什么是谢尔宾斯基三角形
谢尔宾斯基三角形(英语:Sierpinski triangle)是一种分形,由波兰数学家谢尔宾斯基在1915年提出。它是自相似集的例子。它的豪斯多夫维是log(3)/log(2) ≈ 1.585。
形状

构造
递归
- 画一个三角形。(多数使用等边三角形)
- 沿三边中点的连线,将它分成四个小三角形。
- 对其余三个小三角形重复1。
若取一个正方形或其他形状开始,用类似的方法构作,形状也会和谢尔宾斯基三角形相近。
Chaos Game
- 用随机的方法(Chaos Game),都可得到谢尔宾斯基三角形:
- 任意取平面上三点A,B,C,组成一三角形
- 任意取三角形ABC内的一点P,画出 该点
- 画出 P和三角形其中一个顶点的中点
- 重复1
L系统
这条曲线以L系统来记述为:
变量: A , B 常数: + , - 公理: A 规则: A → B-A-B B → A+B+A A,B : 向前
-: 左转60°
+: 右转60°
这里我们使用递归方法画谢尔宾斯基三角形。
思路
1、递归
先根据自己选的三个点 ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , ( x 3 , y 3 ) (x_1, y_1),(x_2, y_2),(x_3, y_3) (x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3)画三条线,然后分别取 ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 3 , y 3 ) ; ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) ; ( x 2 , y 2 ) , ( x 3 , y 3 ) (x_1, y_1),(x_3, y_3);(x_1, y_1),(x_2, y_2);(x_2, y_2),(x_3, y_3) (x1,y1),(x3,y3);(x1,y1),(x2,y2);(x2,y2),(x3,y3)的中点为 ( x 4 , y 4 ) , ( x 5 , y 5 ) , ( x 6 , y 6 ) (x_4,y_4),(x_5,y_5),(x_6,y_6) (x4,y4),(x5,y5),(x6,y6),连接 ( x 4 , y 4 ) , ( x 5 , y 5 ) , ( x 6 , y 6 ) (x_4,y_4),(x_5,y_5),(x_6,y_6) (x4,y4),(x5,y5),(x6,y6)三点。此时除了中间的三角形外形成了三个新的三角形,分别把它们的顶点看做 ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , ( x 3 , y 3 ) (x_1, y_1),(x_2, y_2),(x_3, y_3) (x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3),再重复上面的步骤。
public void x(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int n) {
index = 0;
if (n > 0) {// 迭代条件
n--;
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x3, y3, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x3, y3);
int x4 = (int) ((x1 + x3) / 2);
int y4 = (int) ((y1 + y3) / 2);
int x5 = (int) ((x1 + x2) / 2);
int y5 = (int) ((y2 + y1) / 2);
int x6 = (int) ((x3 + x2) / 2);
int y6 = (int) ((y3 + y2) / 2);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x6, y6, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x6, y6);
// 迭代
x(x1, y1, x5, y5, x4, y4, n);
x(x5, y5, x2, y2, x6, y6, n);
x(x4, y4, x6, y6, x3, y3, n);
}
}
示意图:

2、画窗体
和普通的画窗体没什么区别。
package 谢尔宾斯基三角形;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class DrawUI {
public void intiui() {
// 创建画图板窗口
JFrame jf = new JFrame("谢尔宾斯基三角形");
// 创建监听器对象
Listener ls = new Listener();
// 设置面板属性
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
jf.setSize(800, 700); // 设置大小为800*700
jf.setLocationRelativeTo(null);// 设置居中显示
jf.setLayout(new BorderLayout());// 设置Border布局(JFrame默认为Border布局)
// 创建Panel(且Panel为流式布局)
JPanel jp1 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp2 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp3 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp4 = new JPanel();
jp1.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jp2.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jp1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(70, 100));
jp2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(40, 100));
jf.add(jp1, BorderLayout.WEST);
jf.add(jp2, BorderLayout.EAST);
jf.add(jp3, BorderLayout.CENTER);
jf.add(jp4, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
jp3.addMouseMotionListener(ls);
jp3.addMouseListener(ls);
// 用数组和循环创建按钮并添加监听器 格式:类型[] 数组名 = {"变量","变量"...};
String[] ShapeBtn = { "生成", "清屏" };
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeBtn.length; i++) {
JButton shape = new JButton(ShapeBtn[i]);
jp1.add(shape);
shape.addActionListener(ls);
}
// 创建颜色按钮
Color[] ColorBtn = { Color.BLUE, Color.GREEN, Color.RED, Color.YELLOW, Color.CYAN, Color.BLACK };
Dimension colorBtnSize = new Dimension(30, 30); // 设置颜色方块的大小
for (int i = 0; i < ColorBtn.length; i++) {
JButton color = new JButton(); // 创建颜色按钮对象
color.setBackground(ColorBtn[i]);// 设置按钮的背景颜色
color.setPreferredSize(colorBtnSize);
jp2.add(color);
color.addActionListener(ls);
}
// 设置窗口可见
jf.setVisible(true);
// 获取窗体的画布,并传给监听器对象(必须在设置窗口可见之后)
ls.g = jp3.getGraphics();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DrawUI ui = new DrawUI();
ui.intiui();
}
}
3、监听器
package 谢尔宾斯基三角形;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
public class Listener implements ActionListener, MouseListener, MouseMotionListener {
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
int x3;
int y3;
String action;
Graphics g;
int[] X = new int[3];
int[] Y = new int[3];
int index = 0;
int n = 3;
public void x(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int n) {
index = 0;
if (n > 0) {// 迭代条件
n--;
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x3, y3, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x3, y3);
int x4 = (int) ((x1 + x3) / 2);
int y4 = (int) ((y1 + y3) / 2);
int x5 = (int) ((x1 + x2) / 2);
int y5 = (int) ((y2 + y1) / 2);
int x6 = (int) ((x3 + x2) / 2);
int y6 = (int) ((y3 + y2) / 2);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x6, y6, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x6, y6);
// 迭代
x(x1, y1, x5, y5, x4, y4, n);
x(x5, y5, x2, y2, x6, y6, n);
x(x4, y4, x6, y6, x3, y3, n);
}
}
@Override
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
if (index < 3) {
// 获取三个顶点的坐标
X[index] = e.getX();
Y[index] = e.getY();
System.out.println("第" + (index + 1) + "个点");
g.fillOval(X[index] - 3, Y[index] - 3, 6, 6);
index++;
}
// 把坐标储存在x_i, y_i中
x1 = X[0];
x2 = X[1];
x3 = X[2];
y1 = Y[0];
y2 = Y[1];
y3 = Y[2];
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
action = e.getActionCommand();
if (action.equals("")) {// 颜色
// 获取事件源
Object srcObj = e.getSource();
// 获取按钮
JButton srcBtn = (JButton) srcObj;
// 获取颜色
Color color = srcBtn.getBackground();
g.setColor(color);
} else if ("清屏".equals(action)) {
g.clearRect(0, 0, 2000, 2000);
} else if (action.equals("生成")) {
x(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, n);
}
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
此时已经可以通过改变颜色和 n n n的值来画出不同颜色和迭代次数的谢尔宾斯基三角形,但是通过改变 n n n的值来改变迭代次数未免太没有交互性,因此在窗体和监听器中添加滑动条,我们就可以通过滑动滑动条的滑块来改变 n n n的值。
4、滑动条
在窗体中
// 创建滑动条
JSlider JS = new JSlider();
// 添加滑动条
jp4.add(JS);
JS.setValue(3);
JS.setSnapToTicks(true);
JS.setMaximum(6);
JS.setMinimum(0);
JS.addChangeListener(ls);
在监听器中
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
// 获取滑动条对象
Object Ob = e.getSource();
JSlider Obj = (JSlider) Ob;
n = Obj.getValue();
// 清屏
g.clearRect(0, 0, 2000, 2000);
// 画顶点
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
g.fillOval(X[i] - 3, Y[i] - 3, 6, 6);
}
// 递归
x(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, n);
}
完整代码
DrawUI.java
package 谢尔宾斯基三角形;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JSlider;
public class DrawUI {
public void intiui() {
// 创建画图板窗口
JFrame jf = new JFrame("谢尔宾斯基三角形");
// 创建监听器对象
Listener ls = new Listener();
// 设置面板属性
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
jf.setSize(800, 700); // 设置大小为800*700
jf.setLocationRelativeTo(null);// 设置居中显示
jf.setLayout(new BorderLayout());// 设置Border布局(JFrame默认为Border布局)
// 创建Panel(且Panel为流式布局)
JPanel jp1 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp2 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp3 = new JPanel();
JPanel jp4 = new JPanel();
jp1.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jp2.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jp1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(70, 100));
jp2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(40, 100));
jf.add(jp1, BorderLayout.WEST);
jf.add(jp2, BorderLayout.EAST);
jf.add(jp3, BorderLayout.CENTER);
jf.add(jp4, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
jp3.addMouseMotionListener(ls);
jp3.addMouseListener(ls);
// 创建滑动条
JSlider JS = new JSlider();
// 添加滑动条
jp4.add(JS);
JS.setValue(3);
JS.setSnapToTicks(true);
JS.setMaximum(6);
JS.setMinimum(0);
JS.addChangeListener(ls);
// 用数组和循环创建按钮并添加监听器 格式:类型[] 数组名 = {"变量","变量"...};
String[] ShapeBtn = { "生成", "清屏" };
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeBtn.length; i++) {
JButton shape = new JButton(ShapeBtn[i]);
jp1.add(shape);
shape.addActionListener(ls);
}
// 创建颜色按钮
Color[] ColorBtn = { Color.BLUE, Color.GREEN, Color.RED, Color.YELLOW, Color.CYAN, Color.BLACK };
Dimension colorBtnSize = new Dimension(30, 30); // 设置颜色方块的大小
for (int i = 0; i < ColorBtn.length; i++) {
JButton color = new JButton(); // 创建颜色按钮对象
color.setBackground(ColorBtn[i]);// 设置按钮的背景颜色
color.setPreferredSize(colorBtnSize);
jp2.add(color);
color.addActionListener(ls);
}
// 设置窗口可见
jf.setVisible(true);
// 获取窗体的画布,并传给监听器对象(必须在设置窗口可见之后)
ls.g = jp3.getGraphics();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DrawUI ui = new DrawUI();
ui.intiui();
}
}
Listener.java
package 谢尔宾斯基三角形;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JSlider;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeListener;
public class Listener implements ActionListener, MouseListener, MouseMotionListener, ChangeListener {
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
int x3;
int y3;
String action;
Graphics g;
int[] X = new int[3];
int[] Y = new int[3];
int index = 0;
int n = 3;
public void x(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int n) {
index = 0;
if (n > 0) {
n--;
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x3, y3, x2, y2);
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x3, y3);
int x4 = (int) ((x1 + x3) / 2);
int y4 = (int) ((y1 + y3) / 2);
int x5 = (int) ((x1 + x2) / 2);
int y5 = (int) ((y2 + y1) / 2);
int x6 = (int) ((x3 + x2) / 2);
int y6 = (int) ((y3 + y2) / 2);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x6, y6, x5, y5);
g.drawLine(x4, y4, x6, y6);
// 迭代
x(x1, y1, x5, y5, x4, y4, n);
x(x5, y5, x2, y2, x6, y6, n);
x(x4, y4, x6, y6, x3, y3, n);
}
}
@Override
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
if (index < 3) {
// 获取三个顶点的坐标
X[index] = e.getX();
Y[index] = e.getY();
System.out.println("第" + (index + 1) + "个点");
g.fillOval(X[index] - 3, Y[index] - 3, 6, 6);
index++;
}
// 把坐标储存在x_i, y_i中
x1 = X[0];
x2 = X[1];
x3 = X[2];
y1 = Y[0];
y2 = Y[1];
y3 = Y[2];
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
action = e.getActionCommand();
if (action.equals("")) {// 颜色
// 获取事件源
Object srcObj = e.getSource();
// 获取按钮
JButton srcBtn = (JButton) srcObj;
// 获取颜色
Color color = srcBtn.getBackground();
g.setColor(color);
} else if ("清屏".equals(action)) {
g.clearRect(0, 0, 2000, 2000);
} else if (action.equals("生成")) {
x(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, n);
}
}
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
// 获取滑动条对象
Object Ob = e.getSource();
JSlider Obj = (JSlider) Ob;
n = Obj.getValue();
// 清屏
g.clearRect(0, 0, 2000, 2000);
// 画顶点
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
g.fillOval(X[i] - 3, Y[i] - 3, 6, 6);
}
// 递归
x(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, n);
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
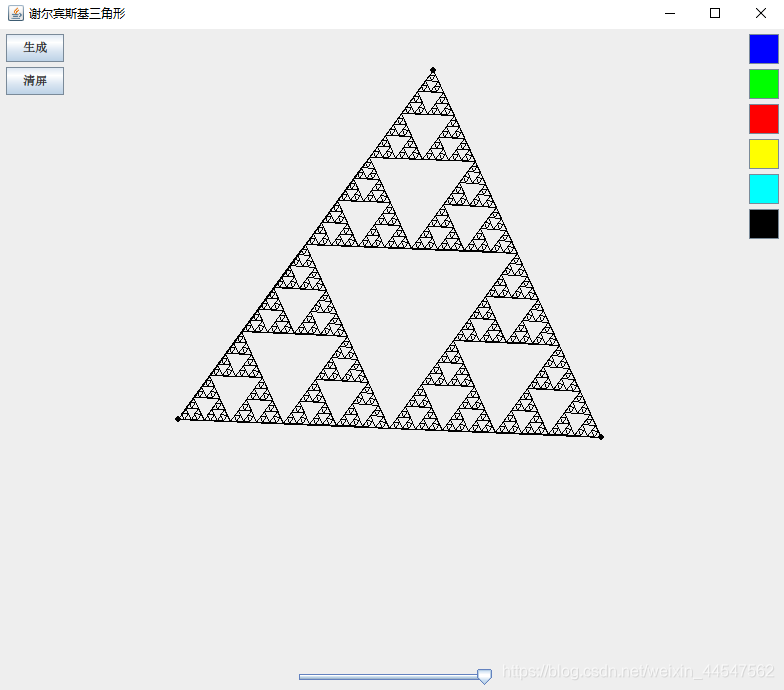
运行
- 在画板中随机选三个点。
- 点击 “生成”。
- 滑动底部的滑动条即可改变谢尔宾斯基三角形的迭代次数。
效果

滑动滑动条的滑块:
























 527
527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








