Question
A new rapid urine test was evaluated as a screening tool for Chlamydia trachomatis(沙眼衣原体) infection in men. The test was compared with the gold standard diagnostic test for chlamydia infection—the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. The rapid urine screening test was reported to have a sensitivity of 82.6% and specificity of 98.5%.
Which of the following statements, if any, are true?
提示:这题是多选题,设计灵敏度与特异度的概念
a) Diagnostic ability: The rapid urine screening test does not provide a diagnosis of chlamydia infection.
b) Definition of sensitivity: out of all of the men with a “positive” result on the rapid urine screening test, 82.6% had a diagnosis of chlamydia infection on the PCR assay.
c) Definition of sensitivity: out of all of the men with a diagnosis of chlamydia infection according to the PCR assay, 82.6% had a “positive” result on the rapid urine screening test.
d) Definition of specificity: out of all of the men without a diagnosis of chlamydia infection on the PCR assay, 98.5% had a “positive” result on the rapid urine screening test.
Answer
a, c—The rapid urine screening test can be administered to large numbers of men much quicker and more cheaply than the PCR diagnostic assay. However, unlike the PCR assay, the rapid urine screening test does not provide an accurate and reliable diagnosis of chlamydia infection. Answer a is, therefore, correct.
The purpose of rapid urine screening is to identify men in the population who are at high risk of chlamydia infection, as indicated by a “positive” result. Such individuals will then be recommended to have a PCR assay to confirm diagnosis. Time and money will be saved by not undertaking diagnostic testing with PCR assay in men for whom there is no suspicion of chlamydia infection, indicated by a “negative” (“low risk”) result on rapid urine screening.
The very nature of screening tests means that diagnosis is not always correctly predicted. In particular, a “negative” result may be obtained on rapid urine screening yet the PCR assay diagnoses chlamydia infection. Equally, a “positive” result may be obtained on rapid urine screening yet the PCR assay test does not diagnose a chlamydia infection.
Sensitivity and specificity are indices that can be used to describe the performance of rapid urine screening when identifying those men who should undergo diagnostic testing with PCR assay. To evaluate these indices, a sample of the population will undergo both the rapid urine screening test and the diagnostic PCR assay, as took place in this study.
Answer c is the correct definition of sensitivity in this instance. Sensitivity describes the accuracy of rapid urine screening at identifying those men who were diagnosed with chlamydia on PCR assay. Of the 109 men in total diagnosed by the PCR assay, 90 (82.6%) had a “positive” result on rapid urine screening. These 90 individuals were, therefore, correctly identified by the rapid urine screening test. The remaining 19 individuals were incorrectly identified by the rapid urine screening test (“negative” result), as the result disagreed with the diagnostic PCR assay.⇓
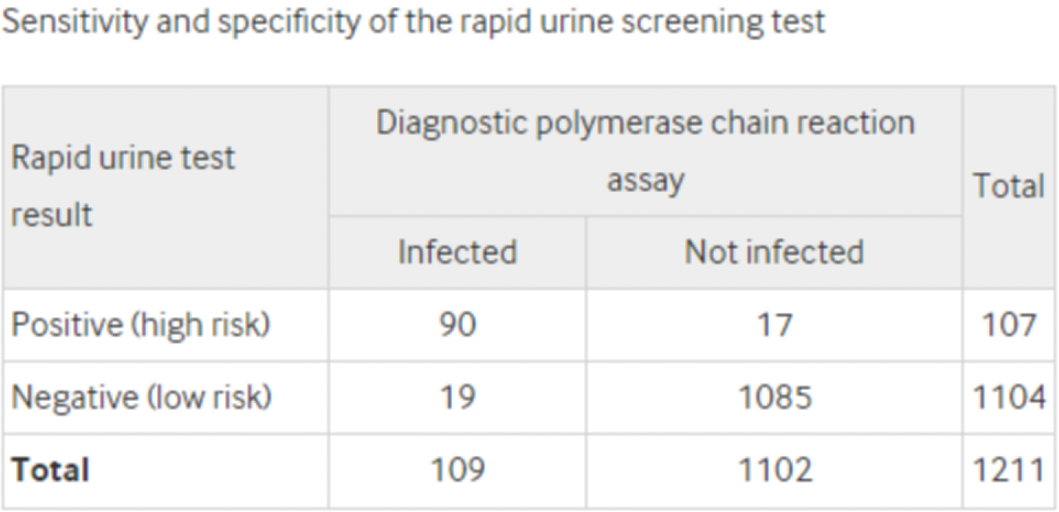
Answer b describes positive predictive value, not sensitivity. The positive predictive value reports the accuracy of a “positive” result on rapid urine screening, namely the percentage of men diagnosed with chlamydia infections on PCR assay who also have a “positive” screening result. Of the 107 men in total that had a “positive” (“high risk”) result on rapid urine screening, 90 (84.1%) had chlamydia infection according to the PCR assay. The remaining 17 (15.9%) men were incorrectly identified by the rapid urine screening test, because the result disagreed with the result of the diagnostic PCR assay.
Answer d is not the correct definition of specificity in this case. Specificity expresses the accuracy of rapid urine screening at identifying those who were not diagnosed with chlamydia on PCR assay. Of the 1102 men in total who were not diagnosed with chlamydia on the PCR assay, 1085 (98.5%) also had a negative (“low risk”) result on rapid urine screening. These 1085 individuals were correctly identified by the rapid urine test, as the result agreed with the diagnostic PCR assay.
所以答案是选择 a c
每天学习一点,你会更强大!







 一项研究比较了快速尿液筛查测试与PCR诊断法在检测男性沙眼衣原体感染中的表现,结果显示快速筛查测试的敏感性为82.6%,特异性为98.5%。然而,它并非确诊工具,而是用于识别高风险人群,后续再进行PCR确认。
一项研究比较了快速尿液筛查测试与PCR诊断法在检测男性沙眼衣原体感染中的表现,结果显示快速筛查测试的敏感性为82.6%,特异性为98.5%。然而,它并非确诊工具,而是用于识别高风险人群,后续再进行PCR确认。
















 2009
2009

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








