目录
1--两数之和 (1)

讲解参考:LeetCode 最热门 100 题
主要思路:
对数组进行从小到大的排序,使用两个指针指向第一个元素和最后一个元素,即左指针指向第一个元素A[l],右指针指向最后一个元素A[R];
判断两个指针当前指向值的和,若 A[l] + A[R] == Target,则返回;
若 A[l] + A[R] < Target,表明和较小,需要左指针右移,即 l++;
若 A[l] + A[R] > Target,表明和较大,需要右指针左移,即 r--;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
std::vector<int> idx;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) idx.push_back(i);
// 通过排序数组 idx 间接排序 nums
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [idx, nums](int i, int j){
return nums[idx[i]] < nums[idx[j]];
});
std::vector<int> rec;
for(int l = 0, r = n - 1; l < n; ){
if(nums[idx[l]] + nums[idx[r]] == target){
rec.push_back(idx[l]);
rec.push_back(idx[r]);
break;
}
else if(nums[idx[l]] + nums[idx[r]] < target){
l++;
}
else{
r--;
}
}
return rec;
}
};2--两数相加 (2)
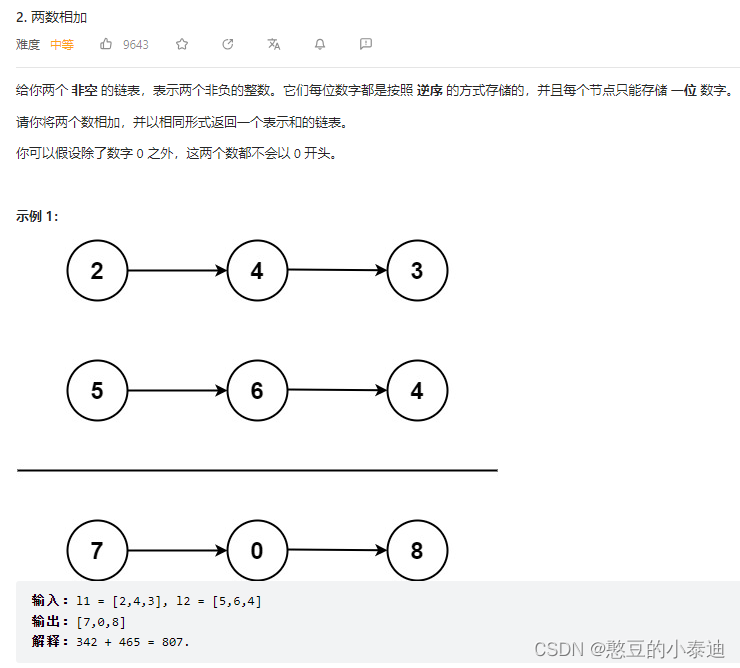
主要思路:
按位相加,用一个 carry 变量记录进位值,用一个 sum 变量记录加和值,不断遍历相加直到链表为空;
新建一个链表记录每个节点的加和值;
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode * H = new ListNode(); // 新建链表存储计算结果
ListNode * ptr = H; // 当前指针
int carry = 0; // 进位值初始化为0
while(l1 || l2 || carry){ // 链表不为空且进位值不为0
int sum = 0;
if(l1){
sum += l1->val;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if(l2){
sum += l2->val;
l2 = l2->next;
}
sum += carry; // 累计上一轮的进位值
carry = sum / 10; // 更新进位值
ListNode *node = new ListNode(); // 新建节点存储加和
node->val = sum % 10;
ptr->next = node;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return H->next; // 返回不带头结点的链表
}
};3--无重复字符的最长子串 (3)
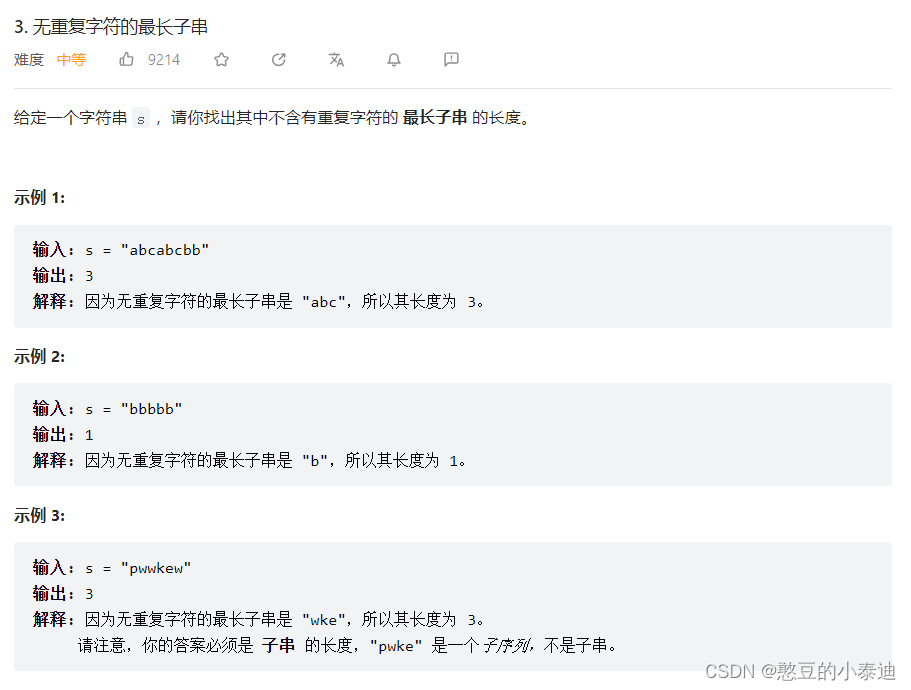
主要思路:
基于滑动窗口和哈希表,用一个滑动窗口遍历字符串的字符,确保滑动窗口内的所有字符都是不重复的,当滑动字符不断扩大遇到重复字符时,将左指针右移,直到没有重复字符,这时比较滑动窗口的长度和最大长度的值,更新最大长度;
用哈希表记录滑动窗口内一个字符出现的次数,当新字符进入时,新字符对应的出现次数加1,当滑动窗口离开字符时,字符对应的出现次数减1;
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int len = s.length(); // 字符串的长度
int l = 0; // 滑动窗口的左指针
std::unordered_map<char, int> count; // 记录当前滑动窗口 char 字符对应的个数(出现的次数)
int max_len = 0; // 返回的最大长度
for(int r = 0; r < len; r++){ // r表示滑动窗口的右指针
count[s[r]]++; // s[r]字符对应的数目加1
while(count[s[r]] > 1){ // 滑动窗口内出现重复字符
count[s[l]]--; // 左指针准备右移,先将当前左指针对应的字符数量减1
l++; // 左指针右移
}
max_len = std::max(max_len, r - l + 1);
}
return max_len;
}
};4--寻找两个正序数组的中位数 (4)
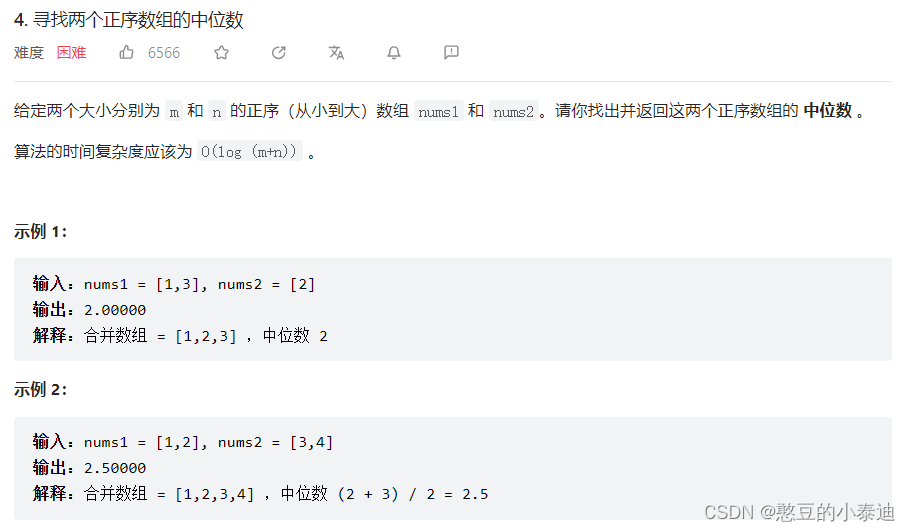
主要思路:二分递归,视频讲解参考
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
int findKth(std::vector<int>& nums1, int sta, std::vector<int>& nums2, int stb, int kth){
// 起始位置超出数组长度,直接返回另外一个数组的位置
if (sta >= nums1.size()) return nums2[stb + kth - 1];
if (stb >= nums2.size()) return nums1[sta + kth - 1];
if (kth == 1) return std::min(nums1[sta], nums2[stb]); // 递归到 k = 1
int h = kth / 2;
int vala = nums1.size() - sta >= h? nums1[sta + h - 1] : nums1.back();
int counta = nums1.size() - sta >= h ? h : nums1.size() - sta;
int valb = nums2.size() - stb >= h? nums2[stb + h - 1] : nums2.back();
int countb = nums2.size() - stb >= h ? h : nums2.size() - stb;
if(vala <= valb){
return findKth(nums1, sta + counta, nums2, stb, kth - counta);
}
return findKth(nums1, sta, nums2, stb + countb, kth - countb);
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(std::vector<int>& nums1, std::vector<int>& nums2) {
int n = nums1.size();
int m = nums2.size();
int t = n + m; // 总长度
// 无论是奇数还是偶数,中位数都是以下索引(奇数的 id0 和 id1 相同)
int id0 = (t + 1) / 2;
int id1 = (t + 2) / 2;
int val0 = findKth(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, id0); // 寻找第 id0 位对应的数值,第1次左起点从0开始
int val1 = findKth(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, id1); // 寻找第 id1 位对应的数值,第1次左起点从0开始
return (val0 + val1) / 2.0;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::vector<int> nums1 = {1, 2};
std::vector<int> nums2 = {3, 4};
Solution s1;
float middle = s1.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2);
std::cout << "middle is: " << middle << std::endl;
}主要思路:利用归并排序,将两个数组合并为一个有序的数组,最后返回其中位数;
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
void Merge_sort(std::vector<int> &nums1, std::vector<int> &nums2, std::vector<int> &nums){
int i = 0, j = 0;
while(i < nums1.size() && j < nums2.size()){
if(nums1[i] <= nums2[j]){
nums.push_back(nums1[i]);
i++;
}
else{
nums.push_back(nums2[j]);
j++;
}
}
if(i >= nums1.size()){
while(j < nums2.size()){
nums.push_back(nums2[j]);
j++;
}
}
if(j >= nums2.size()){
while(i < nums1.size()){
nums.push_back(nums1[i]);
i++;
}
}
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(std::vector<int>& nums1, std::vector<int>& nums2) {
int n = nums1.size();
int m = nums2.size();
int l = n + m;
Merge_sort(nums1, nums2, nums);
int v0 = nums[(l+1) / 2 - 1];
int v1 = nums[(l+2) / 2 - 1];
return (v0+v1) / 2.0;
}
private:
std::vector<int> nums;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::vector<int> nums1 = {1, 2};
std::vector<int> nums2 = {3, 4};
Solution s1;
float middle = s1.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2);
std::cout << "middle is: " << middle << std::endl;
}5--最长回文子串 (5)
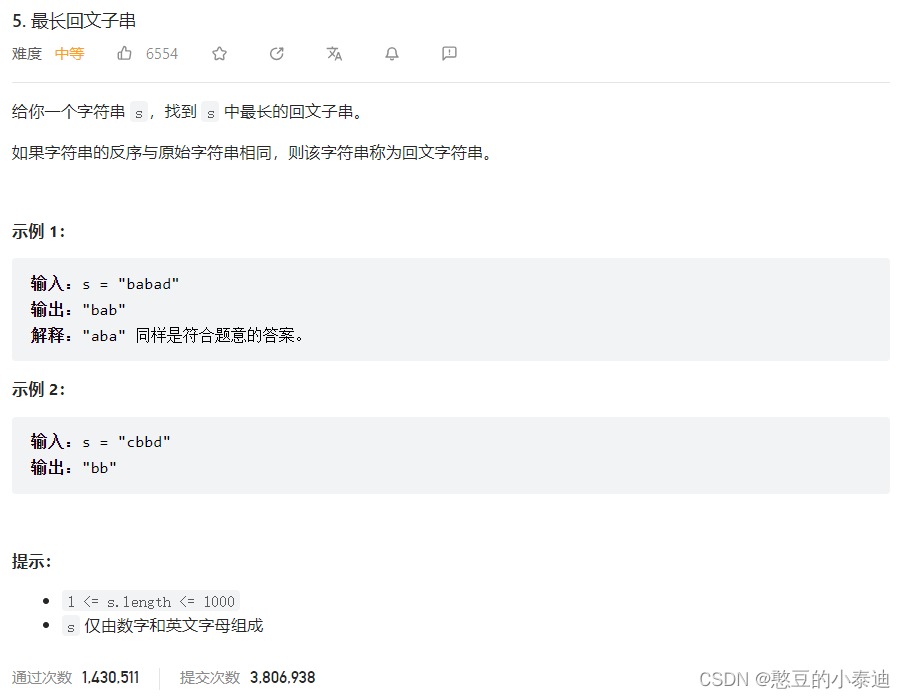
中心扩散法主要思路:
遍历字符串的每个字符,用两个指针 l 和 r 分别指向其左字符和右字符,判断左字符和右字符是否相等,不断贪心向外扩展;
需要注意区分奇数回文子串和偶数回文子串,奇数回文子串首次传入的左指针和右指针相同,都指向当前字符;
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
void search(int l, int r, std::string s){
int len = s.length();
while(l >= 0 && r < len && s[l] == s[r]){
l--;
r++;
}
if((r - l - 1) > max){
max = r - l - 1;
start = l + 1;
}
}
std::string longestPalindrome(std::string s) {
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
search(i, i, s);// 奇数回文子串
search(i, i+1, s); // 偶数回文子串
}
return s.substr(start, max);
}
private:
int max = 1;
int start = 0;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::string s = "cbbd";
Solution s1;
std::string ret = s1.longestPalindrome(s);
std::cout << ret << std::endl;
}6--正则式匹配 (10)

主要思路:
基于动态规划,具体视频讲解参考:正则表达式匹配
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(std::string s, std::string p) {
int n = s.length();
int m = p.length();
s.insert(s.begin(), '0'); // 从索引1开始比较
p.insert(p.begin(), '0');
std::vector<std::vector<bool>> f(n+1, std::vector<bool>(m+1, false));
// f[i][j] 表示s串前i个字符与p串前j个字符是否能够匹配
f[0][0] = true; // 插入的索引0字符为true
// 初始化f[0][j]的情况
for(int j = 1; j <=m; j++){
if(p[j] == '*') f[0][j] = f[0][j-1];
else if(j + 1 > m || p[j+1] != '*') break;
else f[0][j] = true; // a*可以认为是空串
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
if(p[j] == '*'){
f[i][j] = f[i][j-1];
continue;
}
if(j+1 <= m && p[j+1] == '*'){ // p[j] != '*'
// p[j]*为空串
// p[j]*为p[j]
// p[j]*为若干个p[j]
f[i][j] = f[i][j-1] ||
(f[i-1][j-1] && (p[j] == '.' || s[i] == p[j])) ||
(f[i-1][j] && (p[j] == '.' || s[i] == p[j]));
}
else{ // p[j] p[j+1]均不是*的情况
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j-1] && (p[j] == '.' || s[i] == p[j]);
}
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::string s = "aa";
std::string p = "a*";
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.isMatch(s, p);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}7--盛最多水的容器 (11)

主要思路:思路讲解参考LeetCode 最热门 100 题 -- 盛最多水的容器;
使用双指针法,左指针指向左边的容器,右指针指向右边的容器,左容器容量低则左指针自增,右容器容量低则右指针自减,直到两个指针相遇,记录并更新最大容量值,具体原理证明见上面的讲解视频;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(std::vector<int>& height) {
int n = height.size(); // 题目规定: n >= 2
int L = 0, R = n - 1;
int MaxArea = 0;
while(L != R){
MaxArea = std::max(MaxArea, (R - L) * std::min(height[L], height[R]));
if (height[L] < height[R]) L++;
else R--;
}
return MaxArea;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
Solution s1;
std::vector<int> v1 = {1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7};
int MaxArea = s1.maxArea(v1);
std::cout << "MaxArea: " << MaxArea << std::endl;
return 0;
}8--三数之和(15)

主要思路:
两数之和可以使用双指针法来求解,三数之和当确定一个数后,其余两个数的和是常数,因此也可以使用双指针法来计算。
遍历数组中的每一个数,使用双指针计算剩余两个数的和。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "algorithm"
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::vector<int>> threeSum(std::vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 先排序
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result; // 存储结果
int Size = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++){ // 遍历确定一个数
if (i > 0 && nums[i-1] == nums[i]){ // 确定的第一个数重复,直接跳过
continue;
}
int l = i + 1;
int r = Size - 1;
while(l < r){ // 双指针
if (nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r] == 0){
result.push_back({nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]});
l++;
while(nums[l] == nums[l-1] && l < r){ // 确定的第二个数重复,下移
l++;
}
}
else if(nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r] > 0){
r--;
}
else if(nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r] < 0){
l++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::vector<int> nums = {-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4}; // {-4, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2}
Solution s1;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result = s1.threeSum(nums);
int Size = result.size();
for(int i = 0; i < Size; i++){
std::cout << "[" << result[i][0] << ", " << result[i][1] << ", " << result[i][2] << "]" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}9--电话号码的字母组合(17)

主要思路:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::string> letterCombinations(std::string digits) {
std::vector<std::string> res;
if(digits.length() == 0){
return res;
}
std::vector<std::string> dict = {"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
dfs(digits, dict, "", 0, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(std::string digits, std::vector<std::string> dict, std::string t, int cur, std::vector<std::string> &res){
if (cur == digits.length()){
res.push_back(t);
return;
}
int index = digits[cur] - '0' - 2;
for(char c : dict[index]){
dfs(digits, dict, t + c, cur + 1, res);
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
std::string digits = "23";
Solution s1;
std::vector<std::string> res = s1.letterCombinations(digits);
for(std::string s : res){
std::cout << s << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}10--删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(19)
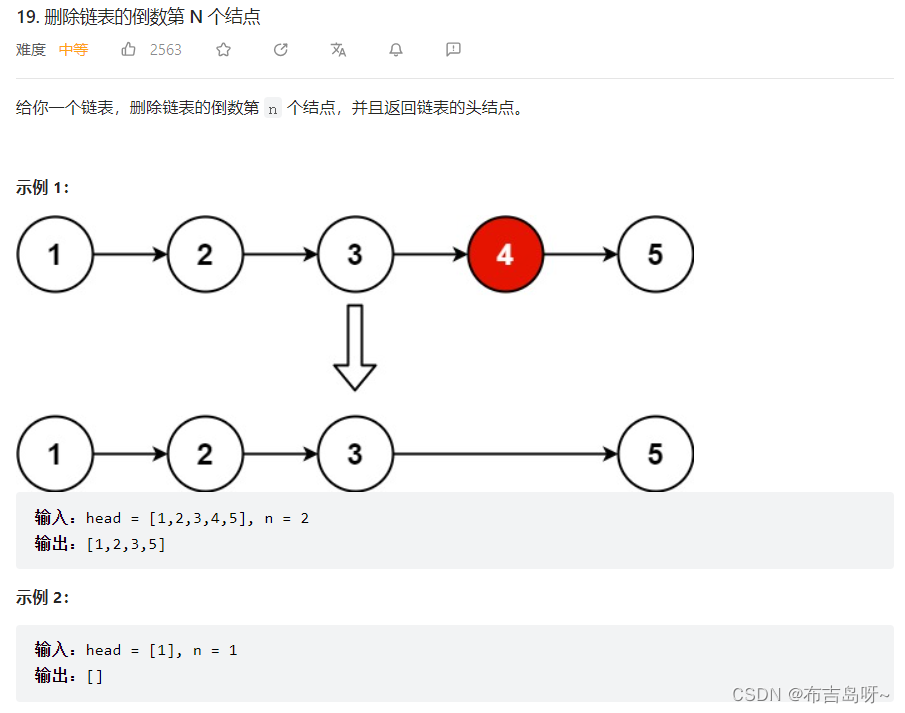
主要思路:前后指针法,先让右指针走 n 步,接着左右指针一起移动,直到右指针为空,这时右指针指向末尾,左右指针的间距为 n,则左指针指向倒数第 n 个结点;
#include <iostream>
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (head == nullptr){
return nullptr;
}
ListNode* Head = new ListNode(); // 头节点,指向第一个数据结点
Head->next = head;
ListNode* left = head;
ListNode* right = head;
ListNode* pre = Head; // 前置指针,指向左指针前一个结点
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ // 右指针先移动 n 步
right = right->next;
}
while(right != nullptr){ // 左右指针一起移动,间距保持在n
right = right->next;
left = left->next;
pre = pre->next;
}
// 删除左指针指向的结点
pre->next = left->next;
return Head->next; // 返回不带头节点的链表
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
ListNode *Node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode *Node2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode *Node3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode *Node4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode *Node5 = new ListNode(5);
Node1->next = Node2;
Node2->next = Node3;
Node3->next = Node4;
Node4->next = Node5;
Solution s1;
ListNode* Node = s1.removeNthFromEnd(Node1, 2);
ListNode* tmp = Node;
while(tmp != nullptr){
std::cout << tmp->val << std::endl;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return 0;
}





















 162
162











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








