- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
一、导入数据
#一、导入数据
'''
1.1设置GPU
'''
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from torchvision.io import read_image
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import torch.utils.data as data
from PIL import Image
import copy
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息--???怎么突然增加一个这个
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
'''
1.2 获取类别名
'''
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
data_dir = '/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P10周:Pytorch实现车牌识别/015_licence_plate'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("/")[8].split("_")[1].split(".")[0] for path in data_paths]
print(classeNames)
#这里一个车牌就是一类,因为我们的这里的数据是没有分类的,一个车牌就是一类
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
data_paths_str = [str(path) for path in data_paths]
print(data_paths_str)
'''
1.3 数据可视化
'''
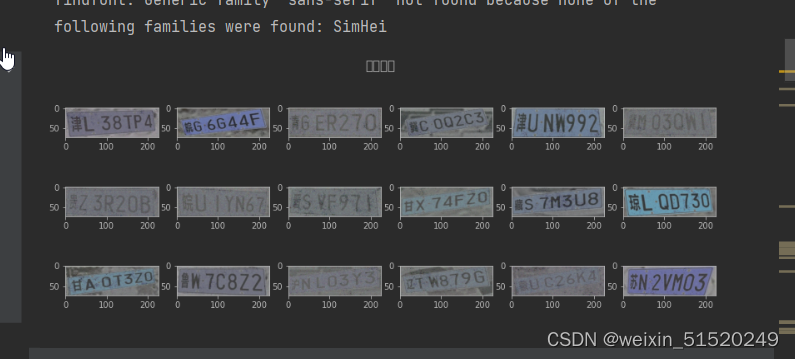
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
plt.suptitle("数据示例", fontsize=15)
for i in range(18):
plt.subplot(3, 6, i+1)
images = plt.imread(data_paths_str[i])
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()
'''
1.4 标签数字化
'''
import numpy as np
char_enum = ["京","沪","津","渝","冀","晋","蒙","辽","吉","黑","苏","浙","皖","闽","赣","鲁",\
"豫","鄂","湘","粤","桂","琼","川","贵","云","藏","陕","甘","青","宁","新","军","使"]
number = [str(i) for i in range(0, 10)] # 0 到 9 的数字
alphabet = [chr(i) for i in range(65, 91)] # A 到 Z 的字母
char_set = char_enum + number + alphabet
char_set_len = len(char_set)
label_name_len = len(classeNames[0])
#将字符串数据化
def text2vec(text):
vector = np.zeros([label_name_len, char_set_len])
for i, c in enumerate(text):
idx = char_set.index(c)
vector[i][idx] = 1.0
return vector
all_labels = [text2vec(i) for i in classeNames]
'''
1.5 加载数据文件
'''
class MyDataset(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, all_labels, data_paths_str, transform):
self.img_labels = all_labels #获取标签信息
self.img_dir = data_paths_str #图像目录路径
self.transform = transform #目标转换函数
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_labels)
def __getitem__(self, index):
image = Image.open(self.img_dir[index]).convert('RGB')
# plt.imread(self.img_dir[index]) # 使用 torchvision.io.read_image 读取图像
label = self.img_labels[index] # 获取图像对应的标签
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
return image, label
total_datadir = '/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/pytorch入门实战/第P10周:Pytorch实现车牌识别/015_licence_plate'
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std =[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = MyDataset(all_labels, data_paths_str, train_transforms)
print(total_data)
'''
1.6 划分数据
'''
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
print(train_size, test_size)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=16,
shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=16,
shuffle=True)
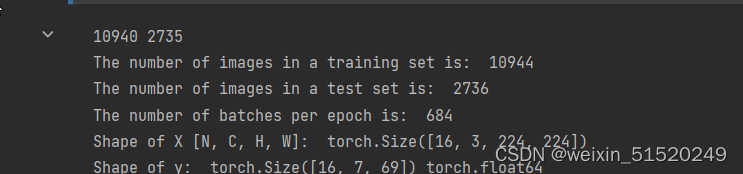
print("The number of images in a training set is: ", len(train_loader)*16)
print("The number of images in a test set is: ", len(test_loader)*16)
print("The number of batches per epoch is: ", len(train_loader))
for X, y in test_loader:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
break
#二、自建模型
class Network_bn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Network_bn, self).__init__()
"""
nn.Conv2d()函数:
第一个参数(in_channels)是输入的channel数量
第二个参数(out_channels)是输出的channel数量
第三个参数(kernel_size)是卷积核大小
第四个参数(stride)是步长,默认为1
第五个参数(padding)是填充大小,默认为0
"""
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
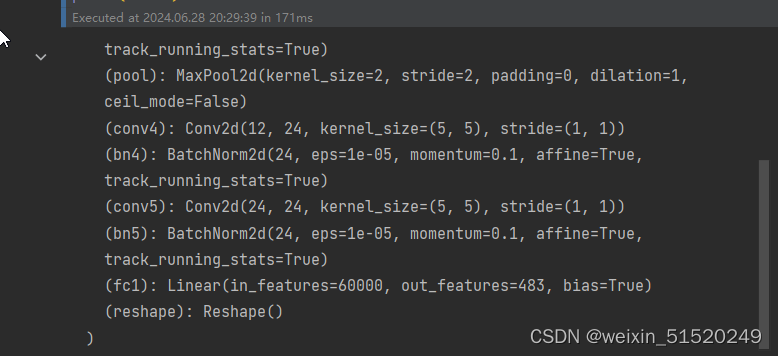
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=24, out_channels=24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(24 * 50 * 50, label_name_len * char_set_len)
self.reshape = Reshape([label_name_len, char_set_len])
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.pool(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.conv5(x)))
x = self.pool(x)
x = x.view(-1, 24 * 50 * 50)
x = self.fc1(x)
# 最终reshape
x = self.reshape(x)
return x
#定义Reshape层
class Reshape(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, shape):
super(Reshape, self).__init__()
self.shape = shape
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), *self.shape)
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = Network_bn().to(device)
print(model)
#三、模型训练
'''
3.1 优化器与损失函数
'''
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4, weight_decay=0.0001)
loss_model = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
'''
3.2 训练函数和测试函数
'''
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
def test(model, test_loader, loss_model):
size = len(test_loader.dataset)
num_batches = len(test_loader)
model.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in test_loader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_model(pred, y).item()
# 计算准确率_它计算了在一个批次(batch)中,模型预测的标签与真实标签相同的数量占总数量的比例
# 假设这里是多类分类任务
#pred_labels = torch.argmax(pred, dim=-1) # [batch, 7]
#true_labels = torch.argmax(y, dim=-1) # [batch, 7]
#correct += (pred_labels == true_labels).float().sum().item() / (y.size(1) * y.size(0))
test_loss /= num_batches
#accuracy = correct / size
print(f"Avg loss: {test_loss:>8f} \n")
#print(f"Avg accuracy: {accuracy:>8f} \n")
return correct, test_loss
def train(model, train_loader, loss_model, optimizer):
model = model.to(device)
model.train()
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader, 0): # 0是标起始位置的值。
images = Variable(images.to(device))
labels = Variable(labels.to(device))
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = loss_model(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('[%5d] loss: %.3f' % (i, loss))
'''
3.3 模型的训练
'''
test_acc_list = []
test_loss_list = []
epochs = 30
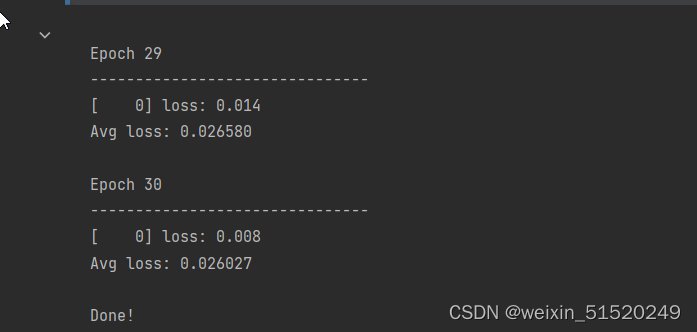
for t in range(epochs):
print(f"Epoch {t+1}\n-------------------------------")
train(model,train_loader,loss_model,optimizer)
test_acc,test_loss = test(model, test_loader, loss_model)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
test_loss_list.append(test_loss)
print("Done!")
#四、结果分析
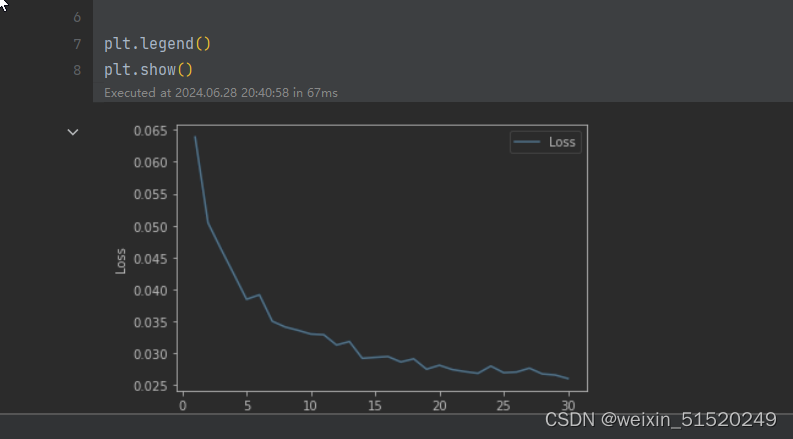
x = [i for i in range(1, 31)]
plt.plot(x, test_loss_list, label='Loss', alpha=0.8)
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
个人总结
参考上面的dataset类,构建了自己的数据集类 Mydataset。
传统计算 准确度:
correct = (pred_labels == y_labels).sum().item() # 计算匹配的数量
total = pred_labels.size(0) # 批次大小
acc = correct / total # 计算准确度





















 899
899











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








