控制器区域网路 (Controller Area Network),允许网路上的多个微控制器或设备直接互相通讯,
且网路上不需要主机(Host)控制通讯。Canbus 具有高扩充性、高可靠度且低成本等特性,同一
个线上的装置必需有相同的 baud rate 才可通讯,其基础网路架构图如下图。
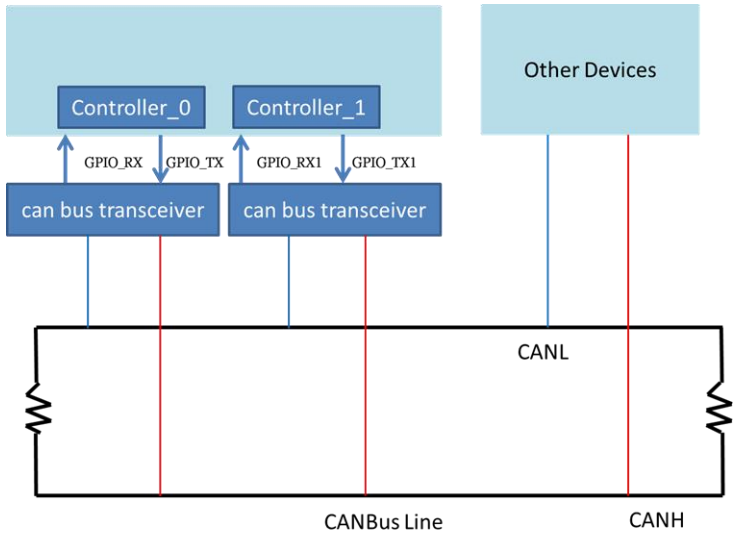
Canbus 讯号介绍:
CANBUS 在传输显性(0)讯号时,会将 CANH 端抬向 5V 高电位,将 CANL 拉向 0V 低电位。
当传输隐性(1)讯号时,并不会驱动 CANH 或者 CANL 端,如下图。

Canbus frame 介绍:
Canbus 通讯以一个 frame 为一个单位,而 CAN 2.0B 有 4 种 frame 类型。
类型 | 用途 |
资料frame | 传输的节点资料的 frame |
远端 frame(RTR) | 请求传输特定识别码的 frame |
错误 frame | 检测到错误的节点传送的 frame |
过载 frame | 资料框或远端 frame 之间插入延迟的 frame |
其中资料 frame (data frame)为使用者最需要自行设定的类型,它有两种资讯结构:
类型(IDE) | 支援 ID bits |
基本 frame 格式(STD frame) | 11 |
扩充 frame 格式(EXT frame) | 29 |
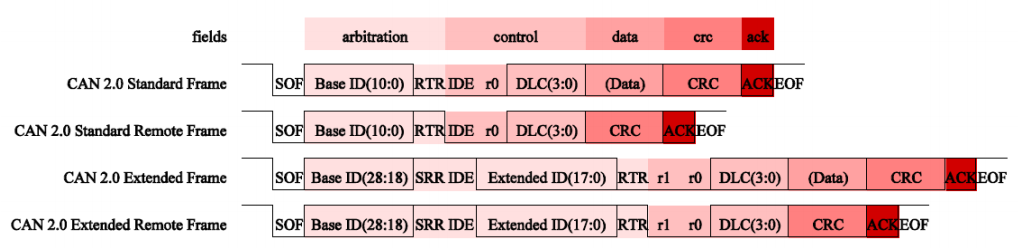
基本 frame 格式说明(CAN 2.0 standard frame):
栏位 | 位元数 | 说明 |
SOF | 1 | 表示 frame 的传输起点 |
BASE ID | 11 | 辨识码(ID),也带有传输优先级涵义 |
RTR | 1 | 远端请求 frame 设定,资料框设(0),远端请求 frame 设(1) |
IDE | 1 | 基本 frame 设(0) |
R0 | 1 | 预留位 |
DLC | 4 | 资料的位元组数 |
Data | Data | 待传输资料(长度由资料长度码 DLC 指定) |
CRC | 16 | CRC 错误检查 |
ACK | 2 | 发信端传送(1)但是任何接收端可以设(0) |
EOF | 7 | 表示 frame 结束必为(1) |
扩充 frame 格式(CAN 2.0 extended frame):
栏位 | 位元数 | 说明 |
SOF | 1 | 表示 frame 的传输起点 |
BASE ID | 11 | 辨识码(ID),也带有传输优先级涵义 |
SRR | 1 | 替代远端请求,必为(1) |
IDE | 1 | 扩充 frame 设(1) |
Extended ID | 18 | 第二部分辨识码(ID),同 BASE ID 带有传输优先级涵义 |
RTR | 1 | 远端请求 frame 设定,资料框设(0),远端请求 frame 设(1) |
R0 | 1 | 预留位 |
DLC | 4 | 资料的位元组数 |
Data | 0-64 | 待传输资料(长度由资料长度码 DLC 指定) |
CRC | 16 | CRC 错误检查 |
ACK | 2 | 发信端传送(1)但是任何接收端可以设(0) |
EOF | 7 | 表示 frame 结束必为(1) |
DLC(Data Length Code)转换表:
DLC | bytes |
0x0000 | 0 |
0x0001 | 1 |
0x0010 | 2 |
0x0011 | 3 |
0x0100 | 4 |
0x0101 | 5 |
0x0110 | 6 |
0x0111 | 7 |
0x1000 | 8 |
Canbus ID filtering 介紹:
Canbus 在传送资料的过程是类似广播的方式进行,所以在装置数量众多的时候,单一装置会收
到所有装置所传出的各种资料,但其实只要接收与它有相关的资料即可,所以在接收端就需要 ID
filter 来过滤资料,好处是可以降低装置处理资料的负担,下图为 filter 作用的示意图。



Canbus Debug 模式介紹:
IT986x支持两种Loop Back mode: internal (LBMI)和external (LBME)。两种模式都会接收到自己传输的帧,这对自检很有用。
在LBMI从CAN总线断开,txd输出被设置为隐性。输出数据流在内部反馈给输入。
在LBME中,保持与收发器的连接,传输的帧将在总线上可见。因此,在SACK=0的LBME中,帧传输有两种可能的结果:

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








