1. 引入高阶退化过程和sinc滤波器

生成各种模糊核,以及sinc滤波器
- 模糊核用于一阶和二阶退化过程中的blur操作
- sinc滤波器用于二阶退化过程最后,为了模拟常见的振铃和过冲伪影。
文件位置 “basicsr/data/realesrgan_dataset.py”
# ------------------------ Generate kernels (used in the first degradation) 一阶退化过程的模糊核------------------------ #
kernel_size = random.choice(self.kernel_range) # 从7到21的奇数中,随机选取一个作为核的尺寸
# ------使用sic滤波器------
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['sinc_prob']: # sinc_prob:0.1 kernel_range:从(0, 1)的均匀分布中随机取样
# this sinc filter setting is for kernels ranging from [7, 21]
if kernel_size < 13: # 根据sinc核的大小,选择不同的参数ω
omega_c = np.random.uniform(np.pi / 3, np.pi)
else:
omega_c = np.random.uniform(np.pi / 5, np.pi)
# 生成sinc滤波器
kernel = circular_lowpass_kernel(omega_c, kernel_size, pad_to=False)
else:
# ------使用其他的模糊算法:iso/aniso:各向同性/异性、generalized_iso/generalized_aniso:广义各向同性/异性、plateau_iso/plateau_aniso平台各向同性/异性------
kernel = random_mixed_kernels(
self.kernel_list,
self.kernel_prob,
kernel_size,
self.blur_sigma,
self.blur_sigma, [-math.pi, math.pi],
self.betag_range,
self.betap_range,
noise_range=None)
# pad kernel 为了保证模糊核的尺寸为固定的21*21
pad_size = (21 - kernel_size) // 2
kernel = np.pad(kernel, ((pad_size, pad_size), (pad_size, pad_size)))
# ------------------------ Generate kernels (used in the second degradation) 二阶退化过程的模糊核------------------------ #
kernel_size = random.choice(self.kernel_range)
# ------使用sic滤波器------
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['sinc_prob2']: # sinc_prob2: 0.1
if kernel_size < 13:
omega_c = np.random.uniform(np.pi / 3, np.pi)
else:
omega_c = np.random.uniform(np.pi / 5, np.pi)
kernel2 = circular_lowpass_kernel(omega_c, kernel_size, pad_to=False)
else: # ------使用其他的模糊算法:iso/aniso:各向同性/异性、generalized_iso/generalized_aniso:广义各向同性/异性、plateau_iso/plateau_aniso平台各向同性/异性------
kernel2 = random_mixed_kernels(
self.kernel_list2,
self.kernel_prob2,
kernel_size,
self.blur_sigma2,
self.blur_sigma2, [-math.pi, math.pi],
self.betag_range2,
self.betap_range2,
noise_range=None)
# pad kernel
pad_size = (21 - kernel_size) // 2
kernel2 = np.pad(kernel2, ((pad_size, pad_size), (pad_size, pad_size))) # 最终blur核尺寸为21*21
# ------------------------------------- the final sinc kernel (最终用于模拟振铃伪影核过冲伪影的sinc滤波器)------------------------------------- #
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['final_sinc_prob']: # final_sinc_prob:0.8
kernel_size = random.choice(self.kernel_range)
omega_c = np.random.uniform(np.pi / 3, np.pi)
sinc_kernel = circular_lowpass_kernel(omega_c, kernel_size, pad_to=21) # 最终sinc滤波器尺寸为21*21
sinc_kernel = torch.FloatTensor(sinc_kernel)
else:
sinc_kernel = self.pulse_tensor # 一个全为1的卷积核,对图像无影响
# BGR to RGB, HWC to CHW, numpy to tensor 将数据转换为张量tensor
img_gt = img2tensor([img_gt], bgr2rgb=True, float32=True)[0]
kernel = torch.FloatTensor(kernel)
kernel2 = torch.FloatTensor(kernel2)
return_d = {'gt': img_gt, 'kernel1': kernel, 'kernel2': kernel2, 'sinc_kernel': sinc_kernel, 'gt_path': gt_path}
return return_d
结果返回一字典dict,其中包含
{
'gt': img_gt, # ground truth图像对应的张量tensor[c, h, w]
'kernel1': kernel, # 用于一阶退化过程的模糊核
'kernel2': kernel2, # 用于二阶退化过程的模糊核
'sinc_kernel': sinc_kernel, # 用于最终模拟振铃伪影和过冲伪影的sinc滤波器
'gt_path': gt_path # ground truth图像的存放路径
}
具体的一阶、二阶退化过程
文件位置 “basicsr/models/realesrgan_model.py”
def feed_data(self, data):
"""Accept data from dataloader, and then add two-order degradations to obtain LQ images.
从dataloader中接受数据,然后添加二阶退化过程去获取 LQ 图像。
"""
if self.is_train and self.opt.get('high_order_degradation', True):
# training data synthesis
self.gt = data['gt'].to(self.device)
self.gt_usm = self.usm_sharpener(self.gt)
self.kernel1 = data['kernel1'].to(self.device)
self.kernel2 = data['kernel2'].to(self.device)
self.sinc_kernel = data['sinc_kernel'].to(self.device)
ori_h, ori_w = self.gt.size()[2:4]
# ----------------------- The first degradation process ----------------------- #
# blur 公式(1)中的模糊操作
out = filter2D(self.gt_usm, self.kernel1) # 对GT图像先进锐化操作,然后与模糊核做卷积运算
# random resize 公式(1)中的缩放操作
updown_type = random.choices(['up', 'down', 'keep'], self.opt['resize_prob'])[0] # resize_prob: [0.2, 0.7, 0.1]
if updown_type == 'up': # 如果r是上采样,则放大比例为:[1, 1.5]的均匀分布
scale = np.random.uniform(1, self.opt['resize_range'][1]) # resize_range: [0.15, 1.5]
elif updown_type == 'down': # 如果r是下采样,则缩放比例为:[0.15, 1]的均匀分布
scale = np.random.uniform(self.opt['resize_range'][0], 1)
else:
scale = 1
mode = random.choice(['area', 'bilinear', 'bicubic']) # 下采样操作的三种算法
out = F.interpolate(out, scale_factor=scale, mode=mode)
# add noise # 公式(1)中的添加噪声操作
gray_noise_prob = self.opt['gray_noise_prob']
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['gaussian_noise_prob']: # gaussian_noise_prob: 0.5
out = random_add_gaussian_noise_pt( # 使用高斯噪声
out, sigma_range=self.opt['noise_range'], clip=True, rounds=False, gray_prob=gray_noise_prob)
else:
out = random_add_poisson_noise_pt( # 使用泊松噪声
out,
scale_range=self.opt['poisson_scale_range'],
gray_prob=gray_noise_prob, # gray_noise_prob: 0.4 灰度噪声默认40%, 颜色噪声为60%
clip=True,
rounds=False)
# JPEG compression # 公式(1)中的JPEG压缩操作
jpeg_p = out.new_zeros(out.size(0)).uniform_(*self.opt['jpeg_range'])
# torch.clamp(): 将输入input张量每个元素的范围限制到区间 [min,max],返回结果到一个新张量。
out = torch.clamp(out, 0, 1) # clamp to [0, 1], otherwise JPEGer will result in unpleasant artifacts
out = self.jpeger(out, quality=jpeg_p)
# ----------------------- The second degradation process ----------------------- #
# blur 模糊
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['second_blur_prob']: # second_blur_prob: 0.8
out = filter2D(out, self.kernel2)
# random resize 下采样
updown_type = random.choices(['up', 'down', 'keep'], self.opt['resize_prob2'])[0] # resize_prob2: [0.3, 0.4, 0.3]
if updown_type == 'up': # 上采样: [1, 1,2]
scale = np.random.uniform(1, self.opt['resize_range2'][1]) # resize_range2: [0.3, 1.2]
elif updown_type == 'down': # 下采样: [0.3, 1]
scale = np.random.uniform(self.opt['resize_range2'][0], 1)
else:
scale = 1
mode = random.choice(['area', 'bilinear', 'bicubic'])
out = F.interpolate(
out, size=(int(ori_h / self.opt['scale'] * scale), int(ori_w / self.opt['scale'] * scale)), mode=mode)
# add noise 噪声
gray_noise_prob = self.opt['gray_noise_prob2'] # gaussian_noise_prob2: 0.5
if np.random.uniform() < self.opt['gaussian_noise_prob2']:
out = random_add_gaussian_noise_pt(
out, sigma_range=self.opt['noise_range2'], clip=True, rounds=False, gray_prob=gray_noise_prob)
else:
out = random_add_poisson_noise_pt(
out,
scale_range=self.opt['poisson_scale_range2'],
gray_prob=gray_noise_prob,
clip=True,
rounds=False)
# JPEG compression + the final sinc filter JPEG压缩+sinc滤波器
# We also need to resize images to desired sizes. We group [resize back + sinc filter] together
# as one operation.
# We consider two orders:
# 1. [resize back + sinc filter] + JPEG compression
# 2. JPEG compression + [resize back + sinc filter]
# Empirically, we find other combinations (sinc + JPEG + Resize) will introduce twisted lines.
# 我们发现其他组合(sinc + JPEG + Resize)会引入扭曲线。
if np.random.uniform() < 0.5:
# resize back + the final sinc filter
mode = random.choice(['area', 'bilinear', 'bicubic'])
out = F.interpolate(out, size=(ori_h // self.opt['scale'], ori_w // self.opt['scale']), mode=mode)
out = filter2D(out, self.sinc_kernel)
# JPEG compression
jpeg_p = out.new_zeros(out.size(0)).uniform_(*self.opt['jpeg_range2'])
out = torch.clamp(out, 0, 1)
out = self.jpeger(out, quality=jpeg_p)
else:
# JPEG compression
jpeg_p = out.new_zeros(out.size(0)).uniform_(*self.opt['jpeg_range2'])
out = torch.clamp(out, 0, 1)
out = self.jpeger(out, quality=jpeg_p)
# resize back + the final sinc filter
mode = random.choice(['area', 'bilinear', 'bicubic'])
out = F.interpolate(out, size=(ori_h // self.opt['scale'], ori_w // self.opt['scale']), mode=mode)
out = filter2D(out, self.sinc_kernel)
# clamp and round #将图像的像素值限制在[0, 1]的范围内,同时进行四舍五入处理
self.lq = torch.clamp((out * 255.0).round(), 0, 255) / 255.
# random crop 随机裁剪给定的高分辨率图像和低分辨率图像,使它们具有相同的裁剪区域
gt_size = self.opt['gt_size']
(self.gt, self.gt_usm), self.lq = paired_random_crop([self.gt, self.gt_usm], self.lq, gt_size,
self.opt['scale'])
# training pair pool
self._dequeue_and_enqueue()
# sharpen self.gt again, as we have changed the self.gt with self._dequeue_and_enqueue
self.gt_usm = self.usm_sharpener(self.gt)
self.lq = self.lq.contiguous() # for the warning: grad and param do not obey the gradient layout contract
else:
# for paired training or validation
self.lq = data['lq'].to(self.device)
if 'gt' in data:
self.gt = data['gt'].to(self.device)
self.gt_usm = self.usm_sharpener(self.gt)
2. 具有SN(光谱归一化)的U-Net鉴别器


文件位置 “basicsr/archs/discriminator_arch.py”
class UNetDiscriminatorSN(nn.Module):
"""Defines a U-Net discriminator with spectral normalization (SN)
具有SN光谱归一化的U-Net判别器设计
It is used in Real-ESRGAN: Training Real-World Blind Super-Resolution with Pure Synthetic Data.
Arg:
num_in_ch (int): Channel number of inputs. Default: 3. 输入通道数,默认3
num_feat (int): Channel number of base intermediate features. Default: 64. 中间特征的通道数,默认是64
skip_connection (bool): Whether to use skip connections between U-Net. Default: True. 是否使用跳跃连接
"""
def __init__(self, num_in_ch, num_feat=64, skip_connection=True):
super(UNetDiscriminatorSN, self).__init__()
self.skip_connection = skip_connection
norm = spectral_norm
# the first convolution (1次卷积操作)
self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(num_in_ch, num_feat, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# downsample (3次下采样操作)
self.conv1 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)) # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 128, h//2, w//2]
self.conv2 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 2, num_feat * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)) # [n, 128, h//2, w//2] --> [n, 256, h//4, w//4]
self.conv3 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 4, num_feat * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)) # [n, 256, h//4, w//4] --> [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
# upsample (3次上采样操作)
self.conv4 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 8, num_feat * 4, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)) # 512 --> 256
self.conv5 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 4, num_feat * 2, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)) # 256 --> 128
self.conv6 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat * 2, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)) # 128 --> 64
# extra convolutions
self.conv7 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv8 = norm(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))
self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, 1, 3, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x): # x[n, 3, h, w]
# downsample
x0 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv0(x), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 3, h, w] --> [n, 64, h, w]
x1 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv1(x0), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 128, h//2, w//2]
x2 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv2(x1), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 128, h//2, w//2] --> [n, 256, h//4, w//4]
x3 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv3(x2), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 256, h//4, w//4] --> [n, 512, h//8, w//8]
# upsample
x3 = F.interpolate(x3, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8] --> [n, 512, h//4, w//4]
x4 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv4(x3), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 512, h//8, w//8] --> [n, 256, h//4, w//4]
if self.skip_connection:
x4 = x4 + x2 # [n, 256, h//4, w//4] + [n, 256, h//4, w//4] = [n, 256, h//4, w//4]
x4 = F.interpolate(x4, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # [n, 256, h//4, w//4] --> [n, 256, h//2, w//2]
x5 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv5(x4), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 256, h//2, w//2] --> [n, 128, h//2, w//2]
if self.skip_connection:
x5 = x5 + x1 # [n, 128, h//2, w//2] + [n, 128, h//2, w//2] = [n, 128, h//2, w//2]
x5 = F.interpolate(x5, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # [n, 128, h//2, w//2] --> [n, 128, h, w]
x6 = F.leaky_relu(self.conv6(x5), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 128, h, w] --> [n, 64, h, w]
if self.skip_connection:
x6 = x6 + x0 # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 64, h, w] = [n, 64, h, w]
# extra convolutions
out = F.leaky_relu(self.conv7(x6), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 64, h, w]
out = F.leaky_relu(self.conv8(out), negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 64, h, w]
out = self.conv9(out) # [n, 64, h, w] --> [n, 1, h, w]
return out
测试
img = torch.randn(32, 3, 256, 256)
net_d = UNetDiscriminatorSN(3, 64)
img_d = net_d(img)
print(img_d.shape)
# summary(net_d, (3, 256, 256), 32, device='cpu') # 使用cpu调试 (运行时间反而更快)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
summary(net_d.to(device), (3, 256, 256), 32) # 使用GPU调试
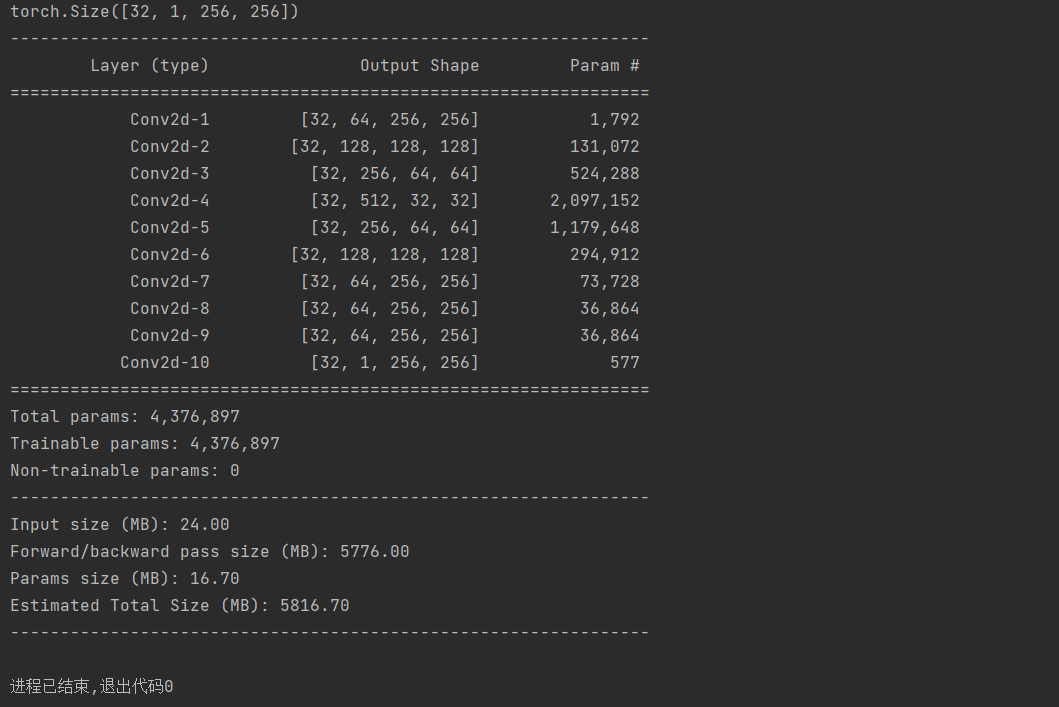
运行结果:








 本文介绍了如何使用sinc滤波器生成模糊核,模拟一阶和二阶退化过程中的图像模糊效果,以及在Real-ESRGAN中结合光谱归一化的U-Net鉴别器进行超分辨率训练。详细描述了数据合成过程中的各种降质操作,如模糊、缩放、噪声添加和JPEG压缩。
本文介绍了如何使用sinc滤波器生成模糊核,模拟一阶和二阶退化过程中的图像模糊效果,以及在Real-ESRGAN中结合光谱归一化的U-Net鉴别器进行超分辨率训练。详细描述了数据合成过程中的各种降质操作,如模糊、缩放、噪声添加和JPEG压缩。
















 7265
7265

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








