前言
TensorFlow是一个面向所有开发人员的开源机器学习框架。 它用于实现机器学习和深度学习应用程序。为了开发和研究有关人工智能,Google团队创建了TensorFlow。 TensorFlow是使用Python编程语言设计的,因此它是一个易于理解的框架。
Tensorflow Tensor的通道排序:[batch, height, width, channel]
1.官方Demo的项目目录
2.模型
代码:
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model
class MyModel(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu') #卷积层:卷积核的个数为32,卷积核的大小为3*3,stride默认为1,激活函数为relu
self.flatten = Flatten()
self.d1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')#全连接层:结点个数为128
self.d2 = Dense(10, activation='softmax')
def call(self, x, **kwargs): #网络的正向传播过程
x = self.conv1(x) # input[batch, 28, 28, 1] output[batch, 26, 26, 32]
x = self.flatten(x) # output [batch, 21632]
x = self.d1(x) # output [batch, 128]
return self.d2(x) # output [batch, 10]
3.训练
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
from model import MyModel
def main():
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist #一个手写数据集
# download and load data
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# Add a channels dimension
#载入的手写数据图片只有宽度+高度信息,故再添加一个深度信息
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
# create data generator
#载入数据的方式是将图像和它所对应的标签以一个元组的形式传入from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(32)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(32)
# create model
model = MyModel()
# define loss
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy()
# define optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
# define train_loss and train_accuracy
train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
# define train_loss and train_accuracy
test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
# define train function including calculating loss, applying gradient and calculating accuracy
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(images)
loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
train_loss(loss)
train_accuracy(labels, predictions)
# define test function including calculating loss and calculating accuracy
@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):
predictions = model(images)
t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
test_loss(t_loss)
test_accuracy(labels, predictions)
EPOCHS = 5
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
train_loss.reset_states() # clear history info
train_accuracy.reset_states() # clear history info
test_loss.reset_states() # clear history info
test_accuracy.reset_states() # clear history info
for images, labels in train_ds:
train_step(images, labels)
for test_images, test_labels in test_ds:
test_step(test_images, test_labels)
template = 'Epoch {}, Loss: {}, Accuracy: {}, Test Loss: {}, Test Accuracy: {}'
print(template.format(epoch + 1,
train_loss.result(),
train_accuracy.result() * 100,
test_loss.result(),
test_accuracy.result() * 100))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
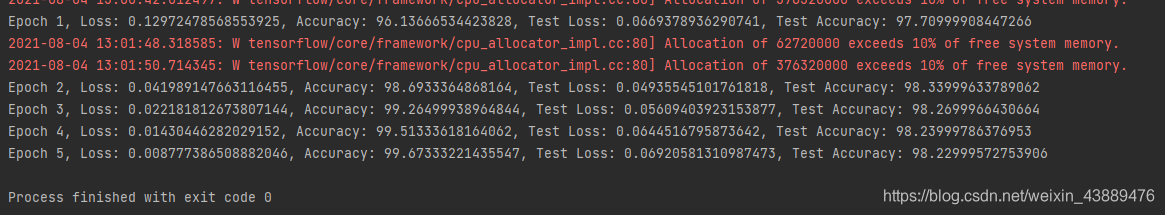
运行结果:






















 557
557











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








