1.数学形态学简介
数学形态学(Mathematical morphology) 是一门建立在格论和拓扑学基础之上的图像分析学科,是数学形态学图像处理的基本理论。其基本的运算包括:腐蚀和膨胀、开运算和闭运算、骨架抽取、极限腐蚀、击中击不中变换、形态学梯度、Top-hat变换、颗粒分析、流域变换等。
1腐蚀
粗略的说,腐蚀可以使目标区域范围“变小”,其实质造成图像的边界收缩,可以用来消除小且无意义的目标物。式子表达为:
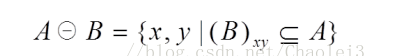
该式子表示用结构B腐蚀A,需要注意的是B中需要定义一个原点,【而B的移动的过程与卷积核移动的过程一致,同卷积核与图像有重叠之后再计算一样】当B的原点平移到图像A的像元(x,y)时,如果B在(x,y)处,完全被包含在图像A重叠的区域,(也就是B中为1的元素位置上对应的A图像值全部也为1)则将输出图像对应的像元(x,y)赋值为1,否则赋值为0。
我们看一个演示图。

B依顺序在A上移动(和卷积核在图像上移动一样,然后在B的覆盖域上进行形态学运算),当其覆盖A的区域为[1,1;1,1]或者[1,0;1,1]时,(也就是B中‘1’是覆盖区域的子集)对应输出图像的位置才会为1。
2.膨胀
粗略地说,膨胀会使目标区域范围“变大”,将于目标区域接触的背景点合并到该目标物中,使目标边界向外部扩张。作用就是可以用来填补目标区域中某些空洞以及消除包含在目标区域中的小颗粒噪声。

该式子表示用结构B膨胀A,将结构元素B的原点平移到图像像元(x,y)位置。如果B在图像像元(x,y)处与A的交集不为空(也就是B中为1的元素位置上对应A的图像值至少有一个为1),则输出图像对应的像元(x,y)赋值为1,否则赋值为0。
演示图为:

小结
也就是说无论腐蚀还是膨胀,都是把结构元素B像卷积操作那样,在图像上平移,结构元素B中的原点就相当于卷积核的核中心,结果也是存储在核中心对应位置的元素上。只不过腐蚀是B被完全包含在其所覆盖的区域,膨胀时B与其所覆盖的区域有交集即可。
3.开运算和闭运算
前面介绍了腐蚀和膨胀,而开运算和闭运算就是2种基本运算的叠加。正如开篇所说的那样,开运算就是先腐蚀再膨胀,闭运算就是先膨胀再腐蚀。这里也就不再赘述。
4.形态学梯度
其实就是一幅图像膨胀与腐蚀的差别。
结果看上去就像前景物体的轮廓。
5.骨架提取
骨架提取,也叫二值图像细化。这种算法能将一个连通区域细化成一个像素的宽度,用于特征提取和目标拓扑表示。
代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Dec 27 17:37:31 2019
@author: yuan
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def rgb2gray(rgb):
"""
rgb 2 gray
Args:
rgb image
Returns:
gray image
"""
gray = rgb[:, :, 0] * 0.299 + rgb[:, :, 1] * 0.587 + rgb[:, :, 2] * 0.114
return gray
def thre_bin(gray_image, threshold=170):
"""
binary image
Args:
gray_image:image with gray scale
threshold:the split standard
Returns:
bin image
"""
threshold_image = np.zeros(shape=(gray_image.shape[0], gray_image.shape[1]), dtype=np.uint8)
# loop for every pixel
for i in range(gray_image.shape[0]):
for j in range(gray_image.shape[1]):
if gray_image[i][j] > threshold:
threshold_image[i][j] = 1
else:
threshold_image[i][j] = 0
return threshold_image
def erode_bin_image(bin_image, kernel):
"""
erode bin image
Args:
bin_image: image with 0,1 pixel value
Returns:
erode image
"""
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
bin_image = np.array(bin_image)
if (kernel_size%2 == 0) or kernel_size<1:
raise ValueError("kernel size must be odd and bigger than 1")
if (bin_image.max() != 1) or (bin_image.min() != 0):
raise ValueError("input image's pixel value must be 0 or 1")
d_image = np.zeros(shape=bin_image.shape)
center_move = int((kernel_size-1)/2)
for i in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[0]-kernel_size+1):
for j in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[1]-kernel_size+1):
d_image[i, j] = np.min(bin_image[i-center_move:i+center_move,
j-center_move:j+center_move])
return d_image
def dilate_bin_image(bin_image, kernel):
"""
dilate bin image
Args:
bin_image: image with 0,1 pixel value
Returns:
dilate image
"""
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
bin_image = np.array(bin_image)
if (kernel_size%2 == 0) or kernel_size<1:
raise ValueError("kernel size must be odd and bigger than 1")
if (bin_image.max() != 1) or (bin_image.min() != 0):
raise ValueError("input image's pixel value must be 0 or 1")
d_image = np.zeros(shape=bin_image.shape)
center_move = int((kernel_size-1)/2)
for i in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[0]-kernel_size+1):
for j in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[1]-kernel_size+1):
d_image[i, j] = np.max(bin_image[i-center_move:i+center_move,j-center_move:j+center_move])
return d_image
'''
erode
'''
img=cv2.imread("./Images/kai.jpg") #read iamge
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8) #kernel size
thresh_image=thre_bin(rgb2gray(img), threshold=170) #thresh
#use opencv
erosion = cv2.erode(thresh_image,kernel,iterations = 1)
#use my function
erosion_2=erode_bin_image(thresh_image, kernel)
#show
plt.figure(1)
#第一行第一列图形
ax1 = plt.subplot(2,3,1)
plt.sca(ax1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("artwork")
#第一行第二列图形
ax2 = plt.subplot(2,3,2)
plt.sca(ax2)
plt.imshow(erosion,cmap="gray")
plt.title("erode")
ax9 = plt.subplot(2,3,3)
plt.sca(ax9)
plt.imshow(erosion_2,cmap="gray")
plt.title("my erode")
'''
dilate
'''
img=cv2.imread("./Images/bi.jpg")
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
thresh_image=thre_bin(rgb2gray(img), threshold=170)
#use opencv
dilate = cv2.dilate(thresh_image,kernel,iterations = 1)
#use my functuon
dilate_2=dilate_bin_image(thresh_image, kernel)
#第一行第3列图形
ax3 = plt.subplot(2,3,4)
plt.sca(ax3)
plt.imshow(img,cmap="gray")
plt.title("arttwork")
#第一行第4列图形
ax4 = plt.subplot(2,3,5)
plt.sca(ax4)
plt.imshow(dilate,cmap="gray")
plt.title("dilate")
ax10 = plt.subplot(2,3,6)
plt.sca(ax10)
plt.imshow(dilate_2,cmap="gray")
plt.title("my dilate")
plt.show()
'''
morphologyEx
'''
img=cv2.imread("./Images/kaibi.jpg")
kernel = np.ones((18,18),np.uint8)
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
plt.figure(2)
#第2行第1列图形
ax5 = plt.subplot(2,2,1)
plt.sca(ax5)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("artwork")
#第2行第2列图形
ax6 = plt.subplot(2,2,2)
plt.sca(ax6)
plt.imshow(opening,cmap="gray")
plt.title("opening")
#第2行第3列图形
ax7 = plt.subplot(2,2,3)
plt.sca(ax7)
plt.imshow(img,cmap="gray")
plt.title("artwork")
#第2行第4列图形
ax8 = plt.subplot(2,2,4)
plt.sca(ax8)
plt.imshow(closing,cmap="gray")
plt.title("closing")
plt.show()
腐蚀膨胀

开运算和闭运算

形态学梯度
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Dec 27 18:11:58 2019
@author: yuan
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def rgb2gray(rgb):
"""
rgb 2 gray
Args:
rgb image
Returns:
gray image
"""
gray = rgb[:, :, 0] * 0.299 + rgb[:, :, 1] * 0.587 + rgb[:, :, 2] * 0.114
return gray
def thre_bin(gray_image, threshold=170):
"""
binary image
Args:
gray_image:image with gray scale
threshold:the split standard
Returns:
bin image
"""
threshold_image = np.zeros(shape=(gray_image.shape[0], gray_image.shape[1]), dtype=np.uint8)
# loop for every pixel
for i in range(gray_image.shape[0]):
for j in range(gray_image.shape[1]):
if gray_image[i][j] > threshold:
threshold_image[i][j] = 1
else:
threshold_image[i][j] = 0
return threshold_image
def erode_bin_image(bin_image, kernel):
"""
erode bin image
Args:
bin_image: image with 0,1 pixel value
Returns:
erode image
"""
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
bin_image = np.array(bin_image)
if (kernel_size%2 == 0) or kernel_size<1:
raise ValueError("kernel size must be odd and bigger than 1")
if (bin_image.max() != 1) or (bin_image.min() != 0):
raise ValueError("input image's pixel value must be 0 or 1")
d_image = np.zeros(shape=bin_image.shape)
center_move = int((kernel_size-1)/2)
for i in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[0]-kernel_size+1):
for j in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[1]-kernel_size+1):
d_image[i, j] = np.min(bin_image[i-center_move:i+center_move,
j-center_move:j+center_move])
return d_image
def dilate_bin_image(bin_image, kernel):
"""
dilate bin image
Args:
bin_image: image with 0,1 pixel value
Returns:
dilate image
"""
kernel_size = kernel.shape[0]
bin_image = np.array(bin_image)
if (kernel_size%2 == 0) or kernel_size<1:
raise ValueError("kernel size must be odd and bigger than 1")
if (bin_image.max() != 1) or (bin_image.min() != 0):
raise ValueError("input image's pixel value must be 0 or 1")
d_image = np.zeros(shape=bin_image.shape)
center_move = int((kernel_size-1)/2)
for i in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[0]-kernel_size+1):
for j in range(center_move, bin_image.shape[1]-kernel_size+1):
d_image[i, j] = np.max(bin_image[i-center_move:i+center_move,j-center_move:j+center_move])
return d_image
img=cv2.imread("./Images/yingbi.jpg") #read image
thresh_image=thre_bin(rgb2gray(img), threshold=170) #thresh
kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8) #kernel size
gradient = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh_image, cv2.MORPH_GRADIENT, kernel) #opencv GRADIENT
#use my function
erosion_2=erode_bin_image(thresh_image, kernel)
dilate_2=dilate_bin_image(thresh_image, kernel)
gradient_2=dilate_2-erosion_2 #my GRADIENT
#show results
plt.figure(1)
#第一行第一列图形
ax1 = plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.sca(ax1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("artwork")
#第一行第二列图形
ax2 = plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.sca(ax2)
plt.imshow(gradient,cmap="gray")
plt.title("gradient")
ax3 = plt.subplot(1,3,3)
plt.sca(ax3)
plt.imshow(gradient_2,cmap="gray")
plt.title("my gradient")









 本文深入探讨了数学形态学在图像处理中的应用,包括腐蚀、膨胀、开运算、闭运算等基本运算,以及如何通过这些运算实现图像边界处理、噪声消除、目标区域分析等功能。
本文深入探讨了数学形态学在图像处理中的应用,包括腐蚀、膨胀、开运算、闭运算等基本运算,以及如何通过这些运算实现图像边界处理、噪声消除、目标区域分析等功能。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








