文章目录
1 什么是KL Divergence(KL散度,也说是KL距离)
KL散度是一种概率分布和另一种概率分布的差异的距离。
公式如下:

2 一个简单的例子

3 KL的性质
- 具有非对称性,且不满足三角不等式形式,即是 D K L ( P ∣ ∣ Q ) ≠ D K L ( Q ∣ ∣ P ) D_{KL}(P||Q)≠D_{KL}(Q||P) DKL(P∣∣Q)=DKL(Q∣∣P),说明KL散度不是用来衡量距离的。
- 如图:

4 KL散度的公式介绍
公式如下:

其中, D K L ( P ∣ ∣ Q ) D_{KL}(P||Q) DKL(P∣∣Q)——概率 P P P与概率 Q Q Q之间的差异,散度越小,则两个概率越接近,那么估计的概率分布也就与真实的概率分布越接近。
KL散度,计算出来的是两者的概率差,可以说KL散度是一种损失,来计算两者的概率差异。
5 Pytorch实现KL散度——F.kl_div()
5.1 函数原型
torch.nn.functional.kl_div(input, target, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
- 参数介绍:
input – Tensor of arbitrary shape
target – Tensor of the same shape as input
size_average (bool, optional) – Deprecated (see reduction). By default, the losses are averaged over each loss element in the batch. Note that for some losses, there multiple elements per sample. If the field size_average is set to False, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch. Ignored when reduce is False. Default: True
reduce (bool, optional) – Deprecated (see reduction). By default, the losses are averaged or summed over observations for each minibatch depending on size_average. When reduce is False, returns a loss per batch element instead and ignores size_average. Default: True
reduction (string, optional) – Specifies the reduction to apply to the output: 'none' | 'batchmean' | 'sum' | 'mean'. 'none': no reduction will be applied 'batchmean': the sum of the output will be divided by the batchsize 'sum': the output will be summed 'mean': the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output Default: 'mean'
{'none' | 'batchmean' | 'sum' | 'mean'}
'none':不进行压缩
'batchmean':输出的总和除以batchsize
'sum':输出的总和
'mean':输出的输出除以输出中的元素数量
默认值:'mean'
-
第一个参数是一个对数概率矩阵,第二个参数是概率矩阵。这里很重要,不然求出来的kl散度可能是个负值。
-
如果现在想用Y指导X,第一个参数要传X,第二个要传Y。就是被指导的放在前面,然后求相应的概率和对数概率就可以了。例如 D K L ( P ∣ ∣ Q ) D_{KL}(P||Q) DKL(P∣∣Q),就是求Q的对数概率,求P的概率。
-
reducebool类型,可选{‘True’, ‘False’},默认值:TRUE.
默认情况下,根据大小的平均值,对每个小批处理的损失进行平均或求和。当reduce为False时,返回每个批元素的损失值,并忽略平均大小。 -
reductionstring类型,可选{‘None’, ‘batchmean’, ‘sum’, ‘mean’},默认值:‘mean’
‘none’:不进行压缩
‘batchmean’:输出的总和除以batchsize
‘sum’:输出的总和
‘mean’:输出的输出除以输出中的元素数量
5.2 简单代码
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 定义两个矩阵
P = torch.tensor([0.25] * 4 + [0])
Q = torch.tensor([0.2] * 5)
print(P, Q)
# 因为要用P指导Q,所以求Q的对数概率,P的概率
log_Q = F.log_softmax(P, dim=-1)
_P = F.softmax(Q, dim=-1)
kl_sum = F.kl_div(log_Q, _P, reduction='sum')
print("SUM:", kl_sum)
-输出如下:
tensor([0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.2500, 0.0000]) tensor([0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000])
SUM: tensor(0.2231)
6 KL散度在R- Drop中的应用
6.1 什么是Dropout?
- 下面这篇文章我已经详细介绍过了,感兴趣的小伙伴可以移步下方链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42521185/article/details/124359544
-
Dropout的使用场景一般是神经元较多的神经网络,因为神经元较多可能会使得预测结果过拟合,采用Dropout随机丢弃一些神经元,可以很好的处理这个问题。 -
但是,
Dropout的缺点也很明显:dropout是随机丢弃,所以训练和预测阶段使用的神经网络不同!
6.2 引入 R-drop
- step1:首先计算
L
L
K
L_{LK}
LLK。
不同模型训练经过不同的dropout可能会产生较大的差异,而我们这里通过KL散度将这些差异缩小,从而能够达到预测较准的情况。
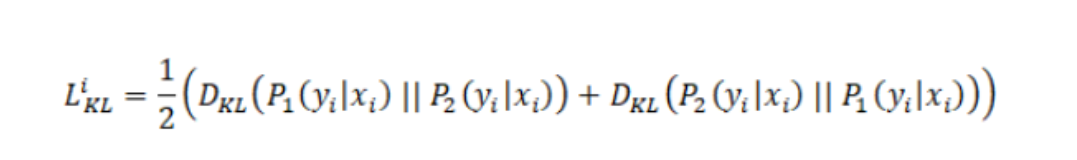
- step2:新的损失函数

6.3 在R-Drop的代码
from tensorflow.keras.losses import kullback_leibler_divergence as kld
def categorical_crossentropy_with_rdrop(y_true, y_pred,alpha=1):
"""配合上述生成器的R-Drop Loss
其实loss_kl的除以4,是为了在数量上对齐公式描述结果。
"""
loss_ce = K.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(y_true, y_pred) # 原来的loss
#这里调用K.Sparse,一部分是常规的交叉熵
loss_kl = kld(y_pred[::2], y_pred[1::2]) + kld(y_pred[1::2], y_pred[::2])
#另一部分是两个模型的对称KL散度
return K.mean(loss_ce) + K.mean(loss_kl) / 4 * alpha
- step1 首先调用交叉熵损失函数。
loss_ce = K.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(y_true,y_pred)
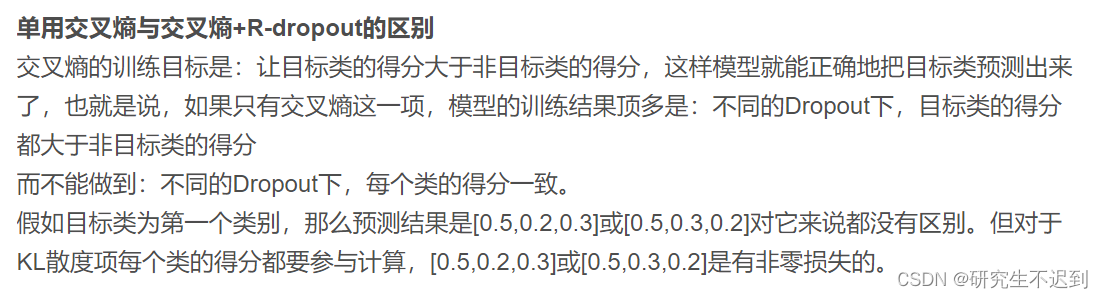
- step2 然后调用KL散度的内容
这里参考“唐僧爱吃唐僧肉的解释”

- 本研究生已疲惫了…

























 2162
2162

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








