欧拉公式图解
欧拉公式
e
i
θ
=
cos
θ
+
i
sin
θ
e^{i \theta}= \cos \theta +i \sin \theta
eiθ=cosθ+isinθ
对于每个实数
θ
\theta
θ,都可以在复平面上的单位元找到对应的一点,如图:

图片来源见水印。
如果 θ \theta θ是随着时间变化的,即 θ ( t ) = w t \theta(t)=wt θ(t)=wt,其中 w w w是角频率(角速度),那么公式变为:
e i θ ( t ) = cos ( θ ( t ) ) + i sin ( θ ( t ) ) = e i w t = cos ( w t ) + i sin ( w t ) e^{i \theta(t)}=\cos (\theta(t)) +i \sin (\theta(t))= e^{i wt}=\cos(wt) +i \sin(wt) eiθ(t)=cos(θ(t))+isin(θ(t))=eiwt=cos(wt)+isin(wt)
相应的图形则是在复平面的实轴,虚轴以外再增加一个时间轴 t t t。函数随时间变化的动态图如下:
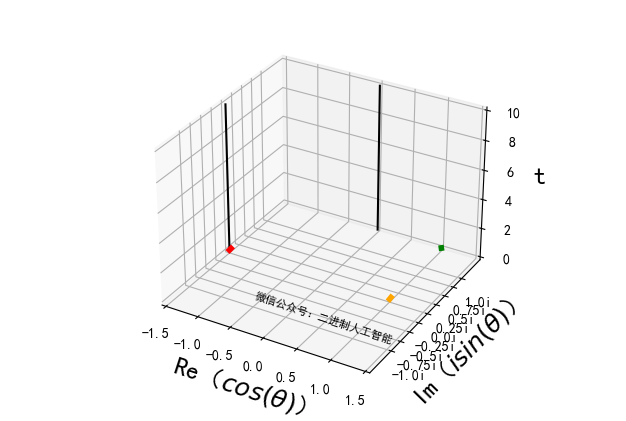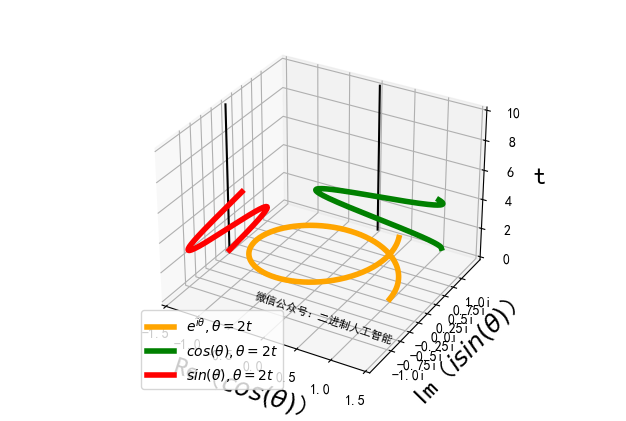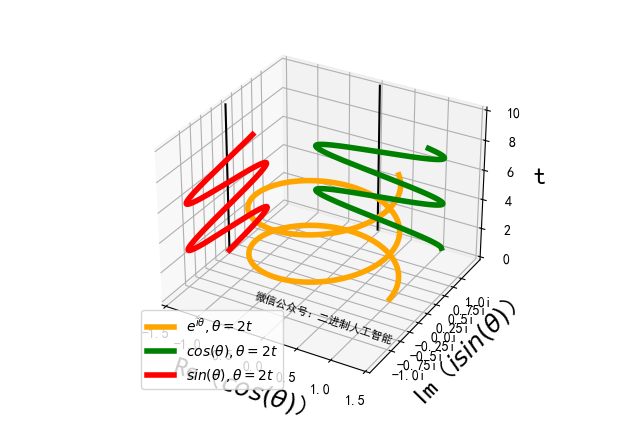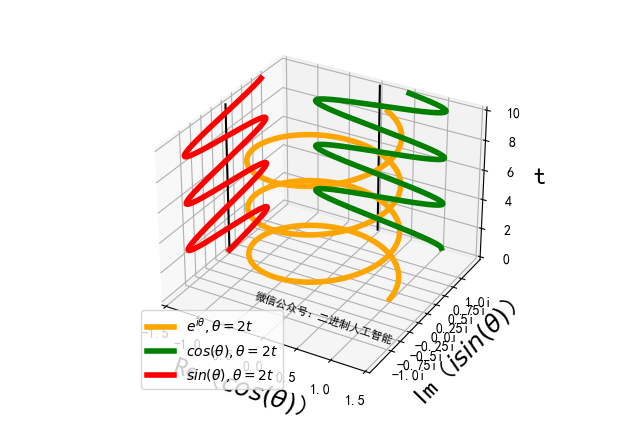
可以看到, e i θ ( t ) e^{i \theta(t)} eiθ(t)沿着实轴投影,得到 i sin θ ( t ) i\sin\theta(t) isinθ(t)的变化图;沿着虚轴投影,得到 cos θ ( t ) \cos\theta(t) cosθ(t)的变化图,沿着时间轴投影,则得到复平面上的单位圆:
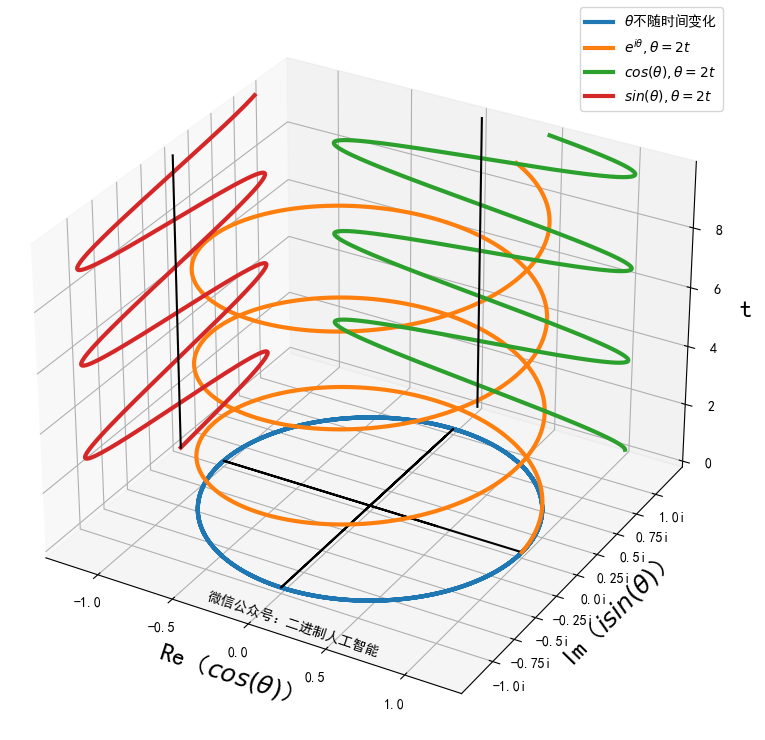
增大 w w w,对比如下:
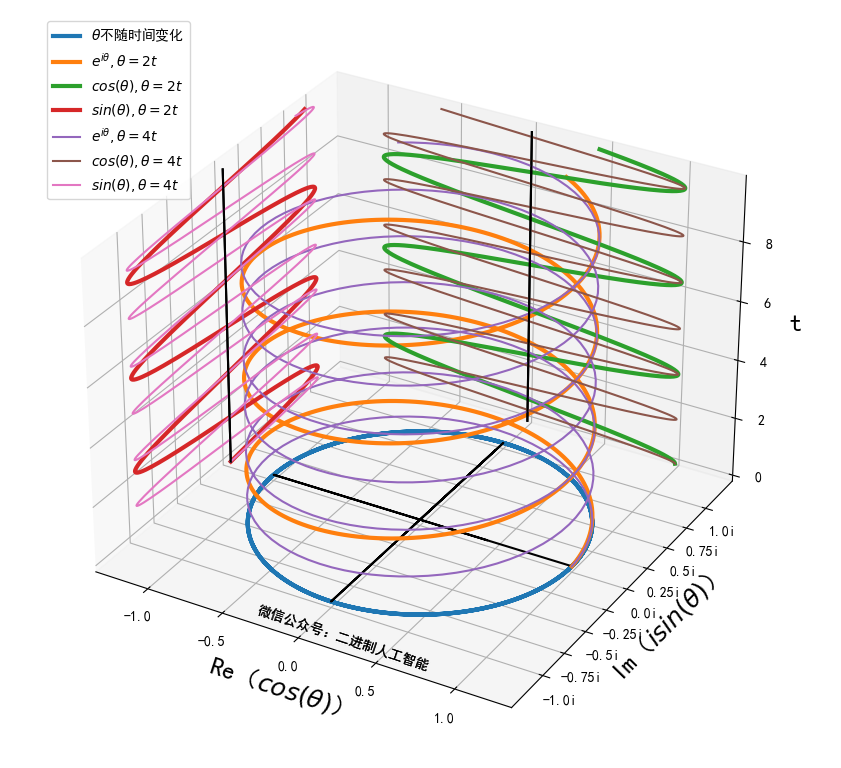
可以看到 w w w越大,单位时间内角度(相角)变化越大,转一圈所需的时间变少,即函数的周期( T = 2 π w T=\frac{2\pi}{w} T=w2π)变小。
python代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用于正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
font = {'size': 18}
lim_value = 1.3
w_list = [2, 4] # 角速度
t = np.arange(0, 10, 0.02)
width = 1.5
for i, w in enumerate(w_list):
re = np.cos(w * t)
im = np.sin(w * t)
width = 1.5
if i == 0:
width = 4 # 为了对比明显
# theta不随时间变化的情况
ax.plot(re, im, zs=0, zdir='z', label=r'$\theta$不随时间变化', linewidth=width)
ax.plot(np.zeros(np.size(im)), im, zs=0, zdir='z', color='black')
ax.plot(re, np.zeros(np.size(re)), zs=0, zdir='z', color='black')
# e^{jwt}
ax.plot(re, im, t, label=r'$e^{i\theta},\theta=%st$' % w, linewidth=width)
# cos(wt)
ax.plot(re, t, zs=lim_value, zdir='y', label=r'$cos(\theta),\theta=%st$' % w, linewidth=width)
ax.plot(np.zeros(np.size(re)), t, zs=lim_value, zdir='y', color='black')
# sin(wt)
ax.plot(im, t, zs=-lim_value, zdir='x', label=r'$sin(\theta),\theta=%st$' % w, linewidth=width)
ax.plot(np.zeros(np.size(im)), t, zs=-lim_value, zdir='x', color='black')
ax.text(0, -1.8, 0, s='微信公众号:二进制人工智能', zdir='x')
stick = np.arange(-1, 1.25, 0.25)
stick_list = ['{}i'.format(k) for k in stick]
plt.yticks(stick, stick_list)
ax.set_xlabel(r'Re($cos(\theta)$)', font)
ax.set_ylabel(r'Im($isin(\theta)$)', font)
ax.set_zlabel('t', font)
plt.xlim((-lim_value, lim_value))
plt.ylim((-lim_value, lim_value))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
角频率和角速度的区别[1]
1、定义不同
点沿着一个以弧度为单位的圆(一个圆周为 2 π 2π 2π,即: 360 ° = 2 π 360°=2π 360°=2π),在单位时间内所走的弧度即为角速度。角频率,也称圆频率,表示单位时间内变化的相角弧度值。
2、研究范围不一样
角频率是在任意的周期性运动中。角速度是在圆周运动中,或者至少是瞬时的圆周运动中。
3、物理意义不一样
角频率是单位时间内的振动次数(频率)与 2 π 2π 2π之积。点沿着一个以弧度为单位的圆,在单位时间内所走的弧度即为角速度。
4、计算方法不一样
角频率的计算公式是 w = 2 π / T w=2π/T w=2π/T。角速度的计算公式为 w = v / r w=v/r w=v/r,其中 v v v为某时刻的线速度。
欧拉公式证明[2]
有许多方式可以证明欧拉公式,这里泰勒级数进行证明。
把函数
e
x
e^x
ex、
cos
x
\cos x
cosx和
sin
x
\sin x
sinx写成泰勒级数形式:
e
x
=
1
+
x
+
x
2
2
!
+
x
3
3
!
+
⋯
e^{x}=1+x+ \frac{x^{2}}{2!}+ \frac{x^{3}}{3!}+\cdots
ex=1+x+2!x2+3!x3+⋯
cos
x
=
1
−
x
2
2
!
+
x
4
4
!
−
x
6
6
!
+
⋯
\cos x=1- \frac{x^{2}}{2!}+ \frac{x^{4}}{4!}- \frac{x^{6}}{6!}+\cdots
cosx=1−2!x2+4!x4−6!x6+⋯
sin
x
=
x
−
x
3
3
!
+
x
5
5
!
−
x
7
71
+
⋯
\sin x=x- \frac{x^{3}}{3!}+ \frac{x^{5}}{5!}- \frac{x^{7}}{71}+\cdots
sinx=x−3!x3+5!x5−71x7+⋯
将
x
=
i
θ
x=i \theta
x=iθ代入
e
x
e^x
ex,得到:
e
i
θ
=
1
+
i
θ
+
(
i
θ
)
2
2
!
+
(
i
θ
)
3
3
!
+
(
i
θ
)
4
4
!
+
(
i
θ
)
5
5
!
+
(
i
θ
)
6
6
!
+
(
i
θ
)
7
7
!
+
(
i
θ
)
8
8
!
+
⋯
e^{i \theta}=1+i \theta+ \frac{(i \theta)^{2}}{2!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{3}}{3!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{4}}{4!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{5}}{5!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{6}}{6!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{7}}{7!}+ \frac{(i \theta)^{8}}{8!}+\cdots
eiθ=1+iθ+2!(iθ)2+3!(iθ)3+4!(iθ)4+5!(iθ)5+6!(iθ)6+7!(iθ)7+8!(iθ)8+⋯
=
1
+
i
θ
−
θ
2
2
!
−
i
θ
3
3
!
+
θ
4
4
!
+
i
θ
5
5
!
−
θ
6
6
!
−
i
θ
7
7
!
+
θ
8
8
!
+
⋯
=1+i \theta- \frac{ \theta^{2}}{2!}- \frac{i \theta^{3}}{3!}+ \frac{ \theta^{4}}{4!}+ \frac{i \theta^{5}}{5!}- \frac{ \theta^{6}}{6!}- \frac{i \theta^{7}}{7!}+ \frac{ \theta^{8}}{8!}+\cdots
=1+iθ−2!θ2−3!iθ3+4!θ4+5!iθ5−6!θ6−7!iθ7+8!θ8+⋯
=
(
1
−
θ
2
2
!
+
θ
4
4
!
−
θ
6
6
!
+
θ
8
8
!
−
⋯
)
+
i
(
θ
−
θ
3
3
!
+
θ
5
5
!
−
θ
7
7
!
+
⋯
)
=(1- \frac{ \theta^{2}}{2!}+ \frac{ \theta^{4}}{4!}- \frac{ \theta^{6}}{6!}+ \frac{ \theta^{8}}{8!}- \cdots)+i( \theta- \frac{ \theta^{3}}{3!}+ \frac{ \theta^{5}}{5!}- \frac{ \theta^{7}}{7!}+ \cdots)
=(1−2!θ2+4!θ4−6!θ6+8!θ8−⋯)+i(θ−3!θ3+5!θ5−7!θ7+⋯)
=
cos
θ
+
i
sin
θ
= \cos \theta+i \sin \theta
=cosθ+isinθ
我们还可以推出:
sin θ = e i θ − e − i θ 2 i \sin \theta=\frac{e^{i \theta}-e^{-i \theta}}{2i} sinθ=2ieiθ−e−iθ
cos θ = e i θ + e − i θ 2 \cos \theta=\frac{e^{i \theta}+e^{-i \theta}}{2} cosθ=2eiθ+e−iθ
参考:
[1 https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/327045010031888125.html
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/zoujiachi666/article/details/70943355
十分感谢三连支持!最靓的公式送给最靓的你:
e i π + 1 = 0 e^{i\pi}+1=0 eiπ+1=0

























 381
381

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










