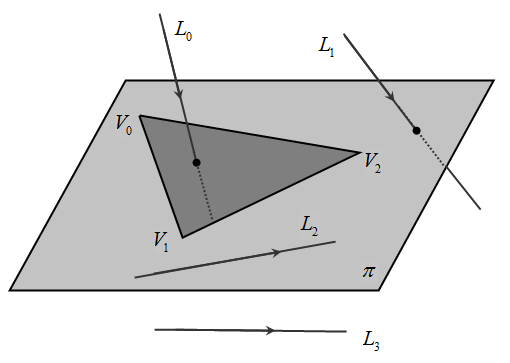

本篇文章介绍一种三维空间下线性对象与三角形的相交测试算法和实现,线性对象包括:直接、射线和线段,它们可以用类似的形式来表示,先以直接为例来阐述算法,射线和线段是直接的特殊情况。
文章目录:
- 算法介绍
- 源码实现
- 参考
算法介绍
在三维空间上,判断线性对象
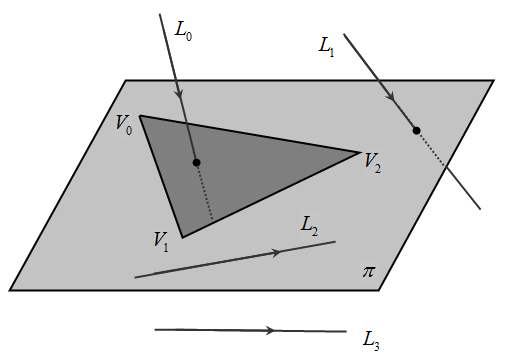
三维空间的模型通常是由一个个三角形面片构成的,线性对象与三角形的相交检测也显得特别的重要。如图1所示,一条直线与三角形可能有四种关系:1)直线
Möller&Trumbore(1997)[1]提出了一种更加高效的射线与三角形相交测试的算法,而且乘法或者除法操作造成的误差叠加较少,精度损失更小,因此性能上更加健壮。
三角形内的任意一点都可以用它相对于三角形的顶点的位置来定义:
其中,
整理,得
这相当于是一个齐次线性方程组,
其中,
如果得到的解
直线与三角形相交测试的算法伪码如下所示:
在三维空间上,判断直线与三角形
是否相交,若相交,求出交点,三角形所在的平面是
![]()

如果需要求射线与三角形的交,必需限定
注意到,在上述的算法伪码中,已经把一些中间变量存储起来,避免重复计算,可以提高算法的速度,例如中间变量
源码实现
基础库源码链接,参见这里,下面是前面所描述的算法的实现。
#include "SrGeometricTools.h"
#include "SrDataType.h"
namespace {
class SrSegment3D
{
public:
SrPoint3D mPoint1;
SrPoint3D mPoint2;
};
class SrRay3D
{
public:
SrPoint3D mBase;
SrPoint3D mDirection;
};
class SrLine3D
{
public:
SrPoint3D mBase;
SrPoint3D mDirection;
};
/**
brief 3D triangle class.
This is a 3D triangle class with public data members.
*/
class SrTriangle3D
{
public:
/**
brief Default constructor, endpoints is set to (0,0).
*/
SrTriangle3D()
{
mPoint[0] = mPoint[1] = mPoint[1] = SrVector3D(0, 0, 0);
}
/**
brief The line is initialized by three points.
*/
SrTriangle3D(const SrPoint3D& p0, const SrPoint3D& p1, const SrPoint3D& p2)
{
mPoint[0] = p0;
mPoint[1] = p1;
mPoint[2] = p2;
}
/**
brief Destructor. Do nothing.
*/
~SrTriangle3D() {}
/**
brief The triangle is valid if the three points are not on a line.
*/
bool isValid() const
{
SrVector3D norm = normal();
if (EQUAL(norm.x, 0) && EQUAL(norm.y, 0) && EQUAL(norm.z, 0))
return false;
return true;
}
/**
brief Compute the normal using Newell method devised by Martin Newell.It relates to the order of the points.
*/
const SrVector3D normal()const
{
SrVector3D norm = (mPoint[1] - mPoint[0]).cross(mPoint[2] - mPoint[0]);
return norm;
}
/**
brief Judge whether or not the line hits the triangle.
return SR_OVERLAPPING if the line is on the plane where the triangle lies;
SR_PARALLEL if the line is parallel to the triangle.
SR_DISJOINT if the line misses the triangle;
SR_INTERSECTING if the line intersects with the triangle and intersection point is not on the edge.
param[out] result If the line intersects with the triangle and the intersection point information is put in 'result'.
*/
int lineHitTest(const SrLine3D& line, SrPoint3D& /*[OUT]*/ result)const
{
SrVector3D ret;
int retFlag = linearIntersectTriangle(line.mBase, line.mDirection, ret);
if (retFlag != SR_INTERSECTING)
return retFlag;
result = line.mBase + ret.z*line.mDirection;
//check whether the intersection point is on the edge.
//if( EQUAL(ret.x+ret.y-1.0,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.x,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.y,0) )
// return SR_INTERSECTING_EDGE;
return SR_INTERSECTING;
}
/**
brief Judge whether or not the ray hits the triangle.
return SR_OVERLAPPING if the ray is on the plane where the triangle lies;
SR_PARALLEL if the ray is parallel to the triangle.
SR_DISJOINT if the ray misses the triangle;
SR_INTERSECTING if the ray intersects with the triangle and intersection point is not on the edge.
param[out] result If the ray intersects with the triangle and the intersection point information is put in 'result'.
*/
int rayHitTest(const SrRay3D& ray, SrPoint3D& /*[OUT]*/ result)const
{
SrVector3D ret;
int retFlag = linearIntersectTriangle(ray.mBase, ray.mDirection, ret);
if (retFlag != SR_INTERSECTING)
return retFlag;
//check t. t>=0
if (LESS(ret.z, 0))
return SR_DISJOINT;
result = ray.mBase + ret.z*ray.mDirection;
//check whether the intersection point is on the edge.
//if( EQUAL(ret.x+ret.y-1.0,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.x,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.y,0) )
// return SR_INTERSECTING_EDGE;
return SR_INTERSECTING;
}
/**
brief Judge whether or not the segment hits the triangle.
return SR_OVERLAPPING if the segment is on the plane where the triangle lies;
SR_PARALLEL if the segment is parallel to the triangle.
SR_DISJOINT if the segment misses the triangle;
SR_INTERSECTING if the segment intersects with the triangle and intersection point is not on the edge.
param[out] result If the segment intersects with the triangle and the intersection point information is put in 'result'.
*/
int segmentHitTest(const SrSegment3D& segment, SrPoint3D& /*[OUT]*/ result)const
{
SrVector3D ret;
SrVector3D direction = segment.mPoint2 - segment.mPoint1;
int retFlag = linearIntersectTriangle(segment.mPoint1, direction, ret);
if (retFlag != SR_INTERSECTING)
return retFlag;
//check t. 0<= t <=1
if (LESS(ret.z, 0) || GREATER(ret.z, 1))
return SR_DISJOINT;
result = segment.mPoint1 + ret.z*direction;
//check whether the intersection point is on the edge.
//if( EQUAL(ret.x+ret.y-1.0,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.x,0) ||
// EQUAL(ret.y,0) )
// return SR_INTERSECTING_EDGE;
return SR_INTERSECTING;
}
public:
SrPoint3D mPoint[3];
private:
/**
brief Judge whether or not the line hits the triangle.The line is base + t*direction.
It is not necessary for direction to be unit length.
return SR_OVERLAPPING if the line is on the plane where the triangle lies;
SR_PARALLEL if the line is parallel to the triangle.
SR_DISJOINT if the line misses the triangle;
SR_INTERSECTING if the line intersects with the triangle.
param[out] result return the result of (u,v,t) if the line intersects with the triangle.
*/
/*
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Devised by Moller and Trumbore,1997. <Fast,minimum storage ray-triangle
intersection>
Any point in a triangle can be defined in terms of its position relative
to the triangle’s vertices:
Qu,v = (1-u-v)V0 + uV1 + vV2 ,0<=u<=1,0<=v<=1,0<=u+v<=1
For the linear component–triangle intersection,
P + t*^d = Qu,v
which can be expanded and applied Cramer’s rule to:
|t| | |P-V0 V1-V0 V2-V0| |
|u| = 1/|-^d V1-V0 V2-V0| | |-^d P-V0 V2-V0| |
|v| | |-^d V1-V0 P-V0| |
| ((P-V0)×(V1-V0))·(V2-V0) |
= 1/(^d×(V2-v0))·(V1-V0) | (^d×(V2-V0))·(P-V0) |
| ((P-V0)×(V1-V0))·^d |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
int linearIntersectTriangle(const SrPoint3D& base, const SrVector3D& direction, SrVector3D& result)const
{
SrReal u, v, tmp;
SrVector3D e1, e2, p, s, q;
e1 = mPoint[1] - mPoint[0];
e2 = mPoint[2] - mPoint[0];
p = direction.cross(e2);
tmp = p.dot(e1);
//If the line is perpendicular to the normal of triangle.
if (EQUAL(tmp, 0))
{
//The line is on the plane.
p = e1.cross(e2);
if (EQUAL(p.dot(base - mPoint[0]), 0))
return SR_OVERLAPPING;
//The line is parallel to the plane.
return SR_PARALLEL;
}
s = base - mPoint[0];
u = p.dot(s) / tmp;
if (LESS(u, 0) || GREATER(u, 1))
return SR_DISJOINT;
q = s.cross(e1);
v = q.dot(direction) / tmp;
if (LESS(v, 0) || GREATER(v, 1) || GREATER(u + v, 1))
return SR_DISJOINT;
result.x = u;
result.y = v;
result.z = e2.dot(q) / tmp;
return SR_INTERSECTING;
}
};
}
参考
[1] Tomas Möller, and Ben Trumbore. "Fast, minimum storage ray-triangle intersection." Journal of graphics tools, vol.2, no.1, pp.21-28, 1997.
[2] Philip J. Schneider, and David H. Eberly. Geometric Tools for Computer Graphics. Morgan Kaufmann, 2002.




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








