最短路径算法
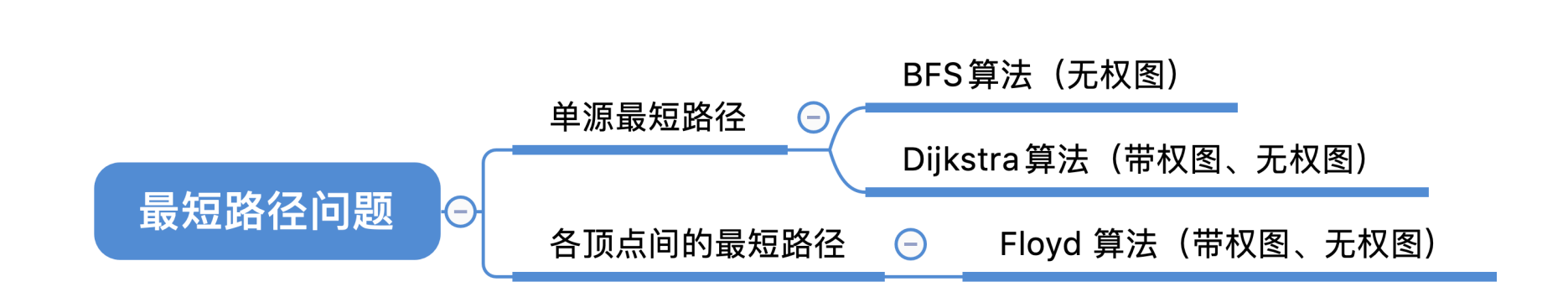
BFS 算法
怎么存储一个图?邻接矩阵 OR 邻接表
对于BFS 算法 广度优先遍历,使用邻接矩阵 邻接表 那种结构更好一点?
BFS 算法 用队列?
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits.h> // 用于定义 INT_MAX
using namespace std;
// 定义图的结构
struct Graph {
int vexnum; // 顶点数量
vector<vector<int>> adjList; // 邻接表
};
// 找到从顶点 u 到其他顶点的最短路径
void BFS_MIN_Distance(const Graph& G, int u) {
vector<int> d(G.vexnum, INT_MAX); // 初始化路径长度为无穷大
vector<int> path(G.vexnum, -1); // 最短路径从哪个顶点来
vector<bool> visited(G.vexnum, false); // 访问标记
queue<int> Q;
d[u] = 0;
visited[u] = true;
Q.push(u);
while (!Q.empty()) {
int curr = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int w : G.adjList[curr]) { // 遍历当前顶点的所有邻接点
if (!visited[w]) { // 如果顶点w尚未访问
d[w] = d[curr] + 1; // 路径长度加1
path[w] = curr; // 最短路径应该从curr到w
visited[w] = true; // 设置已访问标记
Q.push(w); // 顶点w入队
}
}
}
// 打印结果
cout << "d[]: ";
for (int dist : d) {
cout << dist << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "path[]: ";
for (int p : path) {
cout << p << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
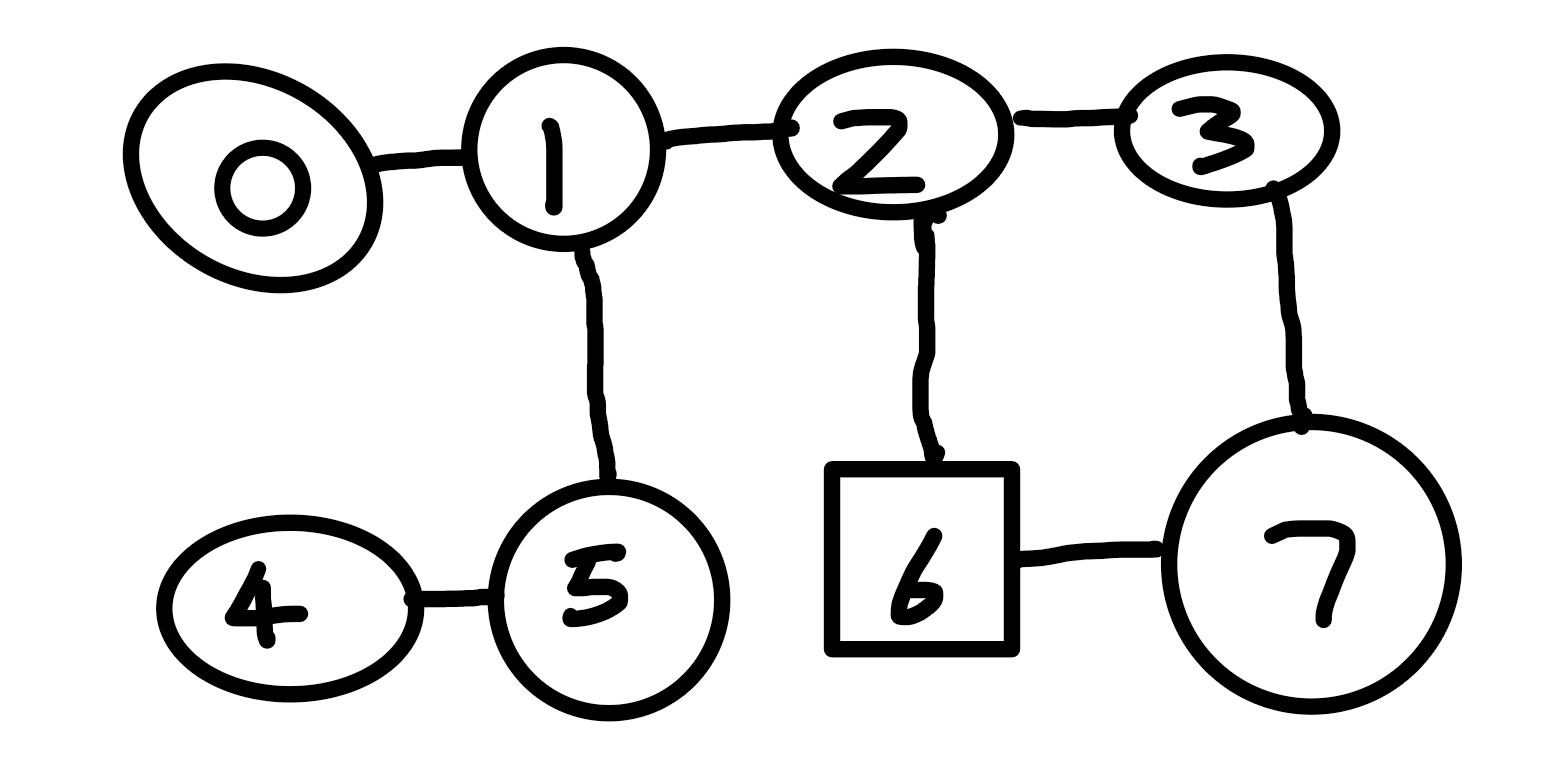
Graph G;
G.vexnum = 8; // 图有8个顶点
G.adjList = {
{1}, // 顶点0的邻接点
{0, 2, 5}, // 顶点1的邻接点
{1, 3, 6}, // 顶点2的邻接点
{2, 7}, // 顶点3的邻接点
{5}, // 顶点4的邻接点
{1, 4}, // 顶点5的邻接点
{2, 7}, // 顶点6的邻接点
{3, 6} // 顶点7的邻接点
};
int startVertex = 0; // 从顶点0开始
BFS_MIN_Distance(G, startVertex);
return 0;
}






















 3767
3767











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








