C++隐式转换与explicit关键字
隐式构造函数
隐含的意思是不会明确告诉你要做什么
隐式转换
C++允许编译器对代码执行一次隐式转换,而不需要使用casr强制转换
例1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
int m_Age;
public:
Entity(const std::string& name)
: m_Name(name), m_Age(-1) {}
Entity(int age)
: m_Name("Unknown"), m_Age(age) {}
};
void PrintEntity(const Entity& entity)
{
// Printing
}
int main()
{
Entity a("Cherno");
Entity b(22);
Entity c = "Cherno"; // 隐式转换
Entity d = 22;
PrintEntity(22);
PrintEntity("Cherno"); // 不能隐式转换,因为"Cherno"不是std::string, 而是一个char数组
std::cin.get();
}
隐式的将22转换成一个Entity,构造出一个Entity
PrintEntity(22)可以
PrintEntity("Cherno")不可以:
因为"Cherno"不是一个std::string, 而是一个char数组,所以要进行两次转换,一次从char数组转换成std::string, 然后再从std::string转换成Entity,然而,只允许做一次隐式转换
PrintEntity(std::string("Cherno"));:
先做一个显式的转换
PrintEntity(Entity("Cherno"));:
或者包含在Entity,因为可以将其隐式地将字符数组转换成std::string
explicit关键字
- 禁用隐式implicit这个功能
- explicit关键字放在构造函数前面,如果有一个explicit构造函数,意味着没有implicit转换。如果要使用整数构造Entity对象,就必须显式调用此构造函数
例2
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
private:
std::string m_Name;
int m_Age;
public:
Entity(const std::string& name)
: m_Name(name), m_Age(-1) {}
explicit Entity(int age)
: m_Name("Unknown"), m_Age(age) {}
};
void PrintEntity(const Entity& entity)
{
// Printing
}
int main()
{
Entity a("Cherno");
Entity b(22);
Entity c = "Cherno";
Entity d = 22;
PrintEntity(22);
PrintEntity("Cherno");
PrintEntity(std::string("Cherno"));
std::cin.get();
}
失效:
Entity d = 22;
PrintEntity(22);
有效:
Entity e = Entity(22);
Entity f(22);
Entity g = (Entity)22;
什么时候使用explicit
使用数学库之类的东西,因为不想总是将数字变成向量,确保代码尽量安全
C++运算符及其重载
运算符
一个符号,通常代替一个函数来执行一些事情
dereference运算符->
+=, &, <<
new, delete
, () []
运算符重载
- 给运算符重载赋予新的含义,添加参数或者创建
- 允许在程序中定义或更改运算符的行为
- 运算符重载的使用,应该是非常少
例3
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
Vector2(float x, float y)
: x(x), y(y) {}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x + other.x, y + other.y);
}
Vector2 Multiply(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x * other.x, y * other.y);
}
};
int main()
{
Vector2 position(4.0f, 4.0f);
Vector2 speed(0.5f, 1.5f);
Vector2 powerup(1.1f, 1.1f);
// 加在一起
Vector2 result = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
std::cin.get();
}
Java只能这样写,因为Java没有操作符重载
可以用this指针:
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return *this + other;
}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return operator+(other);
}
是否可以改成Vector2 result1 = position + speed * powerup;?
例4
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
Vector2(float x, float y)
: x(x), y(y) {}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x + other.x, y + other.y);
// return *this + other;
}
Vector2 operator+(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Add(other);
}
Vector2 Multiply(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x * other.x, y * other.y);
}
Vector2 operator*(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Multiply(other);
// return *this + other;
}
};
int main()
{
Vector2 position(4.0f, 4.0f);
Vector2 speed(0.5f, 1.5f);
Vector2 powerup(1.1f, 1.1f);
// 加在一起
Vector2 result = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result1 = position + speed * powerup; // +运算符重载了
std::cin.get();
}
运算符+和*都进行了重载
<< 操作符
std::cout << result2 << std::endl; //
<< 操作符没有被重载,接收两个参数,一个是输出流cout,另一个是Vector2
例5
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
Vector2(float x, float y)
: x(x), y(y) {}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x + other.x, y + other.y);
// return *this + other;
}
Vector2 operator+(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Add(other);
}
Vector2 Multiply(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x * other.x, y * other.y);
}
Vector2 operator*(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Multiply(other);
// return *this + other;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& stream, const Vector2& other)
{
stream << other.x << "," << other.y;
return stream;
}
};
int main()
{
Vector2 position(4.0f, 4.0f);
Vector2 speed(0.5f, 1.5f);
Vector2 powerup(1.1f, 1.1f);
// 加在一起
Vector2 result = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result1 = position + speed * powerup; // +, * 运算符重载了
std::cout << result << std::endl; // << 操作符重载了
std::cin.get();
}
==操作符
例6
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
Vector2(float x, float y)
: x(x), y(y) {}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x + other.x, y + other.y);
// return *this + other;
}
Vector2 operator+(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Add(other);
}
Vector2 Multiply(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x * other.x, y * other.y);
}
Vector2 operator*(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Multiply(other);
// return *this + other;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& stream, const Vector2& other)
{
stream << other.x << "," << other.y;
return stream;
}
bool operator==(const Vector2& other) const
{
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
};
int main()
{
Vector2 position(4.0f, 4.0f);
Vector2 speed(0.5f, 1.5f);
Vector2 powerup(1.1f, 1.1f);
// 加在一起
Vector2 result1 = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result12 = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result1 = position + speed * powerup; // +, * 运算符重载了
std::cout << result2 << std::endl; // << 操作符重载了
if (result1 == result2) // == 操作符重载了
{
}
std::cin.get();
}
!=操作符
例7
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
struct Vector2
{
float x, y;
Vector2(float x, float y)
: x(x), y(y) {}
Vector2 Add(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x + other.x, y + other.y);
// return *this + other;
}
Vector2 operator+(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Add(other);
}
Vector2 Multiply(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Vector2(x * other.x, y * other.y);
}
Vector2 operator*(const Vector2& other) const
{
return Multiply(other);
// return *this + other;
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& stream, const Vector2& other)
{
stream << other.x << "," << other.y;
return stream;
}
bool operator==(const Vector2& other) const
{
return x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
bool operator!=(const Vector2& other) const
{
return !(*this == other);
// return !operator==(other);
}
};
int main()
{
Vector2 position(4.0f, 4.0f);
Vector2 speed(0.5f, 1.5f);
Vector2 powerup(1.1f, 1.1f);
// 加在一起
Vector2 result1 = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result12 = position.Add(speed.Multiply(powerup));
Vector2 result1 = position + speed * powerup; // +, * 运算符重载了
std::cout << result2 << std::endl; // << 操作符重载了
if (result1 == result2) // == 操作符重载了
{
}
if (result1 != result2) // != 操作符重载了
{
}
std::cin.get();
}
C++的this关键字
- 通过它,可以访问成员函数,即属于某个类的函数
- this是一个指向当前对象实例的指针,该方法属于这个对象实例
- 可以写一个方法,非静态方法,为了调用这个方法,首先需要实例化一个对象,然后调用这个方法;这个方法必须用一个有效的对象来调用,关键字this是指向该对象的指针
例8
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Entity
{
public:
int x, y;
Entity(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
int GetX() const
{
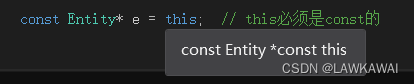
const Entity* e = this; // this必须是const的
}
};
int main()
{
std::cin.get();
}
this是const Entity const 类型:
在类外调用函数,可以使用this:
例9
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
void PrintEntity(Entity* e);
class Entity
{
public:
int x, y;
Entity(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
PrintEntity(this);
}
int GetX() const
{
const Entity* e = this; // this必须是const的
}
};
void PrintEntity(Entity* e)
{
// Printing
}
int main()
{
std::cin.get();
}
void PrintEntity(const Entity& e);
Entity& e = *this;
PrintEntity(this);
void PrintEntity(const Entity& e)
{
// Printing
}
int GetX() const
{
const Entity& e = *this; // this必须是const的
}






















 2565
2565











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








