考虑从基站 (BS) 到两个用户的下行链路传输,d1和d2表示它们与 BS 的距离。
BS 有两个不同的消息X1给用户 1(远用户),以及X2给用户 2(近用户)。 在 NOMA 中,为了促进用户的公平性,给远方用户更多的权重,给近方用户更少的权重。那是,α1>α2个. H1和H2分别表示基站到远端用户和近端用户的信道。
BS 发送的信号为:
x =√P(√α1*X1+√α2*X2)
过信道传播后在远用户处接收
y1=h1x+w1

直接解码将X2将被视为干扰。远用户的信噪比为

可达到的数据速率是
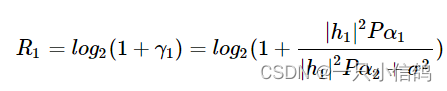
远用户接受到的是
y2=h2x+w2

用户 2在解码他自己的信号之前必须首先执行SIC,在 SIC 之前)的用户 2 处的信号干扰噪声比为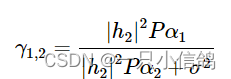
可达到的数据速率是

经过SIC后,信噪比变为: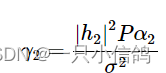
可达速率为
在不同功率下,得到容量图:
clc; clear variables; close all;
N = 10^6;
d1 = 1000; d2 = 500; %Distances of users from base station (BS)
a1 = 0.75; a2 = 0.25; %Power allocation factors
eta = 4; %Path loss exponent
%Generate rayleigh fading coefficient for both users
h1 = sqrt(d1^-eta)*(randn(1,N)+1i*randn(1,N))/sqrt(2);
h2 = sqrt(d2^-eta)*(randn(1,N)+1i*randn(1,N))/sqrt(2);
g1 = (abs(h1)).^2;
g2 = (abs(h2)).^2;
Pt = 0:2:40; %Transmit power in dBm
pt = (10^-3)*10.^(Pt/10); %Transmit power in linear scale
BW = 10^6; %System bandwidth
No = -174 + 10*log10(BW); %Noise power (dBm)
no = (10^-3)*10.^(No/10); %Noise power (linear scale)
%Generate noise samples for both users
w1 = sqrt(no)*(randn(1,N)+1i*randn(1,N))/sqrt(2);
w2 = sqrt(no)*(randn(1,N)+1i*randn(1,N))/sqrt(2);
%Generate random binary data for two users
data1 = randi([0 1],1,N); %Data bits of user 1
data2 = randi([0 1],1,N); %Data bits of user 2
%Do BPSK modulation of data
x1 = 2*data1 - 1;
x2 = 2*data2 - 1;
p = length(Pt);
for u = 1:p
%Do superposition coding
x = sqrt(pt(u))*(sqrt(a1)*x1 + sqrt(a2)*x2);
%Received signals
y1 = h1.*x + w1;
y2 = h2.*x + w2;
%Equalize
eq1 = y1./h1;
eq2 = y2./h2;
%AT USER 1--------------------
%Direct decoding of x1 from y1
x1_hat = zeros(1,N);
x1_hat(eq1>0) = 1;
%Compare decoded x1_hat with data1 to estimate BER
ber1(u) = biterr(data1,x1_hat)/N;
%----------------------------------
%AT USER 2-------------------------
%Direct decoding of x1 from y2
x12_hat = ones(1,N);
x12_hat(eq2<0) = -1;
y2_dash = eq2 - sqrt(a1*pt(u))*x12_hat;
x2_hat = zeros(1,N);
x2_hat(real(y2_dash)>0) = 1;
ber2(u) = biterr(x2_hat, data2)/N;
%-----------------------------------
gam_a = 2*((sqrt(a1*pt(u))-sqrt(a2*pt(u)))^2)*mean(g1)/no;
gam_b = 2*((sqrt(a1*pt(u))+sqrt(a2*pt(u)))^2)*mean(g1)/no;
ber_th1(u) = 0.25*(2 - sqrt(gam_a/(2+gam_a)) - sqrt(gam_b/(2+gam_b)));
gam_c = 2*a2*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
gam_d = 2*((sqrt(a2) + sqrt(a1))^2)*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
gam_e = 2*((sqrt(a2) + 2*sqrt(a1))^2)*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
gam_f = 2*((-sqrt(a2) + sqrt(a1))^2)*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
gam_g = 2*((-sqrt(a2) + 2*sqrt(a1))^2)*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
gc = (1 - sqrt(gam_c/(2+gam_c)));
gd = (1-sqrt(gam_d/(2+gam_d)));
ge = (1-sqrt(gam_e/(2+gam_e)));
gf = (1-sqrt(gam_f/(2+gam_f)));
gg = (1-sqrt(gam_g/(2+gam_g)));
ber_th2(u) = 0.5*gc - 0.25*gd + 0.25*(ge+gf-gg);
gamma1(u) = a1*pt(u)*mean(g1)/(a2*pt(u)*mean(g1) + no);
gamma2(u) = a2*pt(u)*mean(g2)/no;
end
semilogy(Pt, ber1,'r', 'linewidth',1.5); hold on; grid on;
semilogy(Pt, ber2,'b', 'linewidth',1.5);
semilogy(Pt, ber_th1, '*r','linewidth',1.5);
semilogy(Pt, ber_th2, '*b','linewidth',1.5);
xlabel('Transmit power (P in dBm)');
ylabel('BER');
legend('Sim. User 1/Far user','Sim. User 2/Near user','Theo. User 1/Far user','Theo. User 2/Near user');







 该文探讨了非正交多址接入(NOMA)在基站到两个不同距离用户的下行链路传输中的应用。通过给远方用户更多的功率权重,实现了用户公平性。文中详细描述了信号生成、BPSK调制、超级编码过程以及解码策略,包括远用户和近用户的误比特率(BER)计算。通过对不同功率下的仿真,展示了容量图和理论分析的BER比较。
该文探讨了非正交多址接入(NOMA)在基站到两个不同距离用户的下行链路传输中的应用。通过给远方用户更多的功率权重,实现了用户公平性。文中详细描述了信号生成、BPSK调制、超级编码过程以及解码策略,包括远用户和近用户的误比特率(BER)计算。通过对不同功率下的仿真,展示了容量图和理论分析的BER比较。
















 1442
1442

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








