本节目标:
1、为什么要学习string类
2.标准库中的string类
3.vs和g++下string结构说明
1.为什么学习string类
1.1 c语言中的字符串
1.2string类简介
string 是一个类,类内有char *指针,通过容器方式管理字符串。使用string类型需要需要包含头文件string。
2.标准库中的string类
2.1 string类
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string;
需要注意:在使用string类时,必须包含头文件#include,以及using namespace std
2.2string 类的常用接口说明(常用的,对于一些非常用的可以去官网查找手册)
1.string类的构造函数
string常见的构造函数有:无参构造,用c_string构造string类对象,拷贝构造函数
无参构造:string()
c_string构造string类对象:string(const char *str);
拷贝构造:string(const string &str);
初始化字符串为count个c字符:string(int count,char c);代码如下所示:

2 string类对象的容量操作
string 常用的容量操作如下表所示:
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
| empty(重点) | 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| clear(重点) | 清空有效字符 |
| reserve(重点) | 为字符串预留空间** |
| resize(重点) | 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 |
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
std::string str("Test string");
std::cout << "The size of str is " << str.size() << " bytes.\n";
return 0;
}
3. clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
char c;
std::string str;
std::cout << "Please type some lines of text. Enter a dot (.) to finish:\n";
do {
c = std::cin.get();
str += c;
if (c=='\n')
{
std::cout << str;
str.clear();
}
} while (c!='.');
return 0;
}

4. reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于 string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
void TestPushBackReserve()
{
string s;
s.reserve(100);
size_t sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
cout << "making s grow:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
s.push_back('c');
if (sz != s.capacity())
{
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
}
s.clear();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
s.reserve(10);
sz = s.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed: " << sz << '\n';
}
int main()
{
TestPushBackReserve();
return 0;
} 
5. resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字 符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的 元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
// 开空间
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
// 开空间+填值初始化
//s1.resize(200);
s1.resize(200, 'x');
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.resize(20);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.resize(0);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
} 
2.3string 类对象的访问及遍历操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| operator[](重点) | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
| begin+ end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend begin | 获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下个位置迭代器 |
| 范围for | C++11支持更简洁的范围for的新遍历方式 |
1.operator[]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main()
{
std::string str("Test string");
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i)
{
std::cout << str[i];
}
return 0;
}
2.迭代器和范围for

#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::string s1("Test string");
// 迭代器
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// 写
(*it)--;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
// 读
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 范围for
// 底层替换为迭代器
//for (char& ch : s1)
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
}
cout << endl;
for (char ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}3.string类对象的修改操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符c |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
| operator+= (重点) | 在字符串后追加字符串str |
| c_str(重点) | 返回C格式字符串 |
| find + npos(重点) | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 |
push_back 尾插字符,append尾插字符串字面就能理解,其实他们都可以用+=实现,
string的连接是通过加法操作符实现的,加号两边可以随意组合string或是字符串字面量。
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//string的连接
int main()
{
string s1 = "";
string s2 = "";
cout << "请输入两个用空格间隔的字符串:" << endl;
cin >> s1 >> s2 ;
string s3 = s1 + s2 ;
cout << "字符串连接的结果为:" << s3 << endl;
for (int i = 0;i < 3;i++)
{
string s4 = "";
cout << "请输入字符串:" << endl;
cin >> s4;
s3 +=s4;
cout << "字符连接的结果是: " << s3 << endl;
}
return 0;
}字符串的查找与替换
string字符串查找有find、rfind函数。
- find函数是从左往右查找,查找成功返回第一个出现的下标,失败返回-1。
- rfind是查找最后一个出现的下标,失败返回-1。 replace函数实现字符串替换。
//find函数:从左往右查找
返回值:查找成功返回出现的位置,失败返回-1
int find(const string&str,int pos=0)const;//形参pos表示开始查找的起始位置
int find(const char *str,int pos=0)const;
int find(const char *str,int pos=0,int n)const;//从str的第pos开始的前n个字符中str出现的位置
int find(const char c,int pos=0);//查找字符c
//rfind函数:从右往左查找
int rfind(const string &str,int pos=npos);从pos位置开始查找str最后一次出现的位置
int rfind(const char *str,int pos=npos);从pos位置开始查找str最后一次出现的位置
int rfind(const char *str,int pos=pos,int n);从pos开始的前n个字符中str最后一次出现的位置
int rfind(const char c,int pos=0);//查找c最后一次出现的位置
//字符串替换
string &replace(int pos,int n,const string &s);//将字符串的第pos位置开始的n个字符替换成s
string &replace(int pos,int n,const char *s);
#include < iostream >
#include < string >
using namespace std;
void test()
{
string str = "1asd3as456asd4789asd";
int pos = str.find("asd");//查找asd第一次出现的位置
cout << "pos=" << pos << endl;
string temp = "asd";
pos = str.find(temp,7);//从第7个位置开始查找asd出现的位置
cout << "pos=" << pos << endl;
pos = str.rfind(temp);//查找最后一次出现的位置
cout << "pos=" << pos < < endl;
pos = str.rfind("asd",7,2);//从第3个位置开始往前查找,查找"asd"中的前2个字符在str中最后一次位置
cout << "pos=" << pos << endl;
//字符串替换
str.replace(1, 7, "c++");//从第一个位值开始将str的7个字符替换为c++
cout << "str=" << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
函数 功能说明
operator+ 尽量少用, 因为传值返回,导致深拷贝效率低
operator>> (重点) 输入运算符重载
operator<< (重点) 输出运算符重载
getline (重点) 获取一行字符串
relational operators (重点) 大小比较
4string的读写
利用cout可以打印string,即将string输出到标准输出端,也就是命令行窗口。类似的,c++也提供了一种方法从标准输入端,也就是键盘将数据写入string。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//string的读写
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2;
cout << "请输入用两个空格隔开的字符串!" << endl;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
return 0 ;
}
5 字符串比较
string类中字符串比较函compare数有多个重载版本,既可以和C语言风格const char *字符串进行比较,也可以和string类字符串进行比较。相等返回0,不相等返回!0值。
字符串比较:
int compare(const char *str);//相等返回0,否则返回非0值
//比较string的len个字符,从idx位置开始
int string::compare (size_type idx, size_type len, const string& str) const
//从指定位置指定长度开始比较
int string::compare (size_type idx, size_type len, const string&str, size_type str_idx, size_type str_len) const
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < string >
void test()
{
string str1 = "hello,world";
if (str1 == "hello,world")
{
cout << "[const char *]相等" << endl;
}
string str2 = "hello,world";
if (str1 == str2)
{
cout << "[string]相等" << endl;
}
if (!str1.compare("hello,world"))
{
cout << "[compare]相等" << endl;
}
//比较str1的前6个字符
int ret=str1.compare(0,6,"hello,");
cout << "ret=" << ret << endl;
//从str1的第0个开始开始取出6个字符,
//从"c++,hello,"的第4个位置开始,取出6个字符进行比较
ret = str1.compare(0, 6, "c++,hello,", 4, 6);
cout << "ret=" << ret << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
6字符串的插入与删除
string类中插入函数insert支持多种插入方式,有多个重载版本。
字符串删除可以使用erease函数实现。
c++插入:
string& insert(int pos,const char *s);//从第pos位置开始插入s
string& insert(int pos,const string &s);string &insert(int p0, const char *s, int n);//从p0位置开始插入s,插入的s连续n个字符
string &insert(int p0,const string &s, int pos, int n);//从p0位置开始插入s,插入的s从pos开始,连续n个字符string &insert(int p0, int n, char c);//从p0处插入n个字符c
c++删除字符串
string &erase(int pos,int n=npos);//从pos位置开始删除n个字符
#include < iostream >
#include < string >
using namespace std;
void test()
{
string str = "hello,";
str.insert(2,"aaa");//从第2个位置开始插入aaa
cout < < "str=" << str << endl;
str.insert(4, "1234", 1, 2);//从第4个位置插入,从"1234"的第1个位置开始,连续两个字符插入到str中
cout << "str=" << str << endl;
//字符串删除
str.erase(2,4);//从第2个位置开始,删除4个字符
cout << "str=" << str << endl;
str.erase();//清空字符串
cout < < "str=" << str <<"\t长度:"<< str.size()<<endl;
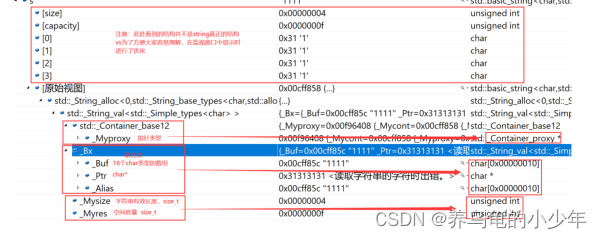
3.vs和g++下string结构说明
3.1vs下string的结构:
- 当字符串长度小于16时,使用内部固定的字符数组来存放
- 当字符串长度大于等于16时,从堆上开辟空间
union _Bxty
{ // storage for small buffer or pointer to larger one
value_type _Buf[_BUF_SIZE];
pointer _Ptr;
char _Alias[_BUF_SIZE]; // to permit aliasing
} _Bx;这种设计也是有一定道理的,大多数情况下字符串的长度都小于16,那string对象创建好之后,内 部已经有了16个字符数组的固定空间,不需要通过堆创建,效率高。 其次:还有一个size_t字段保存字符串长度,一个size_t字段保存从堆上开辟空间总的容量 最后:还有一个指针做一些其他事。 故总共占16+4+4+4=28个字节。
3.2.g++下string的结构
- 空间总大小
- 字符串有效长度
- 引用计数
struct _Rep_base
{
size_type _M_length;
size_type _M_capacity;
_Atomic_word _M_refcount;
};- 指向堆空间的指针,用来存储字符串。






















 717
717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








