶软件已逐渐完善。 令人振奋的消息是,特斯拉一直在对神经网络结构进行重大更新,以使其能够处理4D数据,而不是结合使用2D图像。 因此,随着特斯拉AI团队进一步探索他们计划在2020年底部署的系统的潜力,未来几个月的进展速度可能会更快。
I highly recommend the video below of a presentation by Andrej Karpathy, the director of AI at Tesla, about the state of AI for Full Self Driving. I will now describe some of the main highlights.
我强烈推荐以下特斯拉AI主管Andrej Karpathy演讲的视频,介绍全自动驾驶AI的状态。 我现在将描述一些主要亮点。
The new neural network receives input from all sensors and combines the data in the neural network feature space (Fusion layer in the image below), creating a real-time 3-dimensional representation of the surrounding environment. This representation is then given to a Bird’s Eye View network (BEV Net) from which an extensive set of tasks need to be predicted.
新的神经网络接收来自所有传感器的输入,并在神经网络特征空间(下图中的融合层)中组合数据,从而创建周围环境的实时3D表示。 然后,将这种表示形式提供给鸟瞰网络( BEV Net ),根据该网络需要预测大量的任务。

Another very interesting topic covered in the presentation is how they can deal with the edge cases. The image below shows a good example — the case of stop signs. One would think that stop signs are very easy to capture and learn by the neural network. But what if they are partially occluded? Or what if they have a modifier as in the example below where the plate under the stop says “except right turns”. Autonomous vehicles are expected to be able to work in all those scenarios.
演示文稿中涉及的另一个非常有趣的主题是它们如何处理极端情况。 下图显示了一个很好的例子-停车标志。 人们会认为,停车标志非常容易被神经网络捕获和学习。 但是,如果它们被部分遮挡怎么办? 或者,如果它们具有修饰符(如以下示例所示) ,挡块下方的板显示“右转除外”,该怎么办 ? 预计自动驾驶汽车将能够在所有这些情况下工作。

The process of training the huge neural network to perform well on edge cases like the examples above consists of running a small network in “shadow mode” that retrieves similar samples from the Tesla fleet. The samples obtained are then used to improve the training dataset. Then the big neural net can be retrained to achieve better accuracy. For the case of stop signs, the label “stop sign” needs to have modifiers to cover the edge cases.
训练巨大的神经网络,使其在上述示例中的边缘情况下表现良好的过程包括以“影子模式”运行一个小型网络,该网络从特斯拉车队中检索相似的样本。 然后将获得的样本用于改进训练数据集。 然后可以对大型神经网络进行重新训练,以实现更高的准确性。 对于停车牌,标签“停车牌”需要有修饰符以覆盖边缘情况。
The validation for such a complex multi-task problem is also a very important topic that is covered in the presentation.
这种复杂的多任务问题的验证也是本演示文稿中涵盖的非常重要的主题。
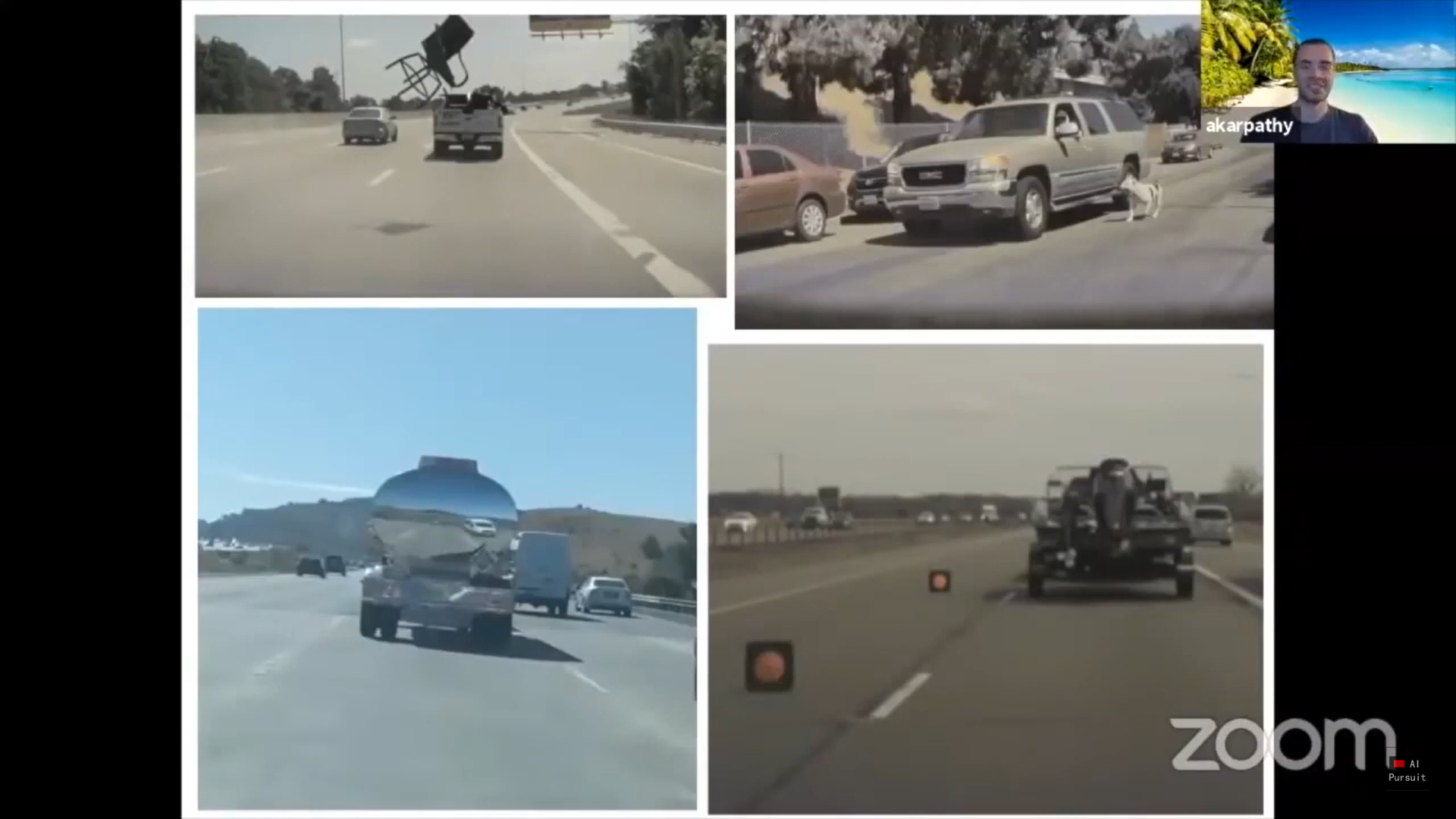
On a recent keynote at CPRV 2020 conference, Karpathy made a similar presentation adding a few interesting examples. Starting with a good example of edge cases. I guess no comment is needed for this one other than these are real images sampled from the Tesla fleet.
在CPRV 2020会议的最近一次主题演讲中,Karpathy做了类似的演讲,并添加了一些有趣的示例。 从边缘案例的一个很好的例子开始。 我想除了这是从特斯拉车队采样的真实图像外,其他人都不需要评论。

Another crazy example is the following image. Can you handle such a roundabout? Regarding this example, Karpathy makes an interesting point that they don’t need to handle every possible case. If the cases that can’t be handled are known, one possible option is to follow a different trajectory that avoids a specific situation. As a human, I would definitely avoid the roundabout in the image below.
下一个图像是另一个疯狂的例子。 你能处理这样的回旋处吗? 关于此示例,Karpathy提出了一个有趣的观点,即他们不需要处理所有可能的情况。 如果已知无法处理的情况,则一种可能的选择是遵循避免特定情况的不同轨迹。 作为一个人类,我绝对会避免下图中的回旋处。
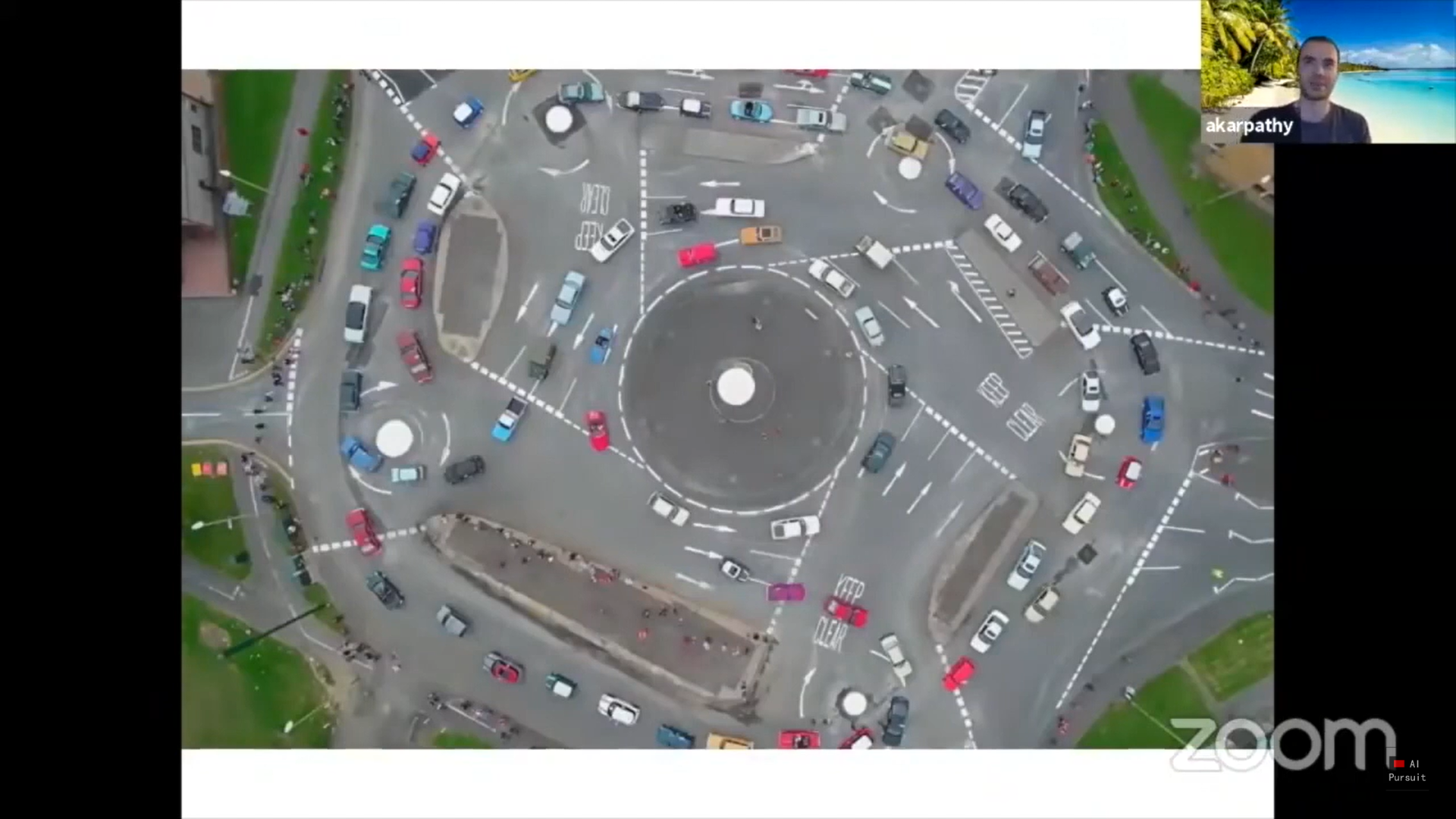

I believe the image above is also a hint that they are now working hard on solving roundabouts and intersections. That’s the logical step to follow after traffic lights and stop signs and an important step towards feature-complete autopilot.
我相信上面的图片也暗示着他们正在努力解决环形交叉路口和交叉路口。 这是遵循交通信号灯和停车标志之后的逻辑步骤,也是迈向功能齐全的自动驾驶仪的重要一步。
我的预测时间表 (My prediction timeline)
On a tweet in 12 of April this year, Elon Musk mentioned that regarding the schedule for robotaxi release, “Functionality still looking good for this year. Regulatory approval is the big unknown”. However, Elon has been overly optimistic about these schedules. Nevertheless, the progress has been steady and we are getting closer and closer.
在今年4月12日的一条推文中,埃隆·马斯克(Elon Musk)提到了关于robotaxi发布的时间表, “今年的功能仍然不错。 监管批准是一个大未知数” 。 但是,Elon对这些时间表过于乐观。 尽管如此,进展一直稳定,我们之间的距离越来越近。
Now let me finally write down my timeline based on all public information about the current state of autopilot that I could find and trying to make an optimistic but yet realistic forecast:
现在,让我最后根据可以找到的有关自动驾驶仪当前状态的所有公共信息写下我的时间表 ,并尝试做出乐观但现实的预测:
Late 2020 or more confidently in 2021: Tesla autopilot will be feature complete. It will be able to navigate in most scenarios but it will be far from perfect. Human supervision will be required all the time and human intervention will be common in city environments.
2020年末或2021年或更有信心:特斯拉自动驾驶仪将完成功能。 它可以在大多数情况下导航,但远非完美。 始终需要人工监督,并且在城市环境中通常会进行人工干预。
2021/2022: improvements will be very steady as more and more data is collected and used to improve the system. Human intervention will be less frequent and trips without intervention will gradually become more frequent.
2021/2022:随着越来越多的数据被收集并用于改进系统,改进将非常稳定。 人为干预将减少,无干预的出行将逐渐变得更加频繁。
2023: autopilot will be able to navigate perfectly in most situations. Human intervention will be sporadic. Most trips won’t require any intervention. It’s possible that robotaxi experiments in selected places may start by this year— level 4 autonomy.
2023年:自动驾驶仪将能够在大多数情况下完美导航。 人为干预将是零星的。 大多数旅行不需要任何干预。 今年4月,可能会在选定的地方开始robotaxi实验-4级自治。
2024: the software will reach a state where it will be safe to travel without human supervision. Edge cases may still exist but solvable with human voice command feedback or by planning the journey to avoid specific problematic situations. Tesla will start the important task of showing regulators that the technology is safe to use as robotaxis without human supervision — level 5 autonomy.
2024年:该软件将达到无需人工监督即可安全旅行的状态。 边缘情况可能仍然存在,但可以通过人声命令反馈或通过计划行程来避免特定的问题情况而解决。 特斯拉将启动一项重要任务,向监管机构展示该技术可以安全地用作无人监督的机器人轴-5级自治。
2025/2026: Tesla will gradually get approval by regulators to operate in more and more regions. The approval will probably occur first in the US (possibly as early as 2024 in some states) and gradually extend to other regions. For Europe, I would expect the approval to be delayed by one year compared to the US.
2025/2026:特斯拉将逐步获得监管机构的批准,可在越来越多的地区运营。 批准可能首先在美国进行(可能在某些州最早在2024年进行),然后逐步扩展到其他地区。 对于欧洲,我希望与美国相比,批准时间会延迟一年。
To wrap up, by 2025 (or maybe 2026 in Europe and other regions) I expect to be able to schedule my robotaxi ride in the app and go to any destination I choose. I’m looking forward to that day!
总结一下,到2025年(也许在欧洲和其他地区可能是2026年),我希望能够在应用程序中安排我的robotaxi骑行路线并前往我选择的任何目的地。 我期待着这一天!
结束语 (Final remarks)
This is just my vision for the future of full self-driving. No one knows what the future will be. There are many uncertainties in the equation. My prediction is just what I think is the most likely scenario. Let me know about your thoughts in the comments.
这只是我对全自动驾驶未来的愿景。 没有人知道未来会怎样。 该方程式有许多不确定性。 我的预测正是我认为最有可能发生的情况。 在评论中让我知道您的想法。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/self-driving-cars-how-close-are-we-from-full-autonomy-ccf31cea771
全自动驾驶论文





















 6753
6753

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








