文章目录
前言
我蛮喜欢这种忙碌的感觉的,碌碌无为无所事事会给我一种焦虑感,不过丢掉焦虑感的代价就是我不能花更多的时间在音乐上了,晚上回去都在和室友玩游戏,这学期开始就没有多少时间在练琴了,下学期一定要弥补上。
这一篇主要是讲一下YOLO的model脚本,这个脚本在./models/common.py路径下,包括了各种通用的网络搭建类模块,比如Conv、C3、SPP等等。
🚀YOLOv5-6.x源码分析(五)---- 模型搭建之model.py
1. 导入需要的包
# 网络模型组件
import json
import math # 数学函数模块
import platform
import warnings
from collections import OrderedDict, namedtuple
from copy import copy # 数据拷贝模块 分浅拷贝和深拷贝
from pathlib import Path # Path将str转换为Path对象 使字符串路径易于操作的模块
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import requests # Python的HTTP客户端库
import torch # pytorch深度学习框架
import torch.nn as nn # 专门为神经网络设计的模块化接口
import yaml
from PIL import Image
from torch.cuda import amp # 混合精度训练模块
from utils.dataloaders import exif_transpose, letterbox # 加载数据集
from utils.general import (LOGGER, check_requirements, check_suffix, check_version, colorstr, increment_path,
make_divisible, non_max_suppression, scale_coords, xywh2xyxy, xyxy2xywh) # 常用的工具函数
from utils.plots import Annotator, colors, save_one_box # 绘制矩形框和标注信息
from utils.torch_utils import copy_attr, time_sync # 与pytorch相关的工具函数
2. 基本组件
由yolov5s.yaml可以看到,有许多的基本组件组成了整个网络。
2.1 autopad
这个模块可以根据输入的卷积核计算卷积模块需要的pad值。用于下面的Conv类和Classify类中。主要是为了把tensor补成原来的形状。
def autopad(k, p=None): # 卷积核的kernel_size, 自动计算的需要pad值(0填充)
'''
v5中只有两种卷积:
1、下采样卷积:conv3x3 s=2 p=k//2=1
2、feature size不变的卷积:conv1x1 s=1 p=k//2=1
k:卷积核的kernel_size
'''
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad 自动计算pad数
return p
这里首先是判断是否有p值:
- 如果有既定的 p ,则直接 return p,自动计算所需要的pad值
- 如果无设定的 p,则 return 使图像在卷积操作后尺寸不变的 p
2.2 Conv
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution 标准卷积+BN+hardswish激活(SiLU)
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x): # 网络的执行顺序
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
"""用于Model类的fuse函数
融合conv+bn 加速推理 一般用于测试/验证阶段
"""
return self.act(self.conv(x)) # 没有BN
没什么好说的,整个网络中最基础的组件,Conv+BN+激活函数SiLU,结构如下
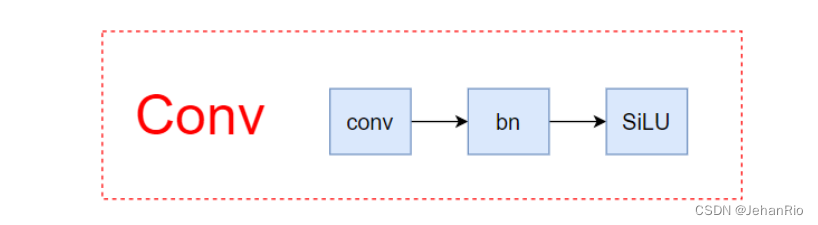
注意这里有个特殊的函数forward_fuse,这是一个前向加速推理模块,在前向传播过程中,通过融合conv + bn层,达到加速推理的作用,一般用于测试或验证阶段。
2.3 DWConv
# 深度可分离卷积(没用到)
class DWConv(Conv):
# Depth-wise convolution class
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__(c1, c2, k, s, g=math.gcd(c1, c2), act=act) # 返回最大公约数
2.4 Bottlenect
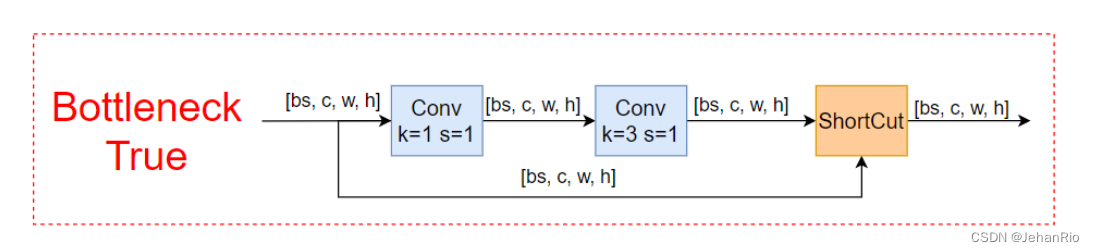
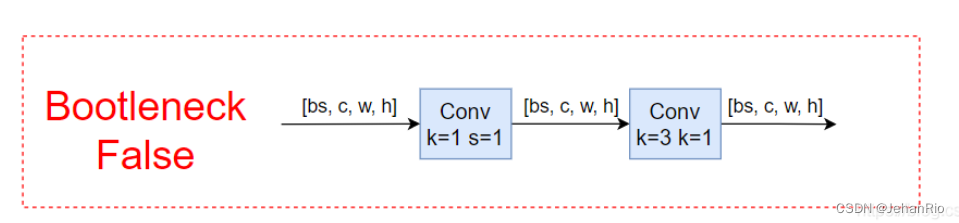
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion; shortcut: bool 是否有shortcut连接 默认是True
# e*c2就是第一个卷积的输出channel=第二个卷积的输入channel
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels 输出减半
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x): # 根据self.add确定是否有shortcut(相加)
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
传入的参数中有一个shortcut,分为true和false,主要作用是是否加入残差连接。
残差连接可以有效地提取特征,可以防止梯度消失和梯度爆炸,并降低过拟合,加快收敛速度。
2.5 BottleneckCSP
# 标准的瓶颈层 1x1conv+3x3conv+残差块
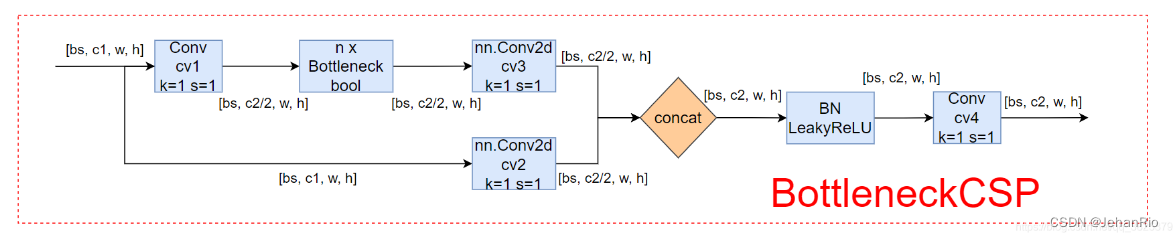
class BottleneckCSP(nn.Module): # BCSPn
# CSP Bottleneck https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = nn.Conv2d(c1, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv3 = nn.Conv2d(c_, c_, 1, 1, bias=False)
self.cv4 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * c_) # applied to cat(cv2, cv3)
self.act = nn.SiLU()
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n))) # *可以把list拆分成独立的元素
def forward(self, x):
y1 = self.cv3(self.m(self.cv1(x)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv4(self.act(self.bn(torch.cat((y1, y2), 1))))
标准的瓶颈层,由Bottlenect和CSP组成
可以将yaml文件中的C3直接更换成这个,但一般C3结构效果更好。
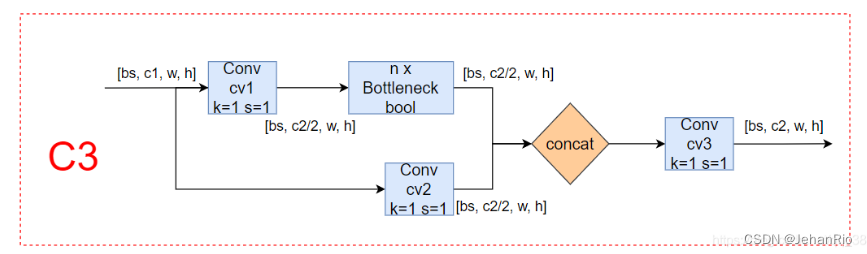
2.6 C3
# 这个模块是一种简化版的BottleneckCSP,因为除了Bottleneck部分只有3个卷积,可以减少参数,所以取名C3。
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), 1)) # 维度1
C3就是简化版的BottlenectCSP,只是少了一个Conv,可以减少参数,所以取名C3。
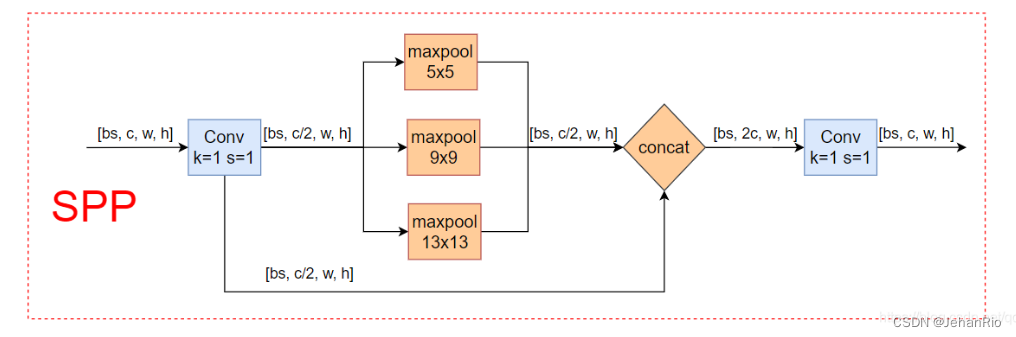
2.7 SPP
这个模块从v3就开始用了,主要目的是将不同分辨率的特征进行融合,得到更多的信息。
# 这个模块的主要目的是为了将更多不同分辨率的特征进行融合,得到更多的信息。
# 空间金字塔池化 在yolo.py的parse_model模块调用
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) layer https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1)) # 对每个m做最大池化,再叠加没有池化的m,再拼接
2.8 SPPF
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))
SPPF是快速版的空间金字塔,池化尺寸等价于:5、9、13,和原来一样,但是计算量减少了。
可以参考这篇博文:YOLOv5中的SPP/SPPF结构详解
2.9 Concat
class Concat(nn.Module):
# Concatenate a list of tensors along dimension
def __init__(self, dimension=1):
super().__init__()
self.d = dimension # 沿某个维度拼接
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat(x, self.d)
这个函数是将自身(a list of tensors)按照某个维度进行concat,常用来合并前后两个feature map,也就是上面yolov5s结构图中的Concat。
注意,这里的x是一个list,一般包括-1和另外一层。
3. 注意力模块
来了来了,注意力模块,我愿称之为深度学习中最为玄学的模块(格局大点,整个深度学习都是玄学doge)。我尝试过加入好多种注意力模块到网络中,最后结果我都愿称之为“实验误差”。不同的数据集,不同的位置,不同的注意力机制都有影响,只有极少数能涨点。
根据网上和我自己实验的经验来看,注意力机制一般放在这几个地方,以下结果不一定正确,还需根据自己相关数据集来看:
- 上采样+concat之后加入注意力机制
- backbone结尾加一个注意力机制
- channel-wise比spatial-wise更好用?
- 每个block(如residual block)结尾使用比每个Conv里使用更好?
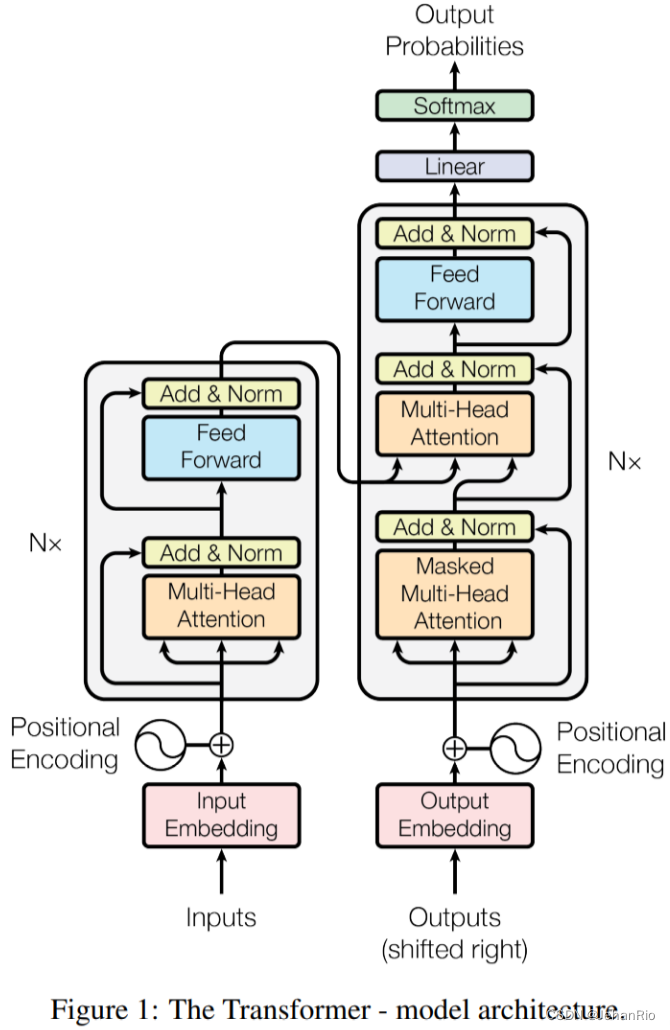
大名鼎鼎的自注意力机制,但是还没有学,打算后面再看,就先只贴代码吧。
如下图是整个transformer的结构,我们这里代码部分只用了左边的Encoding部分:
3.1 TransformerLayer
# transformer自注意力模块
class TransformerLayer(nn.Module):
# Transformer layer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 (LayerNorm layers removed for better performance)
def __init__(self, c, num_heads):
super().__init__()
self.q = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.k = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.v = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
# 输入: query、key、value
# 输出: 0 attn_output 即通过self-attention之后,从每一个词语位置输出来的attention 和输入的query它们形状一样的
# 1 attn_output_weights 即attention weights 每一个单词和任意另一个单词之间都会产生一个weight
self.ma = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=c, num_heads=num_heads)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(c, c, bias=False)
def forward(self, x):
# 多头注意力机制 + 残差(这里移除了LayerNorm for better performance)
x = self.ma(self.q(x), self.k(x), self.v(x))[0] + x
# feed forward 前馈神经网络 + 残差(这里移除了LayerNorm for better performance)
x = self.fc2(self.fc1(x)) + x
return x
3.2 TransformerBlock
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):
# Vision Transformer https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
def __init__(self, c1, c2, num_heads, num_layers):
super().__init__()
self.conv = None
if c1 != c2:
self.conv = Conv(c1, c2)
self.linear = nn.Linear(c2, c2) # learnable position embedding
self.tr = nn.Sequential(*(TransformerLayer(c2, num_heads) for _ in range(num_layers)))
self.c2 = c2
def forward(self, x):
if self.conv is not None:
x = self.conv(x)
b, _, w, h = x.shape
p = x.flatten(2).permute(2, 0, 1)
return self.tr(p + self.linear(p)).permute(1, 2, 0).reshape(b, self.c2, w, h)
4. 模型扩展模块
4.1 C3TR(C3)
# C3TR(C3):继承自 C3,n 个 Bottleneck 更换为 1 个 TransformerBlock
class C3TR(C3):
# C3 module with TransformerBlock()
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e)
self.m = TransformerBlock(c_, c_, 4, n)
这部分继承自C3,相当于把原先的Bottlenect换位了TransformerBlock模块
4.2 AutoShape
# 预处理调整shape
class AutoShape(nn.Module):
# YOLOv5 input-robust model wrapper for passing cv2/np/PIL/torch inputs. Includes preprocessing, inference and NMS
conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
def __init__(self, model, verbose=True):
super().__init__()
if verbose:
LOGGER.info('Adding AutoShape... ')
copy_attr(self, model, include=('yaml', 'nc', 'hyp', 'names', 'stride', 'abc'), exclude=()) # copy attributes
self.dmb = isinstance(model, DetectMultiBackend) # DetectMultiBackend() instance
self.pt = not self.dmb or model.pt # PyTorch model
self.model = model.eval()
if self.pt:
m = self.model.model.model[-1] if self.dmb else self.model.model[-1] # Detect()
m.inplace = False # Detect.inplace=False for safe multithread inference
def _apply(self, fn):
# Apply to(), cpu(), cuda(), half() to model tensors that are not parameters or registered buffers
self = super()._apply(fn)
if self.pt:
m = self.model.model.model[-1] if self.dmb else self.model.model[-1] # Detect()
m.stride = fn(m.stride)
m.grid = list(map(fn, m.grid))
if isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list):
m.anchor_grid = list(map(fn, m.anchor_grid))
return self
@torch.no_grad()
def forward(self, imgs, size=640, augment=False, profile=False):
# Inference from various sources. For height=640, width=1280, RGB images example inputs are:
# file: imgs = 'data/images/zidane.jpg' # str or PosixPath
# URI: = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'
# OpenCV: = cv2.imread('image.jpg')[:,:,::-1] # HWC BGR to RGB x(640,1280,3)
# PIL: = Image.open('image.jpg') or ImageGrab.grab() # HWC x(640,1280,3)
# numpy: = np.zeros((640,1280,3)) # HWC
# torch: = torch.zeros(16,3,320,640) # BCHW (scaled to size=640, 0-1 values)
# multiple: = [Image.open('image1.jpg'), Image.open('image2.jpg'), ...] # list of images
t = [time_sync()]
p = next(self.model.parameters()) if self.pt else torch.zeros(1, device=self.model.device) # for device, type
autocast = self.amp and (p.device.type != 'cpu') # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
if isinstance(imgs, torch.Tensor): # torch
with amp.autocast(autocast):
return self.model(imgs.to(p.device).type_as(p), augment, profile) # inference
# Pre-process
n, imgs = (len(imgs), list(imgs)) if isinstance(imgs, (list, tuple)) else (1, [imgs]) # number, list of images
shape0, shape1, files = [], [], [] # image and inference shapes, filenames
for i, im in enumerate(imgs):
f = f'image{i}' # filename
if isinstance(im, (str, Path)): # filename or uri
im, f = Image.open(requests.get(im, stream=True).raw if str(im).startswith('http') else im), im
im = np.asarray(exif_transpose(im))
elif isinstance(im, Image.Image): # PIL Image
im, f = np.asarray(exif_transpose(im)), getattr(im, 'filename', f) or f
files.append(Path(f).with_suffix('.jpg').name)
if im.shape[0] < 5: # image in CHW
im = im.transpose((1, 2, 0)) # reverse dataloader .transpose(2, 0, 1)
im = im[..., :3] if im.ndim == 3 else np.tile(im[..., None], 3) # enforce 3ch input
s = im.shape[:2] # HWC
shape0.append(s) # image shape
g = (size / max(s)) # gain
shape1.append([y * g for y in s])
imgs[i] = im if im.data.contiguous else np.ascontiguousarray(im) # update
shape1 = [make_divisible(x, self.stride) if self.pt else size for x in np.array(shape1).max(0)] # inf shape
x = [letterbox(im, shape1, auto=False)[0] for im in imgs] # pad
x = np.ascontiguousarray(np.array(x).transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))) # stack and BHWC to BCHW
x = torch.from_numpy(x).to(p.device).type_as(p) / 255 # uint8 to fp16/32
t.append(time_sync())
with amp.autocast(autocast):
# Inference
y = self.model(x, augment, profile) # forward
t.append(time_sync())
# Post-process
y = non_max_suppression(y if self.dmb else y[0],
self.conf,
self.iou,
self.classes,
self.agnostic,
self.multi_label,
max_det=self.max_det) # NMS
for i in range(n):
scale_coords(shape1, y[i][:, :4], shape0[i])
t.append(time_sync())
return Detections(imgs, y, files, t, self.names, x.shape)
AutoShape是一个模型扩展模块,给模型封装成包含前处理、推理、后处理的模块(预处理 + 推理 + nms)。
注意Autoshape模块在train中不会被调用,当模型训练结束后,会通过这个模块对图片进行重塑,来方便模型的预测。
因为这个模块基本没啥用,所以不做细讲。
4.3 Detections
class Detections:
# YOLOv5 detections class for inference results
def __init__(self, imgs, pred, files, times=(0, 0, 0, 0), names=None, shape=None):
super().__init__()
d = pred[0].device # device
gn = [torch.tensor([*(im.shape[i] for i in [1, 0, 1, 0]), 1, 1], device=d) for im in imgs] # normalizations
self.imgs = imgs # list of images as numpy arrays
self.pred = pred # list of tensors pred[0] = (xyxy, conf, cls)
self.names = names # class names
self.files = files # image filenames
self.times = times # profiling times
self.xyxy = pred # xyxy pixels
self.xywh = [xyxy2xywh(x) for x in pred] # xywh pixels
self.xyxyn = [x / g for x, g in zip(self.xyxy, gn)] # xyxy normalized
self.xywhn = [x / g for x, g in zip(self.xywh, gn)] # xywh normalized
self.n = len(self.pred) # number of images (batch size)
self.t = tuple((times[i + 1] - times[i]) * 1000 / self.n for i in range(3)) # timestamps (ms)
self.s = shape # inference BCHW shape
def display(self, pprint=False, show=False, save=False, crop=False, render=False, labels=True, save_dir=Path('')):
crops = []
for i, (im, pred) in enumerate(zip(self.imgs, self.pred)):
s = f'image {i + 1}/{len(self.pred)}: {im.shape[0]}x{im.shape[1]} ' # string
if pred.shape[0]:
for c in pred[:, -1].unique():
n = (pred[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += f"{n} {self.names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
if show or save or render or crop:
annotator = Annotator(im, example=str(self.names))
for *box, conf, cls in reversed(pred): # xyxy, confidence, class
label = f'{self.names[int(cls)]} {conf:.2f}'
if crop:
file = save_dir / 'crops' / self.names[int(cls)] / self.files[i] if save else None
crops.append({
'box': box,
'conf': conf,
'cls': cls,
'label': label,
'im': save_one_box(box, im, file=file, save=save)})
else: # all others
annotator.box_label(box, label if labels else '', color=colors(cls))
im = annotator.im
else:
s += '(no detections)'
im = Image.fromarray(im.astype(np.uint8)) if isinstance(im, np.ndarray) else im # from np
if pprint:
print(s.rstrip(', '))
if show:
im.show(self.files[i]) # show
if save:
f = self.files[i]
im.save(save_dir / f) # save
if i == self.n - 1:
LOGGER.info(f"Saved {self.n} image{'s' * (self.n > 1)} to {colorstr('bold', save_dir)}")
if render:
self.imgs[i] = np.asarray(im)
if crop:
if save:
LOGGER.info(f'Saved results to {save_dir}\n')
return crops
def print(self):
self.display(pprint=True) # print results
print(f'Speed: %.1fms pre-process, %.1fms inference, %.1fms NMS per image at shape {tuple(self.s)}' % self.t)
def show(self, labels=True):
self.display(show=True, labels=labels) # show results
def save(self, labels=True, save_dir='runs/detect/exp'):
save_dir = increment_path(save_dir, exist_ok=save_dir != 'runs/detect/exp', mkdir=True) # increment save_dir
self.display(save=True, labels=labels, save_dir=save_dir) # save results
def crop(self, save=True, save_dir='runs/detect/exp'):
save_dir = increment_path(save_dir, exist_ok=save_dir != 'runs/detect/exp', mkdir=True) if save else None
return self.display(crop=True, save=save, save_dir=save_dir) # crop results
def render(self, labels=True):
self.display(render=True, labels=labels) # render results
return self.imgs
def pandas(self):
# return detections as pandas DataFrames, i.e. print(results.pandas().xyxy[0])
new = copy(self) # return copy
ca = 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax', 'confidence', 'class', 'name' # xyxy columns
cb = 'xcenter', 'ycenter', 'width', 'height', 'confidence', 'class', 'name' # xywh columns
for k, c in zip(['xyxy', 'xyxyn', 'xywh', 'xywhn'], [ca, ca, cb, cb]):
a = [[x[:5] + [int(x[5]), self.names[int(x[5])]] for x in x.tolist()] for x in getattr(self, k)] # update
setattr(new, k, [pd.DataFrame(x, columns=c) for x in a])
return new
def tolist(self):
# return a list of Detections objects, i.e. 'for result in results.tolist():'
r = range(self.n) # iterable
x = [Detections([self.imgs[i]], [self.pred[i]], [self.files[i]], self.times, self.names, self.s) for i in r]
# for d in x:
# for k in ['imgs', 'pred', 'xyxy', 'xyxyn', 'xywh', 'xywhn']:
# setattr(d, k, getattr(d, k)[0]) # pop out of list
return x
def __len__(self):
return self.n # override len(results)
def __str__(self):
self.print() # override print(results)
return ''
这部分是对推理结果进行处理,就上面AutoShape结尾用了一下,基本不用,就不细看了。只需要重点掌握yolo.py中的Detection
4.4 Classify二级分类
# 用于第二级分类(车牌识别)
class Classify(nn.Module):
# Classification head, i.e. x(b,c1,20,20) to x(b,c2)
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.aap = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) # to x(b,c1,1,1) 自适应平均池化操作
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g) # to x(b,c2,1,1)
self.flat = nn.Flatten()
def forward(self, x):
z = torch.cat([self.aap(y) for y in (x if isinstance(x, list) else [x])], 1) # cat if list
return self.flat(self.conv(z)) # flatten to x(b,c2)
什么是二级分类?
比如做车牌识别,先识别出车牌,如果想对车牌上的字进行识别,就需要二级分类进一步检测。如果对模型输出的分类再进行分类,就可以用这个模块。
再比如要做识别人脸面部表情,先要识别出人脸,如果想识别出人的面部表情,就需要二级分类进一步检测。
总结
这部分我将最基本的一些模块给贴了出来,一些在YOLOv5中比较冷门的、偏的我就没写了。大家重点需要掌握的是基础组件部分,其他的像注意力机制这些可以做一下尝试,看能不能涨点。后面第4模块都可以不用看。
2023-04-26 13:39
References
CSDN 满船清梦压星河HK YOLOv5源码逐行超详细注释与解读(7)——网络结构(2)common.py
CSDN 路人贾’ω’ 【YOLOV5-5.x 源码解读】common.py





















 2370
2370











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








