加入极市专业CV交流群,与6000+来自腾讯,华为,百度,北大,清华,中科院等名企名校视觉开发者互动交流!更有机会与李开复老师等大牛群内互动!
同时提供每月大咖直播分享、真实项目需求对接、干货资讯汇总,行业技术交流。关注 极市平台 公众号 ,回复 加群,立刻申请入群~
来源:知乎 作者:Uno Whoiam 链接: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/60747096 本文已由作者授权转载,未经允许,不得二次转载。
一般来说,人脸识别分三步走:
- 找人脸:图片中找出含人脸的区域框出来
- 对齐人脸:将人脸的眼镜鼻子嘴巴等标出来,以此作为依据对齐人脸
- 识别:将对齐的人脸进行识别,判定这张脸究竟是谁
本篇要介绍的损失函数,用于第三步骤,聚焦于更准确地识别这张脸究竟属于谁,本质上属于一个分类问题。
一言以蔽之ArcFace、SphereFace、CosFace三个损失函数相对于前辈们而言,改进的一个核心思路就是:
只有平常(train)更刻苦的训练,才有可能在比赛中(test)中得到更好的结果。
它们都对卷积神经网络提出了更高的目标,在训练阶段更为艰难,也因此让其成为了一个更好的分类器。
一、从前辈说起
首先谈谈他们的前辈:
维基百科介绍:
Softmax函数,或称归一化指数函数[1],是逻辑函数的一种推广。 它能将一个含任意实数的K维向量 “压缩”到另一个K维实向量 中,使得每一个元素的范围都在 之间,并且所有元素的和为1。 该函数的形式通常按下面的式子给出:
简单来说 softmax 将一组向量进行压缩,使得到的向量各元素之和为 1,而压缩后的值便可以作为置信率,所以常用于分类问题。另外,在实际运算的时候,为了避免上溢和下溢,在将向量丢进softmax之前往往先对每个元素减去其中最大值,即:
想了解更多,可以参考: 忆臻: softmax函数计算时候为什么要减去一个最大值?https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29376573
再谈谈一个容易搞混的东西:
上面我们丢入一个长度为 的 向量,得到 ,而softmax loss呢,则是:
其中 是一个长度为 的one-hot向量,即 ,只有ground truth对应的 。所以也可以简写为:
到这里我们不妨在看看交叉熵 :
其中 是真实分布,在分类任务中, 实际上等价于上面的 。而 则是预测分布,在分类任务中 实际上等价于上面的 。这样一来进行化简就得到:
我咋觉得这么眼熟呢...
所以,我们可以得到:
参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/u014380165/article/details/77284921
二、SphereFace
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.08063.pdf
要想增强 的分类能力,其实就是要在分布上做到两点:
让同类之间距离更近
让不同类之间距离更远
不妨继续看看 :
其中 代表两个向量 之间的夹角,如果对 归一化,将偏置 置为0,即 ,则有:
下标 表示 。
对于 我们乘上一个大于等于1的整数 :
这样不仅放大了类之间的距离,也因放大了同类 与 之间的间隔而使类内更聚拢。
不过上述公式仍有问题:原来的 ,如今 超出了向量之间的夹角函数 定义域范围 咋办?
那就变个函数呗,把n个cos怼起来变成一个递减的连续的函数:
这样一来:
如此我们就得到了SphereFace的损失函数
原论文则是:
其中 表示第 个样本, 表示第 个样本的 标签, 表示第 和样本 之间的夹角。
论文中的可视化图片:
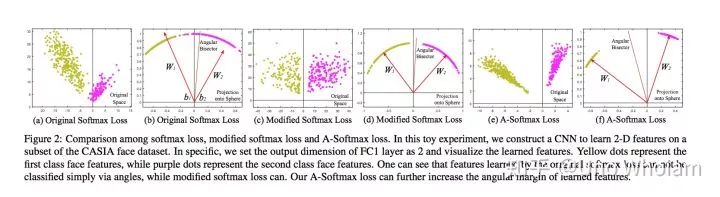
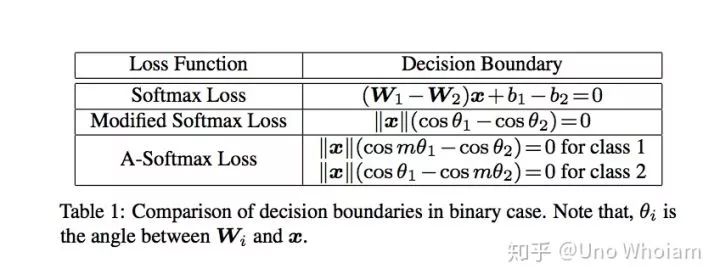
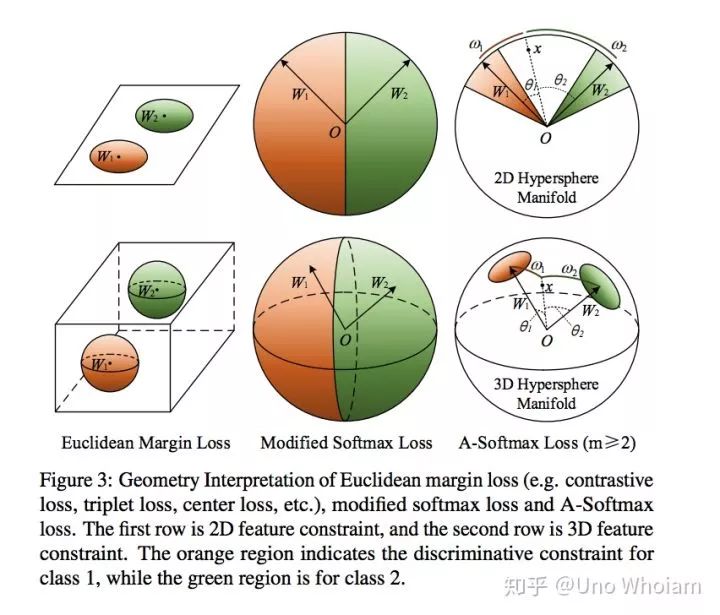
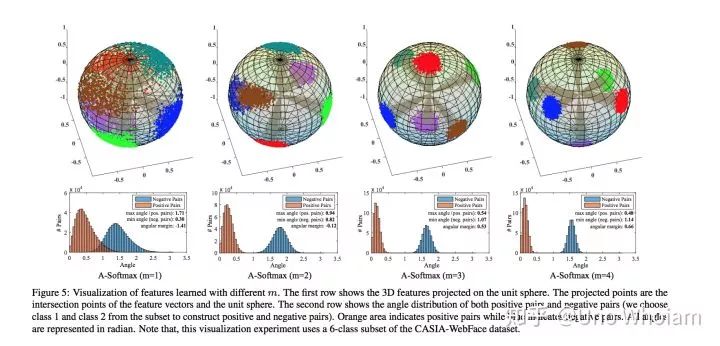
pytorch代码实现:
# SphereFace
class SphereProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin cosine distance: : Args: in_features: size of each input sample out_features: size of each output sample m: margin cos(m*theta) """
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, m=4):
super(SphereProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.m = m
self.base = 1000.0
self.gamma = 0.12
self.power = 1
self.LambdaMin = 5.0
self.iter = 0
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform(self.weight)
# duplication formula
# 将x\in[-1,1]范围的重复index次映射到y\[-1,1]上
self.mlambda = [
lambda x: x ** 0,
lambda x: x ** 1,
lambda x: 2 * x ** 2 - 1,
lambda x: 4 * x ** 3 - 3 * x,
lambda x: 8 * x ** 4 - 8 * x ** 2 + 1,
lambda x: 16 * x ** 5 - 20 * x ** 3 + 5 * x
]
""" 执行以下代码直观了解mlambda import matplotlib.pyplot as plt mlambda = [ lambda x: x ** 0, lambda x: x ** 1, lambda x: 2 * x ** 2 - 1, lambda x: 4 * x ** 3 - 3 * x, lambda x: 8 * x ** 4 - 8 * x ** 2 + 1, lambda x: 16 * x ** 5 - 20 * x ** 3 + 5 * x ] x = [0.01 * i for i in range(-100, 101)] print(x) for f in mlambda: plt.plot(x,[f(i) for i in x]) plt.show() """
def forward(self, input, label):
# lambda = max(lambda_min,base*(1+gamma*iteration)^(-power))
self.iter += 1
self.lamb = max(self.LambdaMin, self.base * (1 + self.gamma * self.iter) ** (-1 * self.power))
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
cos_theta = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
cos_theta = cos_theta.clamp(-1, 1)
cos_m_theta = self.mlambda[self.m](cos_theta)
theta = cos_theta.data.acos()
k = (self.m * theta / 3.14159265).floor()
phi_theta = ((-1.0) ** k) * cos_m_theta - 2 * k
NormOfFeature = torch.norm(input, 2, 1)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
one_hot = torch.zeros(cos_theta.size())
one_hot = one_hot.cuda() if cos_theta.is_cuda else one_hot
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1), 1)
# --------------------------- Calculate output ---------------------------
output = (one_hot * (phi_theta - cos_theta) / (1 + self.lamb)) + cos_theta
output *= NormOfFeature.view(-1, 1)
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(' \
+ 'in_features=' + str(self.in_features) \
+ ', out_features=' + str(self.out_features) \
+ ', m=' + str(self.m) + ')'三、CosFace
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.09414.pdf
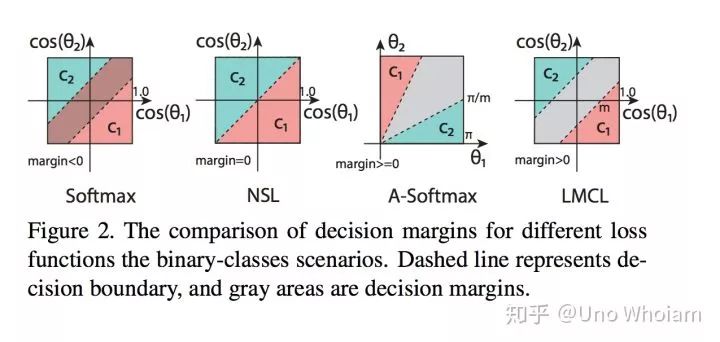
和SphereFace类似,CosFace也是从 的余弦表达形式入手,令 。与此同时,作者发现 对于分类并没有啥帮助,所以干脆将其固定 ,所以有:
应该代表归一化的 。
接下来与上文 类似的是也引入了常数 ,不同的是这里的 是加上去的:
以上我们就得到了CosFace中提出的Large Margin Cosine Loss
 代码实现:
代码实现:
# CosFace
class AddMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin cosine distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta) - m
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.40):
super(AddMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
phi = cosine - self.m
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
# one_hot = one_hot.cuda() if cosine.is_cuda else one_hot
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine)
# you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(' \
+ 'in_features=' + str(self.in_features) \
+ ', out_features=' + str(self.out_features) \
+ ', s=' + str(self.s) \
+ ', m=' + str(self.m) + ')'四、ArcFace
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.07698.pdf
话不多说,直接上公式:
可以看到和CosFace非常类似,只是将 作为角度加上去了,这样就强行拉大了同类之间的角度,使得神经网络更努力地将同类收得更紧。
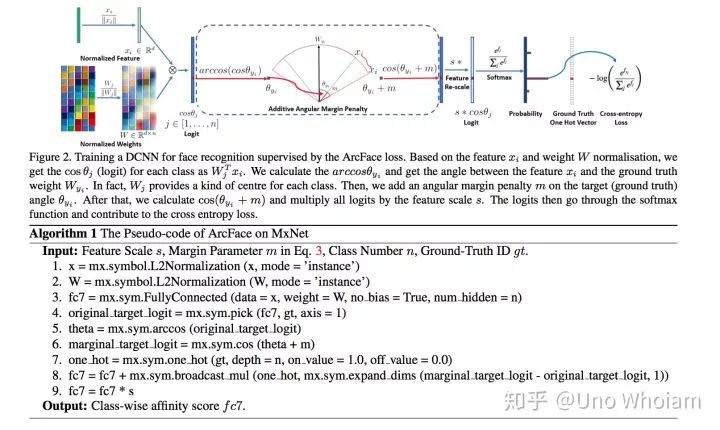
伪代码实现步骤:
- 对 进行归一化
- 对 进行归一化
- 计算 得到预测向量
- 从 中挑出与ground truth对应的值
- 计算其反余弦得到角度
- 角度加上m
- 得到挑出从 中挑出与ground truth对应的值所在位置的独热码
- 将 通过独热码放回原来的位置
- 对所有值乘上固定值
# ArcFace
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin arc distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta + m)
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.50, easy_margin=False):
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
# Parameter 的用途:
# 将一个不可训练的类型Tensor转换成可以训练的类型parameter
# 并将这个parameter绑定到这个module里面
# net.parameter()中就有这个绑定的parameter,所以在参数优化的时候可以进行优化的
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/d8b77cc02410
# 初始化权重
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.easy_margin = easy_margin
self.cos_m = math.cos(m)
self.sin_m = math.sin(m)
self.th = math.cos(math.pi - m)
self.mm = math.sin(math.pi - m) * m
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
# torch.nn.functional.linear(input, weight, bias=None)
# y=x*W^T+b
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
sine = torch.sqrt(1.0 - torch.pow(cosine, 2))
# cos(a+b)=cos(a)*cos(b)-size(a)*sin(b)
phi = cosine * self.cos_m - sine * self.sin_m
if self.easy_margin:
# torch.where(condition, x, y) → Tensor
# condition (ByteTensor) – When True (nonzero), yield x, otherwise yield y
# x (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is True
# y (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is False
# return:
# A tensor of shape equal to the broadcasted shape of condition, x, y
# cosine>0 means two class is similar, thus use the phi which make it
phi = torch.where(cosine > 0, phi, cosine)
else:
phi = torch.where(cosine > self.th, phi, cosine - self.mm)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
# one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), requires_grad=True, device='cuda')
# 将cos(\theta + m)更新到tensor相应的位置中
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
# scatter_(dim, index, src)
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine)
# you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
到此ArcFace、SphereFace、CosFace的损失函数就介绍完啦~
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fuwenyan/article/details/79657738
—— END ——
*延伸阅读
超轻量级通用人脸检测模型
3D人脸技术漫游指南
人脸聚类那些事儿:利用无标签数据提升人脸识别性能
PS:新年假期,极市将为大家分享计算机视觉顶会 ICCV 2019 大会现场报告系列视频,欢迎前往B站【极市平台】观看,春节也学习,极市不断更,快来打卡点赞吧~ https://www.bilibili.com/video/av83518299 点击 阅读原文,可跳转浏览本文内所有网址链接
CV细分方向交流群
添加极市小助手微信(ID : cv-mart),备注:研究方向-姓名-学校/公司-城市(如:目标检测-小极-北大-深圳),即可申请加入目标检测、目标跟踪、人脸、工业检测、医学影像、三维&SLAM、图像分割等极市技术交流群(已经添加小助手的好友直接私信),更有每月大咖直播分享、真实项目需求对接、干货资讯汇总,行业技术交流,一起来让思想之光照的更远吧~

△长按添加极市小助手

△长按关注极市平台
觉得有用麻烦给个在看啦~ 




















 643
643











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








