1.质数
1.质数的判定——试除法
1)大于1的
2)约束只有1和本身
3)时间复杂度sqrt(n)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool is_prime(int x)
{
if (x < 2) return false;//质数要严格大于1
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//这里用到了约数都是成对出现的性质,实践复杂度为根号n
if (x % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
if (is_prime(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
2.分解质因数——试除法
时间复杂度sqrt(n)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void divide(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )//只包含一个大于根号n的质因子,所以枚举到根号n
if (x % i == 0)//i 一定是质数
{
int s = 0;
while (x % i == 0) x /= i, s ++ ;
cout << i << ' ' << s << endl;
}
if (x > 1) cout << x << ' ' << 1 << endl;//把大于根号n的质因子单独打印出来
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
divide(x);
}
return 0;
}
3.质数的判定——筛子法
//朴素筛法(埃式)
//朴素筛法筛掉p之前的所有数的倍数
//埃式筛掉p之前所有质数的倍数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N= 1000010;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];//true代表不是质数,false代表是质数
void get_primes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (st[i]) continue;//如果为真,则跳过
primes[cnt ++ ] = i;//如果是质数,则加入到primes数组里
for (int j = i; j <= n; j += i)//把所有i的倍数标记为true,这行代码只有i为质数时才会执行,所以就达到了埃式算法的目的
st[j] = true;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
get_primes(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
//线性筛法
//n只会被其最小质因子筛掉,例如4被2筛掉,36被2筛掉。。。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N= 1000010;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )//枚举n个数
{
if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++ ] = i;//如果是质数,加到表里
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )//从小到大枚举所有的质数
{
st[primes[j] * i] = true;//把当前质数和i的乘积筛掉
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;//primes[j]一定是i的最小质因子
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
get_primes(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
线性筛法参考连接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f16d318efe9b
| j=2 | j=3 | j=4 | j=5 | |
| i=2 | 2X2 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| i=3 | 2X3 | 3X3 | 12 | 15 |
| i=4 | 2X4 | 12 | 16 | 20 |
| i=5 | 2X5 | 3X5 | 12 | 5X5 |
| i=6 | 2X6 | 18 | 24 | 30 |
| i=7 | 2X7 | 3X7 | 28 | 5X7 |
如表所示,所有的合数只会被其最小质因数筛掉,
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
这句代码的意思就是:当i能被primes[j]整除时,说明i不能再作为乘积中的一项了,乘积中的另一项一定会比i小了,当前的合数将交给乘积中的另一项(primes[j])去筛除。
j是在枚举最小质因子,i是在枚举最小质因子要乘以的另一项
2.约数
1.试除法求所有约束
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> get_divisors(int x)
{
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 1; i <= x / i; i ++ )//只枚举小于sqrt(n)的一半,另一个可以算出来
if (x % i == 0)
{
res.push_back(i);
if (i != x / i) res.push_back(x / i);//防止出现平方的情况
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());//排序
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
auto res = get_divisors(x);
for (auto x : res) cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.约数的个数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<int, int> primes;//存质因数及其指数
//step1:分解质因式
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
primes[i] ++ ;
}
if (x > 1) primes[x] ++ ;
}
//step2:利用公式计算约数个数
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : primes) res = res * (p.second + 1) % mod;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
4.约数求和
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<int, int> primes;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
primes[i] ++ ;
}
if (x > 1) primes[x] ++ ;
}
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : primes)
{
LL a = p.first, b = p.second;
LL t = 1;
while (b -- ) t = (t * a + 1) % mod;//公式
res = res * t % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
5.最大公约数(辗转相除法)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("%d\n", gcd(a, b));
}
return 0;
}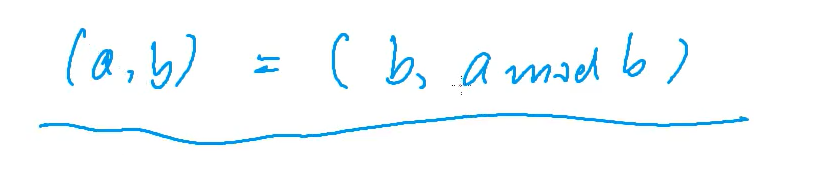






















 305
305











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








