目标检测—CIOU原理及代码实现
最近刚写完一篇YOLO V4-tiny的blog,其中Tensorflow2.0—YOLO V4-tiny网络原理及代码解析(三)- 损失函数的构建涉及到了CIOU。所以特地单独领出来写一篇blog记录一下。
在YOLO V3中,对于位置的损失函数,使用的还是普通的smooth-l1损失函数,但是到了YOLO V4中,关于位置的损失函数已经变成CIOU了。
一、原理,公式
关于它的原理,在YOLOV4与YOLOV3的区别中已经有了大致的介绍。
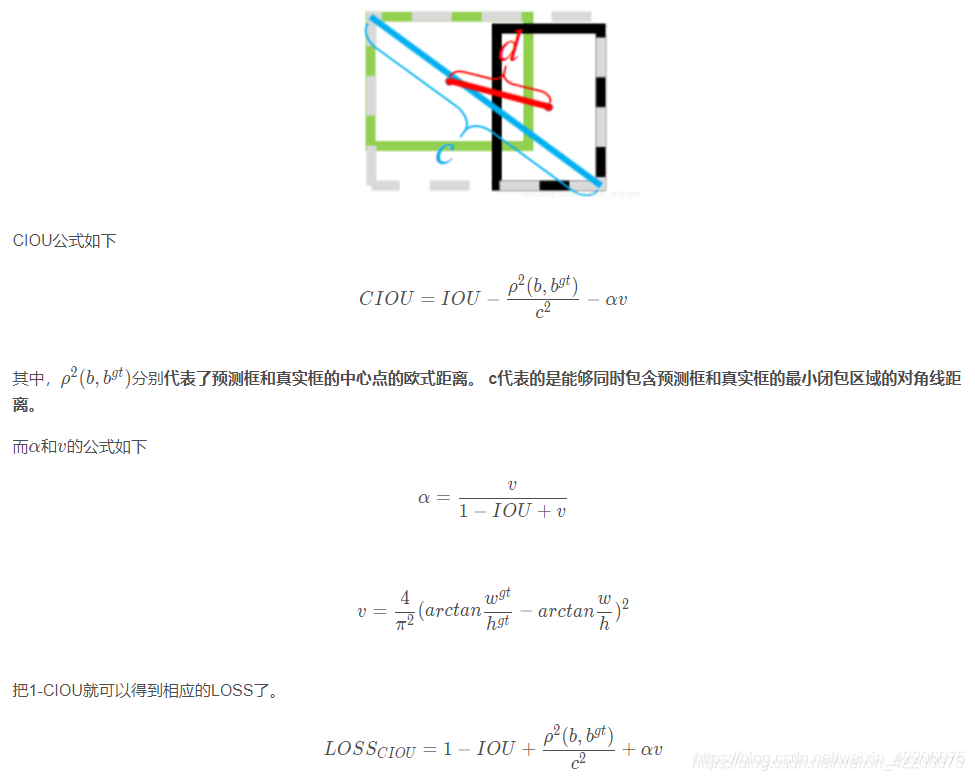
二、优点
相比于IOU的优点:
1.IOU没有考虑到两个框之间的位置信息,如果两个框没有重叠,它的IOU=0,没法进行反向传播。
2.还有一点,就是为什么之前的所有目标检测的网络中没有用iou直接作为损失函数。就是因为对于大小不同的框,iou值相同,但是其重叠程度却不同(说白了,就是对尺度不敏感)。在ciou中,由于有v这个概念,所以就使这种情况不可能再出现(个人理解,不对还请指正)。
三、代码实现
先来看下输入参数:
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
'''输入为:
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
'''
这里,我就用yolo系列的一个yolo head为例:b1和b2的shape=(2,13,13,3,4),其中4表示的是xywh。
第一步:先将输入的进行转换,转化为xyxy格式,其中b1_mins,b1_maxes ,b2_mins ,b2_maxes 的shape=(2,13,13,3,2)
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
第二步:计算真实与预测的iou值
intersect_mins = K.maximum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = K.minimum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / K.maximum(union_area,K.epsilon())
第三步:计算两个框的中心点的距离(ρ)
center_distance = K.sum(K.square(b1_xy - b2_xy), axis=-1)
第四步:计算两个框的最小闭包区域的对角线大小(c)
enclose_mins = K.minimum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = K.maximum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = K.maximum(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, 0.0)
enclose_diagonal = K.sum(K.square(enclose_wh), axis=-1)
第五步:计算α
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / K.maximum(enclose_diagonal ,K.epsilon())
v = 4*K.square(tf.math.atan2(b1_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b1_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon())) - tf.math.atan2(b2_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b2_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon()))) / (math.pi * math.pi)
alpha = v / K.maximum((1.0 - iou + v), K.epsilon())
值得注意的是,v和alpha的shape都是为(2,13,13,3)
第六步:计算最终的ciou,并在最后一维增加一个维度
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
ciou = K.expand_dims(ciou, -1)
最终,输出的ciou的shape为(2,13,13,3,1)。
完整代码如下:
import math
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras import Input
def box_ciou(b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
ciou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
# b1_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b1_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
# b2_mins (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
# b2_maxes (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 2)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
# iou (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = K.maximum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = K.minimum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.)
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / K.maximum(union_area,K.epsilon())
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
# center_distance (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = K.sum(K.square(b1_xy - b2_xy), axis=-1)
enclose_mins = K.minimum(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = K.maximum(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = K.maximum(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, 0.0)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
# enclose_diagonal (batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = K.sum(K.square(enclose_wh), axis=-1)
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / K.maximum(enclose_diagonal ,K.epsilon())
v = 4*K.square(tf.math.atan2(b1_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b1_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon())) - tf.math.atan2(b2_wh[..., 0], K.maximum(b2_wh[..., 1],K.epsilon()))) / (math.pi * math.pi)
alpha = v / K.maximum((1.0 - iou + v), K.epsilon())
ciou = ciou - alpha * v
ciou = K.expand_dims(ciou, -1)
return ciou
if __name__ == '__main__':
b1 = Input(shape=(13,13,3,4))
b2 = Input(shape=(13,13,3,4))
ciou = box_ciou(b1,b2)
代码转载于: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/107302710?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501




























 1066
1066

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










