🔐的标记题目有必要斟酌思路和边界条件
🌿🥚标记的表示题型有点离谱
数据结构
数组
数组中重复数字
题目:一个长度为N的数,组中的所有数字都是在0~N-1的范围内,数组中某些数字是重复的,但是不知道有几个数的重复,也不知道每个数字重复了几次,请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字作为返回值。
- 充分利用下标和数值之间的对应关系
- 和桶排序有异曲同工之妙
public class Main {
/**
* @param arr 目标数组
* 时间复杂度:O(N)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
*/
public static Integer repetition(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
while (arr[i] != i) {
// 若果没有这样的return 语句那么可能导致该循环不会退出
// 该条件的意思是已经存在arr[i]为下标值为arr[i]的值,此时出现俩个arr[i]
if (arr[arr[i]] == arr[i]) {
return arr[i];
}
// 交换此时下标为i和下标为arr[i]的值
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[temp];
arr[temp] = temp;
}
}
return null;
}
}
思考:输出数组中缺失和重复的元素。
public class Main {
// 存储数组中重复出现的元素
public static HashSet<Integer> repetitionHashSet = new HashSet<>();
// 存储数组中在0~N-1之间缺失的元素
public static ArrayList<Integer> restNumList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void repetition(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
modify(arr, i);
}
// 此时所以元素都应该在对应位置,除非不存在对应值
// 不存在的位置都会存在一个和其他值重复的值
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] != i) {
repetitionHashSet.add(arr[i]);
restNumList.add(i);
}
}
}
private static void modify(int[] arr, int index) {
// 首先要保证arr[index]和对应的值不为index
// 另外arr[index]为下标的元素不能已经在正确位置,防止进入死循环
// 每一次运行都仅仅改变元素位置,不能改变arr中元素值
while (arr[index] != index && !(arr[arr[index]] == arr[index])) {
// 将下标为index和下标为arr[index]的两个值进行交换
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = arr[temp];
arr[temp] = temp;
}
}
}
不修改数组寻找重复元素
问题 :在长度为N+1的数组里面的所有数字都在1~N的范围内,所以数组中至少有一个数字是重复的,请找出数组中任意一个重复数字,但不能够修改输入的数组。要求空间复杂度O( 1 )
- 二分法将数据进行分类,判断重复数据在二分情况下的左右位置。
- 数据个数大于范围中整数个数就在该范围中定存在重复值
public class Main {
/**
* @param arr 目标数组
* @return 重复值
* 时间复杂度O(NlogN)
* 空间复杂度O(1)
*/
public static Integer repetition(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int left = 1;
int right = arr.length - 1;
// 当left==right时,我们并不知道是否为重复数据,所以还要进行一次countRange方法调用进行判断。
while (left <= right) {
int med = ((right - left) >> 1) + left;
// 计算left..med之间数据个数
int count = countRange(arr, left, med);
if (left == right) {
if (count > 1) {
return left;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 若数据个数比left...med之间的整数个数多则定有重复值
// 根据数据个数定重复值范围,从而缩小重复数据所在范围
if (count > (med - left + 1)) {
right = med;
} else {
left = med + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static int countRange(int[] arr, int left, int med) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (left <= arr[i] && arr[i] <= med) {
++count;
}
}
return count;
}
}
二维数组中的查找
题目 : 在一个二维数组中每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下的递增的顺序排序,完成一个函数输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否还有这样的整数。
- 在arr中邻近目标值的数值附近的范围进行数据搜索
public class Main {
public static boolean process(int[][] arr, int x) {
// 异常条件
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0].length == 0 || arr[0][0] > x
|| arr[arr.length - 1][arr[0].length - 1] < x) {
return false;
}
int row = 0;
int line = 0;
// 控制范围
while (row >= 0 && row < arr.length && line >= 0 && line < arr[0].length) {
// 目标值比arr[row][line]大就有向右和向下两个方向
if (arr[row][line] < x) {
// 向右满足吗?
if (line + 1 < arr[0].length && arr[row][line + 1] < x) {
++line;
} else {
++row;
}
// 目标值比arr[row][line]小
} else if (arr[row][line] > x) {
--line;
} else {// 等于目标值
return true;
}
}
// 因为范围出界返回不存在
return false;
}
}
字符串
替换空格
题目 : 请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格转换为 %20
- 若是从左向右依次进行时间复杂度O(N²),造成时间浪费的主要原因就是没能够将字符直接填到他应该在的位置。
- 要想能够直接将它放在相应的位置,就需要知道一共有多少个空格。
- 并且在便利扩充的过程中,必须要从右向左,以防数据的覆盖。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = new char[100];
System.out.println(arr.length);
arr[0] = ' ';
arr[1] = 'a';
arr[2] = ' ';
arr[3] = 'a';
arr[4] = 'a';
arr[5] = 'a';
arr[6] = ' ';
arr[7] = 'a';
arr[8] = 'a';
arr[9] = ' ';
process(arr, 10, 100);
}
/**
* @param arr 数组对象
* @param thisLen 当前数组长度
* @param maxLen arr最大容量
* 时间复杂度O(N)
* 空间复杂度O(1)
*/
public static void process(char[] arr, int thisLen, int maxLen) {
if (arr == null || maxLen <= 0 || thisLen <= 0) {
return;
}
// 统计空格数量
int sumK = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < thisLen; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ' ') {
++sumK;
}
}
// 计算新数组长度
int newLen = sumK * 2 + thisLen;
if (newLen > maxLen) {
return;
}
// 两个指针进行遍历
int index = thisLen - 1;
int newIndex = newLen - 1;
while (index >= 0) {
if (arr[index] == ' ') {
arr[newIndex--] = '0';
arr[newIndex--] = '2';
arr[newIndex] = '%';
} else {
arr[newIndex] = arr[index];
}
--index;
--newIndex;
}
}
}
链表
从尾到头打印链表
题目 : 输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个节点的值。
- 三种方式之实现
- 其中栈结构和递归实现时间复杂度常数较低 1 * O(N),反序实现为 3 * O(N)
- 栈结构和递归空间复杂度O(N),和反序为O(1)
- 这时典型的空间换时间的案例。
public class Main {
//栈实现
public static void process_1(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node tail = header;
while (tail != null) {
stack.push(tail);
tail = tail.nextNode;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop().num);
}
}
// 递归实现
public static void process_2(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
process_2(header.nextNode);
System.out.println(header.num);
}
// 反序链表实现
public static void process_3(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return;
}
Node pre = null;
Node tail = header;
Node post = null;
while (tail != null) {
post = tail.nextNode;
tail.nextNode = pre;
pre = tail;
tail = post;
}
header = pre;
while (pre != null) {
System.out.println(pre.num);
pre = pre.nextNode;
}
pre = null;
tail = header;
post = null;
while (tail != null) {
post = tail.nextNode;
tail.nextNode = pre;
pre = tail;
tail = post;
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node nextNode;
public Node(int num, Node nextNode) {
this.num = num;
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
}
}
树
重建二叉树🔐
题目 : 输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建二叉树。假设输入的前驱和后继的节点都没有重复的数字,函数要返回树的根节点 。
- 注意我们是根据前序遍历中的第一个值在中序遍历位置来判断此时root根节点左右两个子树的个数。
- 注意判断左右子树是否存在,否则范围会出现ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException错误,两种方式均可。
- 这是一个大范围数据转化成小范围,也就是大问题转化成了本质相同的小问题,那么通常是用递归实现。
public class Main {
public static Node construction(int[] pre, int[] in) {
if (pre == null || in == null ||
pre.length == 0 || in.length == 0 || pre.length != in.length) {
return null;
}
return construction(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1);
}
/**
* @param pre 前序遍历
* @param preStart 前序遍历部分的首元素
* @param preEnd 前序遍历部分的尾元素
* @param in 中序遍历
* @param inStart 中序遍历部分的首元素
* @param inEnd 中序遍历部分的尾元素
* @return pre[preStart]对应的当前节点
* 注意 : pre[preStart...preEnd] 和 in[inStart...inEnd]中包含的元素完全相同
*/
private static Node construction(int[] pre, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] in, int inStart, int inEnd) {
// if(preStart>preEnd)return null;添加上这一句可以代替左右子树的节点存在判断
// 建立当前节点pre[preStart]
Node root = new Node(pre[preStart]);
if (preStart == preEnd) {
return root;
}
// 根据pre[preStart]查找in中数据位置记作数据A,
// A前面的元素个数用leftNum记录
int leftNum = 0;
int tail = inStart;
while (pre[preStart] != in[tail]) {
++leftNum;
++tail;
}
/*
* 实际上在该函数一开始时加上一个判断
* if(preStart>preEnd)return null;
* 也可以避免root左右子树不存在情况,不过这样的方式更好理解
*
* 另外注意观察左右子树建立时的范围:
* 前序遍历:
* pre[preStart]为当前根节点
* pre[preStart+1...preStart + leftNum]为左子树范围
* pre[preStart + leftNum + 1...preEnd]为右子树范围
* 中序遍历:
* in[inStart...inStart + leftNum - 1]为左子树范围
* in[inStart + leftNum]为当前根节点
* in[inStart + leftNum + 1...inEnd]为右子树范围
*/
// 若leftNum > 1 说明当前root有左子树就设置
if (leftNum > 0) {
root.leftNode = construction(pre, preStart + 1, preStart + leftNum,
in, inStart, inStart + leftNum - 1);
}
// 判断是否存在右子树
if (leftNum < preEnd - preStart) {
root.rightNode = construction(pre, preStart + leftNum + 1, preEnd,
in, inStart + leftNum + 1, inEnd);
}
return root;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
public Node(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
}
二叉树的下一个节点
题目:给定一颗二叉树和其他一个节点,如何找到中序遍历的下一个节点?另外组成该树的节点类型记录了该节点的父节点。
- 目标节点存在右子树,就是右子树中最左边的元素(循环向左查找)。
- 目标节点不存在右子树,就是祖先节点中的某个节点记作(A),其中定满足:目标节点是祖先节点A的左子树中的元素(循环向上查找)。
public class Main {
public static Node nextNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// 若该节点存在右节点
if (node.rightNode != null) {
return leftestNode(node.rightNode);
}
// 没有右节点,那么下一个元素必定为父类节点以及以上节点中记为A
// 并且该node节点定为在A的左子树中,否则不存在
return leftChildOfParent(node);
}
// 查找在那个节点的左子树中
private static Node leftChildOfParent(Node node) {
Node parent = node.parentNode;
while (parent != null && parent.rightNode == node) {
node = parent;
parent = parent.parentNode;
}
return parent;
}
// 查找最左节点
private static Node leftestNode(Node rightNode) {
Node tail = rightNode;
while (tail.leftNode != null) {
tail = tail.leftNode;
}
return tail;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
Node parentNode;
public Node(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
}
栈和队列
双栈实现队列
题目 : 用两个栈结构完成队列的功能,实现两个方法,appendTail : 增加元素,deleteHeader:删除元素。
- 栈结构我们可以理解为能将数据反序。那么两个反序就是正序,所以两个栈结构即可实现队列结构。
public class Main {
Stack<Integer> addStack;
Stack<Integer> deleteStack;
public Main() {
this.addStack = new Stack<Integer>();
this.deleteStack = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void appendTail(int num) {
addStack.push(num);
}
public Integer deleteHeader() {
//一定要将deleteStack中元素删除完才能从addSrtack中取出元素给deleteStack.
if (!deleteStack.isEmpty()) {
return deleteStack.pop();
}
if (addStack.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
//每次从addStack中删除到deleteStack中时,定将addStack中元素删除完
while (!addStack.isEmpty()) {
deleteStack.add(addStack.pop());
}
return deleteStack.pop();
}
}
双队列实现栈
题目 : 用两个队列结构完成栈的功能,实现两个方法,add: 增加元素,poll:删除元素。
- 新增时只在有元素的队列中增加,若都空,那么随意。
- 删除时用队列将元素来回颠倒,删除剩余最后的那个元素。
- 注:保持其中一个队列在每次新增删除后都是空的。
public class Main {
private ArrayDeque<Integer> deque1;
private ArrayDeque<Integer> deque2;
private boolean hasNum_1 = true;
private boolean hasNum_2 = false;
private boolean flag;//为true时,表示deque1有元素,false时表示deque2有元素。
public Main() {
deque1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
flag = hasNum_1;
}
public void add(int num) {
if (flag) {
deque1.add(num);
}else {
deque2.add(num);
}
}
public Integer poll() {
if (flag) {
if (deque1.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
while (deque1.size()!=1) {
deque2.push(deque1.poll());
}
flag=hasNum_2;
return deque1.poll();
}else {
if (deque2.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
while (deque2.size()!=1) {
deque1.push(deque2.poll());
}
flag=hasNum_1;
return deque2.poll();
}
}
}
算法和数据操作
递归和循环
- 递归:将大问题换化成子问题进行求解
斐波那契数列
问题:求第N个斐波那契数。
- 由于递归的调用要要保存变量、返回参数和创建临时变量,整体性能和速度上不如循环。
- 循环对于性能最好的,递归对代码量较少。
public class Main {
//递归实现
private static Integer process(int N) {
if (N==1||N==2) {
return 1;
}
return process(N-1)+process(N-2);
}
//循环实现
private static Integer process(int N) {
if (N<=0) {
return null;
}
if (N<3) {
return 1;
}
int pre=1;
int post=1;
int res=0;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
res=pre+post;
pre=post;
post=res;
}
return res;
}
}
青蛙跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳 2 级台阶,求青蛙正好跳 N 阶台阶有多少种跳法。
- 到第N阶有两种可能,从N-1 或 N-2 ,再将N-1 和 N-2 看成目标台阶。
- 直至1和2个台阶时,1阶有一种跳法,2阶有两种跳法。
- 典型类斐波那契问题
public class Main {
private static Integer process(int N) {
if (N<=0) {
return null;
}
if (N==1) {
return 1;
}
if (N==2) {
return 2;
}
int pre=1;
int post=2;
int res=0;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
res=pre+post;
pre=post;
post=res;
}
return res;
}
}
查找和排序
- 顺序、二分、哈希表、二叉树。
- 哈希表虽然时间复杂度为O(1),但是需要额外空间复杂度。
- 在不同条件下,不同数据状况下,不同约束条件下要有不能选择。
- 例如: 快速排序在基本排好序的数据中时间复杂度接近O( N )
- 再例如 : 在小量数据和能开辟空间状况下,且被比较的数据为一般数据类型,桶排序是最好的选择,时间复杂度O(N)。
旋转数组(已排序)后的最小值🔐
题目:将一个已排序数组的最开始的若干个元素搬到数组末尾,输出该旋转后的数组的最小值,空间复杂度 O(1)。例如{3,4,5,1,2,2},最小值为 1
- 若使用O(N)的顺序查找,条件:已经有序就没用了。
- 显然想到二分查找,我们将二分查找的缩小范围的条件改变,让范围向着我们目标数组进行靠近就行了。
- 但是却遇见了不知道缩小方向的情况,所以要进行线性查找。
public class Main {
public static Integer process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int tail_1 = 0;
int tail_2 = arr.length - 1;
// 如果条件满足,说明整体有序,arr是一个有序数组。
if (arr[tail_1] < arr[tail_2]) {
return arr[0];
}
// 因为tail_1指向左有序序列,tail_2指向右有序序列,定相差 >= 1 ,当相差为 1 时,tail_2指向的就是最小值
while (tail_2 - tail_1 != 1) {
int med = ((tail_2 - tail_1) >> 1) + tail_1;
//若果三值同在后续过程中无法判断缩小范围的方向,所以从此要进行线性查找。
//像 { 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3 } { 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3 } 的数组不能确定向左还是向右.
if (arr[tail_1] == arr[tail_2] && arr[tail_1] == arr[med]) {
return process(arr, tail_1, tail_2);
}
// 这样的判断和移动范围方式,使tail_1始终在arr前面的有序部分,tail_2始终在arr后面的有序部分
// 因为在进行该判读前已经判断arr[tail_1],arr[tail_2],arr[med]三个值不全同。
// 所以在进行判断时,如果arr[med] == arr[tail_1]成立,那么arr[med] > arr[tail_2]成立,所以tail_1向右动
// 等号必须在tail_1向左移动的条件上。
if (arr[med] >= arr[tail_1]) {
tail_1 = med;
} else if (arr[med] < arr[tail_2]) {
tail_2 = med;
}
}
return arr[tail_2];
}
private static Integer process(int[] arr, int tail_1, int tail_2) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 在当前范围中查找最小值。
for (int i = tail_1; i <= tail_2; i++) {
min = Math.min(min, arr[i]);
}
return min;
}
}
简洁代码:
class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < nums[right]) right = mid;
else if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) left = mid + 1;
else right--;
}
return nums[right];
}
}
回溯法
矩阵中的路径
题目 : 请设计请设计一个函数用来判断在矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径,路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个位置开始,每部可以在矩阵中的上下左右四个方向移动,如果一条路径已经经过了矩阵的某一个格子,那么该路径就不能够再次进入该格子。
- 对于每个格子均有可能是起始节点,并且每个路径和其他路径没有太多可利用关系,所以要进行所有的格子作为起始结点来判断。
- 由于要进行方向定位,像迷宫一样进行递归回缩。
public class Main {
public static boolean process(char[][] matrix, char[] str) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0 || str.length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length;
int line = matrix[0].length;
// 用于记录是否走过该路径
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[rows][line];
int pathLen = 0;
// 对于每一个元素进行起始的判断
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < line; j++) {
if (hasSuccessPath(matrix, i, j, str, 0, isVisited)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* @param matrix 元素矩阵
* @param row 判断matrix中行位置元素
* @param line 判断matrix中列位置元素
* @param str 寻找的目标串
* @param index 目标串的第几个元素
* @param isVisited 记录是否走过的表格
* @return 该路径是否可行
*/
private static boolean hasSuccessPath(char[][] matrix, int row, int line, char[] str, int index,
boolean[][] isVisited) {
// 此时说明index前面的所有元素均已经匹配成功
if (str.length == index) {
return true;
}
// 不符合条件返回不通行
if (row >= matrix.length || line == matrix[0].length || row < 0 || line < 0 || isVisited[row][line]
|| matrix[row][line] != str[index]) {
return false;
}
++index;
// 标记该路已经走过
isVisited[row][line] = true;
// 向四个方向均进行尝试
boolean hasPath = hasSuccessPath(matrix, row + 1, line, str, index, isVisited)
|| hasSuccessPath(matrix, row, line + 1, str, index, isVisited)
|| hasSuccessPath(matrix, row - 1, line, str, index, isVisited)
|| hasSuccessPath(matrix, row, line - 1, str, index, isVisited);
// 若没有成功将isVisited值进行还原避免影响后续判断,若为真那么在该步骤结束时循环,不会对后来的产生影响
if (!hasPath) {
isVisited[row][line] = false;
}
return hasPath;
}
}
机器人的运动范围
题目: 地上有一个M行N列的方格,一个机器人从坐标( 0, 0 )的个格子开始移动,他每次可向左右上下四个方向移动一个格子,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的各个位数之和大于K值,并且到达每个格子之前必定可以通过其他格子到达该格子。例如: k=18,机器人可以进入(35,37),3+5+3+7=18<=18能进入,(36,38),3+6+3+8=20>18,不能进入。
- 该题目实际上和上一题本质相同,仅仅是改变了限制条件和起始范围
- 该题的起始范围已经给定(0,0),只需要向上下左右进行递归回溯,另外在递归时要记录路径个数。
public class Main {
public static int process(int k, int rows, int lines) {
if (k < 0 || rows <= 0 || lines <= 0) {
return 0;
}
boolean[][] isVisited = new boolean[rows][lines];
return movingCount(k, rows, lines, 0, 0, isVisited);
}
/**
* @param k 限制条件k
* @param rows 矩阵总行数
* @param lines 矩阵总列数
* @param i 当前元素行数量
* @param j 当前元素列数量
* @param isVisited 是否已经访问过
* @return 可以选择的个数
*/
private static int movingCount(int k, int rows, int lines, int i, int j, boolean[][] isVisited) {
int count = 0;
// 如果满足限制条件就进行标记,并以此为展开进行递归搜索
if (canVisited(k, rows, lines, i, j, isVisited)) {
isVisited[rows][lines] = true;
count += movingCount(k, rows, lines, i + 1, j, isVisited)
+ movingCount(k, rows, lines, i - 1, j, isVisited)
+ movingCount(k, rows, lines, i, j + 1, isVisited)
+ movingCount(k, rows, lines, i, j - 1, isVisited);
}
return count;
}
private static boolean canVisited(int k, int rows, int lines, int i, int j, boolean[][] isVisited) {
if (i >= 0 && i < rows && j >= 0 && j < lines && !isVisited[i][j] && getDigitSum(i) + getDigitSum(j) <= k) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 计算num和各位数字之和
private static int getDigitSum(int num) {
int sum = 0;
while (num > 0) {// 不能 = 0
sum += num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
}
动态规划和贪婪算法
剪绳子🌿🥚
题目: 给你一根长度为N的绳子,请把绳子剪成M段 , M和N都是整数且均大于1,每段绳子的长度记作K1,K2 … Km,请问它们相乘的最大乘积是多少?
- 该问题对于任意的值N,都可以分解为两个字问题 i 和 N-i (i 从1到N-1),这些子问题中的最大值就是结果,对于每个字问题也可以分成更小的子问题。显然是一个经典递归案例。
递归实现
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
if (N < 2) {
return 0;
} else if (N == 2) {
return 1;
} else if (N == 3) {
return 2;
}
return process(N);
}
public static int process(int N) {
if (N == 1) {
return 1;
} else if (N == 2) {
return 2;
} else if (N == 3) {
return 3;
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N / 2; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, process(i) * process(N - i));
}
return max;
}
}
- 由于在运算过程中会出现多次调用process函数的现象,递归时将他们重复的计算,造成了·时间复杂度成指数级别增加,那么若我们将每次计算的值记录就会将复杂度将为平方级别,这就是动态规划思想。
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
if (N < 2) {
return 0;
} else if (N == 2) {
return 1;
} else if (N == 3) {
return 2;
}
int[] maxValues = new int[N + 1];
maxValues[0] = 0;
maxValues[1] = 1;
maxValues[2] = 2;
maxValues[3] = 3;
int max = 0;
//动态规划主体思想
for (int i = 4; i <= N; i++) {
max = 0;
//将N看成i计算i的最大值
for (int j = 1; j <= i / 2; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, maxValues[j] * maxValues[i - j]);
}
maxValues[i] = max;
}
//返回该值
return maxValues[N];
}
}
贪心思想
- 我们在余数不为1的情况下尽可能多的选取3,在余数为1时,将之前分开的3和余数1进行分割成2和2,这样就能最大限度的拼成最大值。
- 这种贪心思想不容易理解和想出,需要进行严格的数学证明,这里就不赘述,关于贪心算法只能尽可能的多见题型才能相对熟悉。
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
if (N < 2) {
return 0;
} else if (N == 2) {
return 1;
} else if (N == 3) {
return 2;
}
// 尽可能多的使用3为划分
int timesOf3 = N / 3;
// 若最后剩余1,此时应该将之前分开的3.1转换成2.2,这样就能最大限度的进行转化成最大值。
if (N % 3 == 1) {
timesOf3 -= 1;
}
// 2需要出现的次数
int timesOf2 = (N - timesOf3 * 3) / 2;
return (int) Math.pow(3, timesOf3) * (int) Math.pow(2, timesOf2);
}
}
位运算
整数二进制1的个数
题目:请实现一个函数,输入一个整数,返回该值二进制下多包含1 的个数。
- 整数范围有正树个负数,所以要充分考虑到负数的情况,特别是在对输入的负数值进行右移运算时,注意最高位自动补1。
位运算右移输入整数
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
int num=0;
// 指定运算32次,处理负数
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
if ((N & 1) == 1) {
++num;
}
N>>=1;
}
return num;
}
}
位运算左移1
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
int num = 0;
int flag = 1;
while (flag != 0) {
if ((flag & N) == flag) {
++num;
}
flag <<= 1;
}
return num;
}
}
将输入整数依次减1,拆分该整数的1
public class Main {
public static int processMain(int N) {
int num = 0;
while (N != 0) {
++num;
N = (N - 1) & N;// 每次运行都会将一个1消去,
}
return num;
}
}
高质量代码
规范性
- 代码的规范性:思路书写,代码布局的规范,变量方法的命名规范,
完整性
- 代码的完整性:功能完整,边界测试,负面测试,针对错误的处理能给予相应的提示。
从1打印到最大的N位数🌿🥚
题目:给定一个整数 N , 打印从1到N为整数的最大值。
- 显然这个问题不仅仅是一个简单的整数问题,若我们使用int 或 long int 表示数据大小,很有限,所以要使用字符串进行模拟数据的运算
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
processMain(3);
}
public static void processMain(int N) {
if (N <= 0) {
return;
}
char[] arr = new char[N];
Arrays.fill(arr, '0');
// 没有到达最大值就继续进行
while (!TreeIncrement(arr)) {
PrintNumbers(arr);
}
}
private static void PrintNumbers(char[] arr) {
boolean isBegin = true;
int len = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 输出要从第一个不为0的位置开始,用isBegin标记开始位置
if (isBegin && arr[i] != '0') {
isBegin = false;
}
if (!isBegin) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
private static boolean TreeIncrement(char[] arr) {
int nTakeOver = 0;// 进位标记 1
int len = arr.length;
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
char nSum = (char) (arr[i] + nTakeOver);
// 最低位要 +1
if (i == len - 1) {
nSum++;
}
if (nSum - '0' == 10) {
// 最高位变成10了,此时说明溢出了,就返回
if (i == 0) {
return true;
} else {
// 该位变成是10了,要进位,进行下一步操作。
nTakeOver = 1;// 进位 1
arr[i] = '0';// 该值变成 0
}
} else {
// 该值不为10,所以允许,直接返回
arr[i] = nSum;
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
删除链表结点
题目: 在O(1)时间内删除节点,得等单链表的·头指针个一个结点指针,定义一个函数,在规定时间复杂度内删除节点。删除节点定在该链表内。
- 单链表不能直接改变将前驱结点的next指针
- 通过将下一个值复制到删除节点,就可以删除删除借点的下一个节点来完成删除操作。
public class Main {
public static void processMain(Node header, Node deleteNode) {
if (header == null || deleteNode == null) {
return;
}
//删除节点不是尾节点,通过复制内容直接删除下一个节点
if (deleteNode.nextNode != null) {
deleteNode.num = deleteNode.nextNode.num;
deleteNode.nextNode = deleteNode.nextNode.nextNode;
} else if (header == deleteNode) {//header只有一个结点,并且就是删除的节点
header = null;
} else {//删除的借点为尾节点,只能进行遍历查找
Node tail = header;
while (tail.nextNode != deleteNode) {
tail = tail.nextNode;
}
tail.nextNode = null;
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node nextNode;
}
}
删除有序链表的重复节点
题目:在一个排序链表中,如何删除重复节点。
- 有点简单,没有思考 . . .
public class Main {
public static void processMain(Node header) {
if (header==null) {
return;
}
Node tail=header;
Node preNode=header;
while (preNode.nextNode!=null) {
Node thisNode=preNode.nextNode;
if (preNode.num!=thisNode.num) {
preNode=thisNode;
}else {
preNode.nextNode=thisNode.nextNode;
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node nextNode;
}
}
调整数组顺序使奇数位在前偶数在后
题目:输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中的数字顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数字的前半部分,所有的偶数位位于数组的后半部分。
- 显然就是一个简单的快速排序的一部分。
- 不过我们最好将比较的方法进行单写出,这样可以增加代码的复用性,更加规范。
public class Main {
public static void processMain(int [] arr) {
if (arr==null||arr.length==0) {
return;
}
int left=0;
int right=arr.length-1;
while (left<right) {
while (left<right&&!cmp(arr,left)) {
left++;
}
while (left<right&&cmp(arr, right)) {
right--;
}
if (left<right) {
int temp=arr[left];
arr[left]=arr[right];
arr[right]=temp;
}
}
}
private static boolean cmp(int[] arr, int left) {
return (arr[left]&1)==0;
}
}
鲁棒性
- 代码的鲁棒性:判断输入是否符合规范要求,对于不符合要求的输入进行适当的处理。
返回链表的倒数第k个节点
题目:给定一个单链表,和整数 K,返回单链表中倒数的第K个节点。
- 一般思路为遍历两遍链表,第一次计算总节点个数,然后在遍历走 总节点个数 - K
- 但是我们用两个步数相差K的两个指针一起遍历,在快的结束时慢的就是我们所要寻找的.
public class Main {
public static Node processMain(Node header, int k) {
if (header == null) {
return null;
}
Node tailNode = header;
int i = 0;
// 保证节点存在
while (tailNode != null && i < k) {
tailNode = tailNode.nextNode;
}
// 因为节点不存在,说明该链表一共都不存在那么多节点
if (tailNode == null) {
return null;
}
// 两个指针同时前进,直到前面的到达链表末端
Node preNode = header;
while (tailNode != null) {
tailNode = tailNode.nextNode;
preNode = preNode.nextNode;
}
return preNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
}
}
链表中环的入环节点
题目:给定一个链表的头节点,该链表包含一个环,返回该入环节点。
- 利用快慢指针第一次相遇的节点node1开始,此时让另一个指针指向头节点node2,走相同的步数就是入环节点。
public class Main {
public static Node processMain(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return null;
}
boolean flag = false;
Node quick = header;
Node slow = header;
while (quick.nextNode != null && quick.nextNode.nextNode != null) {
slow = slow.nextNode;
quick = quick.nextNode.nextNode;
// 存在环,就退出循环
if (slow == quick) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
// 无环就返回null
if (!flag) {
return null;
}
// 走相同的步数找入环节点
Node tailNode = header;
while (tailNode != slow) {
tailNode = tailNode.nextNode;
slow = slow.nextNode;
}
// 相交节点就是入环节点
return tailNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
}
}
反转单链表
题目:给定一个链表的头结点,返回链表反转后的头结点。
public class Main {
public static Node processMain(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return null;
}
Node preNode = null;
Node tempNode = null;
Node thisNode = header;
while (thisNode != null) {
tempNode = thisNode.nextNode;
thisNode.nextNode = preNode;
preNode = thisNode;
thisNode = tempNode;
}
return preNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
}
}
合并两个排序链表
输入两个有序链表的头结点,返回合并后的有序链表头结点。要求空间复杂度为O(1)。
递归实现
public class Main {
public static Node merge(Node header_1, Node header_2) {
if (header_1 == null) {
return header_2;
} else if (header_2 == null) {
return header_1;
}
Node mergeHeader = null;
if (header_1.num < header_2.num) {
mergeHeader = header_1;
mergeHeader.nextNode = merge(header_1.nextNode, header_2);
} else {
mergeHeader = header_2;
mergeHeader.nextNode = merge(header_1, header_2.nextNode);
}
return mergeHeader;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node nextNode;
}
}
循环实现
public class Main {
public static Node merge(Node header_1, Node header_2) {
if (header_1 == null) {
return header_2;
} else if (header_2 == null) {
return header_1;
}
Node mergeHeader = header_1.num < header_2.num ? header_1 : header_2;
Node tailNode = mergeHeader;
Node tempNode;
while (header_1 != null && header_2 != null) {
if (header_1.num < header_2.num) {
tailNode.nextNode = header_1;
header_1 = header_1.nextNode;
} else {
tailNode.nextNode = header_2;
header_2 = header_2.nextNode;
}
tailNode = tailNode.nextNode;
}
tailNode.nextNode = header_1 == null ? header_2 : header_1;
return mergeHeader;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node nextNode;
}
}
树的子结构🔐
输入两棵二叉树根节点A、B,判断 B 是不是 A 的子树。
- 遍历A树,若某个节点和B根节点值相同就从该节点判断。
- 每个状态的判断情况均需要考虑,当一次判断成功均整个程序返回成立。
- 注意在调用时,一定要注意是否为null,以免出现异常。
public class Main {
public static boolean subTree(Node A, Node B) {
boolean isSub = false;
if (A != null && B != null) {
if (A.num == B.num) {
isSub = com(A, B);// 判断B是否为从A开始的子树
}
// 未成功
if (!isSub) {
isSub = subTree(A.leftNode, B);// 向左方向尝试
}
// 未成功
if (!isSub) {
isSub = subTree(A.rightNode, B);// 向右方向尝试
}
}
return isSub;
}
private static boolean com(Node a, Node b) {
if (b == null) {
return true;
}
if (a == null) {
return false;
}
if (a.num != b.num) {
return false;
}
// 保证每一子步均成立
return com(a.leftNode, b.leftNode) && com(a.rightNode, b.rightNode);
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
解决面试思路
抽象问题形象化
二叉树的镜像
题目:请完成一个函数,输入一个树的根节点,返回该二叉树镜像的根节点。
- 可以将大问题换成一个个子问题,将转化成递归问题实现
- 该题就是将每个节点作为根节点,将左右节点进行左右交换,注意 防止节点的覆盖。
方法一
public class Main {
public static Node resverse(Node header) {
if (header==null) {
return null;
}
//为什么要先存起来呢?因为在下一步运行时,会将header.leftNode指向改变,造成无法定位之前的Node节点
Node tempNode=header.leftNode;
header.leftNode=resverse(header.rightNode);
header.rightNode=resverse(tempNode);
return header;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
方法二
public class Main {
public static void resverse(Node header) {
if (header==null) {
return;
}
if (header.leftNode==null&&header.rightNode==null) {
return;
}
Node tempNode=header.leftNode;
header.leftNode=header.rightNode;
header.rightNode=tempNode;
if (header.leftNode!=null) {
resverse(header.leftNode);
}
if (header.rightNode!=null) {
resverse(header.rightNode);
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
判断对称二叉树🔐
题目:请完成一个函数,用于判断二叉树是否是对称的,给定根节点,输出boolean数据。(所有的非满二叉树均不对称)
- 在保证节点非空情况下,保证每次进入一个函数时,走到的两个节点均相对于该树对称
- 建立两个指针tail1,tail2均从header根节点开始,两个指针移动时一直保证步调方向总是相反的,即:tail1左,tail2就向右,tail1右,tail2就向左。
public class Main {
public static boolean isSym(Node header) {
return isSym(header,header);
}
private static boolean isSym(Node tail1, Node tail2) {
if (tail1==null&&tail2==null) {
return true;
}
if(tail1==null||tail2==null) {
return false;
}
if(tail1.num!=tail2.num) {
return false;
}
// 两个方向均保证步调相反
return isSym(tail1.leftNode,tail2.rightNode)&&
isSym(tail1.rightNode,tail2.leftNode);
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
顺时针打印矩阵
题目:顺时针打印矩阵。
- 采用宏观调度的方法,不拘泥于一个个细节问题。
- 只要获取并根据每个大循环的限制条件进行限制输出。
class Main {
public static void print(int[][] arr) {
int firstRow = 0;
int firstLine = 0;
int secondRow = arr.length - 1;
int secondLine = arr[0].length - 1;
// 宏观限制单词打印的限制条件
while (firstLine <= secondLine && firstRow <= secondRow) {
print(arr, firstRow++, firstLine++, secondRow--, secondLine--);
}
}
// 宏观的单词输出函数
private static void print(int[][] arr, int firstRow, int firstLine, int secondRow, int secondLine) {
if (firstLine == secondLine) {
for (int i = firstRow; i <= secondRow; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][firstLine] + " ");
}
} else if (firstRow == secondRow) {
for (int i = firstLine; i <= secondLine; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[firstRow][i] + " ");
}
} else {
int curR = firstRow;
int curL = firstLine;
while (curL != secondLine) {
System.out.print(arr[firstRow][curL++] + " ");
}
while (curR != secondRow) {
System.out.print(arr[curR++][secondLine] + " ");
}
while (curL != firstLine) {
System.out.print(arr[secondRow][curL--] + " ");
}
while (curR != firstRow) {
System.out.print(arr[curR--][firstLine] + " ");
}
}
}
}
抽象问题具体化
包含min的数据栈结构
题目:请完成一个栈结构,能随时获取栈中最小元素,push、pop、getMin函数的时间复杂度均为 O(1)
- push和pop函数时间复杂度时间复杂度均为O(1)
- getMin函数要想实现O(1),定说明最小值可以直接获取,实际上在最开始push的时候,我们仅能判断push进来的元素和之前栈中最小元素的大小关系,并且之前的最小值也是根据每一次push进来的元素进行判断的。那么我呢就只在push的时候判断并记录即可。
class MyStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MyStack() {
this.stack = new Stack<>();
this.minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(Integer x) {
stack.add(x);
minStack.add(!minStack.isEmpty() && minStack.peek() < x ? minStack.peek() : x);
}
public Integer pop() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) return null;
minStack.pop();
return stack.pop();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
栈的压入弹出序列🔐
题目:给定两个整数序列,第一个为压入顺序,在压入过程中随时可以弹出元素,判断第二个序列是否可能为正确的弹出顺序。
public class Main {
public static boolean isSuccess(int[] pushARR, int[] popArr) {
if (pushARR == null || popArr == null || pushARR.length != popArr.length) {
return false;
}
int N = pushARR.length;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int pushIndex = 0, popIndex = 0;
while (popIndex < N) {
while (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != popArr[popIndex]) {
// 若已经输入完了还没有和popArr此时相匹配的,此时退出就返回false
// 此时的栈必定不为空,若为空:
// 上次必匹配成功了,栈中删除一个元素,此时,pushIndex, popIndex值相同
// - 若均为N,那个在上次删除后不满足:popIndex == N ,不会进入循环
// - 若 popIndex < N 不能进入该判断
if (pushIndex == N) {
return false;
}
// 如果栈空间有限制,可以在此处判断栈是否为满
// if(stack.size() > maxNum)
// return false;
stack.push(pushARR[pushIndex++]);
}
stack.pop();
popIndex++;
}
// 若退出循环 popIndex==N 、stack.isEmpty() 均成立
return true;
}
}
从上到下打印二叉树
题目:请完成一个函数,给定头结点,横向打印二叉树。
public class Main {
public static void process(Node root) {
if (root==null) {
return;
}
Deque<Node> deque=new ArrayDeque<>();
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node tempNode=deque.poll();
System.out.print(tempNode.num+" ");
// 左不空
if (tempNode.leftNode==null) {
deque.add(tempNode.leftNode);
}
// 右不空
if (tempNode.rightNode==null) {
deque.add(tempNode.rightNode);
}
}
}
public static class Node{
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
分行从上到下打印二叉树🔐
题目:在上一题的基础上将每一行的节点值打印在不同的行上。
public class Main {
public static void process(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 遍历该层的最后一个节点
Node thisFloorLastNode = root;
// 遍历该层节点下一层的最后一个节点,用于更新thisFloorLastNode作为结束标志
Node nextFloorLastNode = null;
Deque<Node> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
Node tempNode = deque.poll();
System.out.print(tempNode.num + " ");
// 随时不管是左还是右有节点,都要更新nextFloorLastNode节点指向
if (tempNode.leftNode == null) {
deque.add(tempNode.leftNode);
nextFloorLastNode = tempNode.leftNode;
}
if (tempNode.rightNode == null) {
deque.add(tempNode.rightNode);
nextFloorLastNode = tempNode.rightNode;
}
// 该层结束,就要更新层结束标志。
if (tempNode == thisFloorLastNode) {
thisFloorLastNode = nextFloorLastNode;
nextFloorLastNode = null;
System.out.println();// 分行
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
盘旋式打印二叉树结点
题目:实现一个函数,给定根节点,第一行节点从左向右打印,第二行从右向左打印,第三行从左向右打印,以此类推。
- 假设第N行从左向右遍历,将通过第N层获取N+1层节点是从左向右的,但是N+1层我们的需求是从右向左的,显然用栈存储通过第N层遍历的元素。
- 而且存储N+1层的时候不能覆盖第N层的元素,所以要用两个栈结构。
public class Main {
public static void process(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 创建两个栈结构
Stack<Node>[] stack = new Stack[] { new Stack<>(), new Stack<>() };
int current = 0;// 当前需要遍历的层需要的栈索引
int next = 1;// 遍历(删除)stack[current]时,填充stack[next]位置的栈空间
stack[current].push(root);// 将根节点放入当前栈中
while (!stack[0].isEmpty() || !stack[1].isEmpty()) {
Node tempNode = stack[current].pop();
// 由于遍历不同层所需要的填入stack[next]顺序不同,所以要分开。
if (current == 0) {
// 不为空就要入栈
if (tempNode.leftNode != null) {
stack[next].push(tempNode.leftNode);
}
if (tempNode.rightNode != null) {
stack[next].push(tempNode.rightNode);
}
} else {
// 不为空就要入栈
if (tempNode.rightNode != null) {
stack[next].push(tempNode.rightNode);
}
if (tempNode.leftNode != null) {
stack[next].push(tempNode.leftNode);
}
}
// 若当前栈空,说明该层节点结束,进行遍历另一个栈结构
if (stack[current].isEmpty()) {
System.out.println();
// 转换栈结构的索引
current = 1 - current;
next = 1 - next;
}
}
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
二叉搜索树的后序遍历🔐
题目:给定一个数组,判断该数组能否转成某一个一搜索二叉树的后序遍历的便利结果,返回 boolean类型数据。
- 还是要知道二叉搜索树的后序遍历特征,最后一个元素定能将前面的元素分成两个部分,一小一大。
- 然后用递归继续判断分成两份的元素是否都符合
public class Main {
public static boolean process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length <= 2) {
return true;
}
return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
/**
* @param arr 目标数组
* @param start 起始索引
* @param end 结尾索引
* @return 是否符合特征
*/
private static boolean process(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
// 递归结束条件
if (start == end) {
return true;
}
int gap = arr[end];
int i = start;
// 后序遍历的最后一个节点定能将搜索二叉树分成两份,左小,右大
for (; i < end; i++) {
if (arr[i] > gap) {
break;
}
}
// 此时的arr[i]为大于gap的最小值
int j = i;
// 判断arr[i...end-1]是否均比gap大
for (; j < end; ++j) {
if (arr[j] < gap) {
return false;
}
}
// 左右两份分别进行判断
// 左为小的,不包括arr[i]
boolean left = process(arr, start, i - 1);
// 右为大的,包括arr[i],但是注意不能包含arr[end],因为已经判断过了
boolean right = process(arr, i, end - 1);
// 左右均成立才整体成立
return left && right;
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
二叉树中和为某一路径
题目:给定一个二叉树根节点和一个 整数 Intend ,打印二叉树中所有从根节点到叶子节点路径和为 Intend 的所有路径。
- 很显然就是一个简单的递归回溯函数。
public class Main {
public static void process(Node root, int intend) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
process(root, intend, 0, stack);
}
/**
* @param node 当前节点
* @param intend 目标值
* @param curNum 当前值
* @param stack 存储路径
*/
private static void process(Node node, int intend, int curNum, Stack<Node> stack) {
curNum += node.num;
stack.add(node);// 路径添加
// 为叶子节点且和目标值相同
if (node.leftNode == null && node.rightNode == null && intend == curNum) {
for (Node n : stack) {
System.out.print(n.num);
}
System.out.println();
}
if (node.leftNode != null) {
process(node.leftNode, intend, curNum, stack);
}
if (node.rightNode != null) {
process(node.rightNode, intend, curNum, stack);
}
// 路径删除
stack.pop();
}
public static class Node {
int num;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
分解问题简单化
复杂链表的复制
题目:给定一个链表,该链表除了有nextNode外,还有一个指针complexNode,该指针可以指向链表任意位置。给定头结点,范围复制节点后的头结点。
节点类型:
class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
Node complexNode;
}
借助map实现
public class Main {
public static Node copy(Node header) {
if (header == null) {
return null;
}
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
Node tail = header;
// 遍历填入哈希表
while (tail != null) {
map.put(tail, new Node(tail.value));
tail = tail.nextNode;
}
tail = header;
// 根据哈希表一一对应情况,按照所给的链表链接情况连接复制链表。
while (tail != null) {
map.get(tail).nextNode = map.get(tail.nextNode);
map.get(tail).complexNode = map.get(tail.complexNode);
tail = tail.nextNode;
}
// 返回赋值后的链表头结点,直接在map中获取
return map.get(header);
}
class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
Node complexNode;
}
}
相对位置模拟map实现
public class Main {
public static Node copy(Node header) {
if (header == null)
return null;
Node tail = header;
Node n;
// 在每个原来所给链表节点后再添加一个copy节点,本质还是使用位置信息模拟了map方法
while (tail != null) {
n = tail.nextNode;
tail.nextNode = new Node(tail.value);
tail.nextNode.nextNode = n;
tail = n;
}
tail = header;
Node copyTail;
// 复制处理complexNode节点(只对原节点判断)
while (tail != null) {
copyTail = tail.nextNode;
if (tail.complexNode != null)
copyTail.complexNode = tail.complexNode.nextNode;
tail = tail.nextNode.nextNode;//该节点不为空,必定存在下一个节点
}
// 确定原链表和复制链表的头结点。
Node copyHeader = header.nextNode;// 若不提前标记会被回收
tail = header;
// 原链表和复制链表分离
while (tail != null) {
n = tail.nextNode.nextNode;
copyTail = tail.nextNode;// 复制链表的节点
if (n != null)
copyTail.nextNode = n.nextNode;// 连接复制的链表
tail.nextNode = n;// 连接原链表
tail = n;// 更新判断下一轮
}
return copyHeader;
}
class Node {
int value;
Node nextNode;
Node complexNode;
}
}
二叉搜索树和双向链表🔐
题目:输入一棵搜索二叉树,将二叉树转成双向链表的形式。leftNode为前驱结点,rightNode为后继节点。
- 注意遍历方向,防止空指针出现。
- 向左右遍历过程中注意前驱结点的变化情况。
public class Main {
public static Node process(Node root) {
Node firstNode = null;
convertNode(root, firstNode);
return firstNode;
}
/**
* @param pThisNode 当前节点
* @param pLastNode 二叉树中序遍历的上一个节点
*/
private static void convertNode(Node pThisNode, Node pLastNode) {
if (pThisNode == null) {
return;
}
// 向左寻找节点
if (pThisNode.leftNode != null) {
convertNode(pThisNode.leftNode, pLastNode);
}
// 连接前驱结点
pThisNode.leftNode = pLastNode;
// 连接上一个节点的后继节点
if (pLastNode != null) {
pLastNode.rightNode = pThisNode;
}
// 如果存在右节点,就将该节点作为前驱节点向右遍历
if (pThisNode.rightNode != null) {
convertNode(pThisNode.rightNode, pThisNode);
}
}
class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
字符串的全排列🔐
题目:给定一个字符串,输出所有字符串的所有排列组合。
- 我们通常都思路都是将所有字符依次放在最前面,例如ABC,第一位为A,B,C,然后判断第二位,那么我们如何在字符串中标记该字符已经被我们安排在前面了?
- 若我们使用下标的方式,那么在每次选择都会产生一个下标,这样会很乱。
- 于是我们可以通过将欲放在前面的字符就直接放在前面(将字符一次和后面的交换),用一个下标指引我们前面已经定了多少的元素。
- 但是若我们交换后在后续调用时,数据顺序已经打乱,我们可能会造成重复情况,所以我们在每次运行后再将数据交换变成原来位置。
- 但是当数据有重复字符时,会出现重复的全排列,这是我们就要判断交换的字符是否和之前交换的相同,若相同,就不用交换
class Main {
public static List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
public static void process(String string){
char[] chars = string.toCharArray();
process(chars,0);
}
private static void process(char[] chars, int i){
if (i==chars.length){//结果
list.add(new String(chars));
return;
}
boolean[] isVisited=new boolean[26];//默认只有大写字母
for (int j=i;j<chars.length;j++){
if (!isVisited[chars[j]-'A']){//是否重复
isVisited[chars[j]-'A']=true;
swap(chars,i,j);//交换
process(chars,i+1);//递归
swap(chars,i,j);//恢复
}
}
}
private static void swap(char[] chars,int i, int j) {
char c = chars[i];
chars[i]=chars[j];
chars[j]=c;
}
}
优化时间和空间效率
- JAVA中字符串经常拼接用StringBuffer,String会浪费很大空间和时间。
时间效率
最小的k个数
题目:给定一个随机整数数组和一个整数 k,输出数组中最小的 k个数字。
快排子过程partition实现
- 会改变数组本身
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
public class Main {
public static void process(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr.length < k) {
return;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
// 以partition为分界点
int index = partition(arr, 0, right);
while (index != k - 1) {
// partition基准值大了
if (index > k - 1) {
right = index - 1;
index = partition(arr, left, right);
} else {// partition基准值小了
left = index + 1;
index = partition(arr, left, right);
}
}
// 输出数据
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
// 快排子过程
private static int partition(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
int base = arr[left];
int i = left;
int j = right;
while (i != j) {
while (i != j && arr[j] >= base) {
j--;
}
while (i != j && arr[i] <= base) {
i++;
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
int temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
return i;
}
}
优先队列实现
- 时间复杂度O(N*logk)
public class Main {
public static void process(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr.length < k) {
return;
}
// 大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> deQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o2, o1));
// 保持大根堆数据等于k
for (int i : arr) {
if (deQueue.size() < k) {
deQueue.add(i);
} else if (deQueue.peek() > i) {
deQueue.poll();
deQueue.add(i);
}
}
// 输出数据
while (!deQueue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(deQueue.poll());
}
}
}
数据流中的中位数
题目:连续给定未知个整数,可以随时以时间复杂度 O(1) 实现这些树中的中位数的获取。
- 构建两个堆,一个大堆,一个小堆,大堆放较小的元素,小堆放较大的元素
- 持续保持两个堆的元素个数差不超过1
- 超过1,将大堆中堆顶元素放进小堆或将小堆堆顶元素放进大堆。
- 这样中位数就一直只和两个堆的堆顶元素相关
class Tree {
private PriorityQueue<Double> little;// 存较大数据,取出较小元素
private PriorityQueue<Double> large;// 存较小数据,取出较大元素
public Tree() {
little = new PriorityQueue<>();
large = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2, o1));
}
public void add(Double x) {
// 若都没有元素,优先在其中任意一个存放该元素。
if (little.size() == 0 && large.size() == 0)
large.add(x);
else {
// 往那个堆中放
if (large.peek() < x) {
little.add(x);
} else {
large.add(x);
}
// 若两个堆大小差值绝对值大于1,要调整,以便更好输出中位数。
if (little.size() - large.size() > 1)
large.add(little.poll());
else if (little.size() - large.size() < -1)
little.add(large.poll());
}
}
public Double getMed() {
if (little.size()==0&&large.size()==0)
return null;
else if (little.size() == large.size())
return (little.peek() + large.peek()) / 2;
else if (little.size() - large.size() > 0)
return little.peek();
else
return large.peek();
}
}
连续子数组的最大和🔐
题目:给定一个数组吗,其中均为整数,返回数组中一个或多个连续的元素组成的累加和的最大值。时间复杂度 O(N)
- 若想获取连续累加和最大值,那么前面的累加和定为非负数,若前面一部分的累加和值为负数,定不能在当前计算的最大累加和中。
public class Main {
public static Integer maxLenNum(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
return null;
}
// 记录最大值
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int cur = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
// cur记录累加,现在不更新,等判断后更新。
cur += i;
res = Math.max(res, cur);
// cur记录累加和,若累加和小于0,就重置cur为0,从新开始累加。
cur = Math.max(cur, 0);
}
return res;
}
}
整数1~N中1出现的次数🔐
题目:从 1~N 所有整数中出现 1 的次数。
解决思路:
- 例如:1 ~ 46372和1 ~ 12345
- 先拆分76372成1 ~ 6372和 6373 ~ 76372
- 先看6373 ~ 76372,最高位7,在最高位不为零时计算最高位中1出现次数和最高位出现时除最高位以外1出现的次数。
- 对于最高位若为不为1,对于6373 ~ 76372就是最高位出现1的情况有 10^4,就是只能在10000~19999出现。
- 最高位为1,就像2346~12345,万位就是10000 ~ 12345,就是2345+1个
- 计算6373 ~ 76372中除了最高位(万位)中1出现的次数,就是简单的排列组合。7 *(10^4) * 4
- 此时6373 ~ 76372中的1就计算完成,然后计算1 ~ 6372中1的出现次数,递归实现。
public class Main {
public static int process(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
return process(arr, 0);
}
private static int process(char[] arr, int index) {
// 判断最高位是否为1,进而判断1在最高位出现的次数
int first = arr[index] - '0';
// 看看除了最高位外,还剩多少位,用于判断最高位和除去最高位剩余数的出现次数
int len = arr.length - index;
// 若此时是最后一位,就根据first判断≤first的值中出现1的个数。
if (len == 1 && first == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (len == 1 && first > 0) {
return 1;
}
// 记录当前最高位1出现的次数
int numFirstDigit = 0;
// 若最高位不是 > 1,那么在最高位出现的1的次数定为10的倍数
// 比如 42346 numFirstDigit就是10000~42346最高位1的个数,也就是10000~19999
// 若为1,最高位出现的次数就是根据当前最高位后面的值大小确定
// 比如 12345,就是10000~12345
if (first > 1) {
numFirstDigit = (int) Math.pow(10, len - 1);
} else if (first == 1) {
// 从0开始,别忘了+1
numFirstDigit = Integer.parseInt(new String(arr).substring(index + 1)) + 1;
}
// 当最高位为<=first情况下,从当前最高位后出现的1的个数。
// 比如 42346
// 最高位4,numOtherDigits就是2347~42346除去万位上的1的个数,万位的个数已经得出过,就是:numFirstDigit
int numOtherDigits = first * (len - 1) * ((int) Math.pow(10, len - 2));
// 根据上一个例子:numRecursive就是剩余1~2346中1出现的个数。递归来求。
int numRecursive = process(arr, index + 1);
return numFirstDigit + numOtherDigits + numRecursive;
}
}
数字序列中的某一位数🔐
题目:数字以012345678910111213145…的格式序列化到一个字符序列中。在这个序列中,第5位(从0开始计数)是5,第13位是1,第19位是4,等等。请写一个函数,求任意第n位对应的数字。
- 先确定该值在几位组成的序列中。
- 根据值和几位确定在序列中的索引位置。
public class Main {
public static int process(int index) {
if (index < 0) {
return -1;
}
int digits = 1;
while (true) {
// digits位数一共有几个
int numbers = countOfIntegers(digits);
// numbers * digits表示digits位数一共占据那么多位置索引
if (index < numbers * digits) {// 是否在digits位数字的范围内
return digitAtIndex(index, digits);
}
// 迭代后的位置占据
index -= digits * numbers;
++digits;
}
}
private static int digitAtIndex(int index, int digits) {
// (int)Math.pow(10, digits-1)表示小于digits位数的数一共有多少+1
// index / digits表示此时digits位数的 第几个-1
// 我们所要得值就在number中
int number = (int) Math.pow(10, digits - 1) + index / digits;
// index % digits表示number的第几位
// indexFromRight是从右边数第几位是我们的目标值
int indexFromRight = digits - index % digits;
// 将目标值放在个位
number /= ((int) Math.pow(10, indexFromRight - 1));
// 返回个位的值
return number % 10;
}
private static int countOfIntegers(int digits) {
if (digits == 1) {
return 10;
}
int count = (int) Math.pow(10, digits - 1);
return 9 * count;
}
}
把数组排成最小的数
题目:给定一个数组,把数组中所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出所有拼接数字中最小的数字。例如{ 3 , 32, 321 },组成最小值为321323。
- 两个数字n、m,若nm<mn,就先打印n,后打印m,反之先m后n。
- 该思想可以推广到N个数字,推广过程略。
- 另外若数组过长就不能用整数存储,就需要用StringBuffer存储判断。
public class Main {
public static void process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return;
}
String[] strings = new String[arr.length];
// 防止溢出
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
strings[i] = String.valueOf(arr[i]);
}
// 按照所需排序
Arrays.sort(strings, (o1, o2) -> (o1 + o2).compareTo(o2 + o1));
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.print(string);
}
}
}
数字翻译成字符
题目:给定数字字符串,按照一下规则翻译成字母,问一共有几种方式。规则:1–>‘a’、2–>‘b’、3–>‘c’、…… 、26–>‘z’ 。
- 仅仅是一个从左向右的递归尝试模型。
public class Main {
public static int process(String s, int i) {
// 若一个不剩或这还剩一个,就返回1(保证剩的不为0),若此时不返回,说明还剩至少两个字符
if (s.length() == i || (s.length() == i + 1 && s.charAt(i) != '0'))
return 1;
if (s.charAt(i) == '0')
return 0;// 没有0开头匹配的元素
int res = process(s, i + 1);// 一个字符的
if (Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i, i + 2)) <= 26)
res += process(s, i + 2);// 若满足匹配条件,进行两个字符的
return res;// 累加的结果返回就行了
}
}
礼物的最大值
题目:给定一个整数矩阵,从左上开始到右下角,只能向下或者右移动,问路径上的最大的是多少?
- 简单的递归尝试模型。
- 可以转化成动态规划。
暴力递归
public class Main {
public static int process(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return process(arr, arr.length - 1, arr[0].length - 1, 0, 0);
}
public static int process(int[][] arr, int M, int N, int row, int line) {
if (row == M && line == N) {
return arr[row][line];
}
if (row == M) {
return process(arr, M, N, row, line + 1) + arr[row][line];
}
if (line == N) {
return process(arr, M, N, row + 1, line) + arr[row][line];
}
return Math.max(process(arr, M, N, row + 1, line), process(arr, M, N, row, line + 1)) + arr[row][line];
}
}
动态规划
public class Main {
public static int process(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int M = arr.length;
int N = arr[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[M][N];
// 临界值填入
dp[M - 1][N - 1] = arr[M - 1][N - 1];
for (int i = M - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
dp[i][N - 1] = dp[i + 1][N - 1] + arr[i][N - 1];
}
for (int i = N - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
dp[M - 1][i] = dp[M - 1][i + 1] + arr[M - 1][i];
}
// dp表根据动态规划依赖填充
for (int row = M - 2; row >= 0; --row) {
for (int line = N - 2; line >= 0; --line) {
dp[row][line] = Math.max(dp[row + 1][line], dp[row][line + 1]) + arr[row][line];
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
最长不含重复字符的子字符串🔐
题目:给定一个只包含小写字母的字符串,找出最长不重复在子字符串,并返回该最长子字符串的长度。例如 “asadfgsg” 最长为“sadfg”,返回 5
- 假设有一个遍历下标 i,以arr[ i ]结尾的最长不重复子串的开头为:arr[ i ]字符上次出现的位置和之前为了满足 i 前面其他这种行为的位置的离 i 最近的位置就是最长的子字符串。
public class Test {
public static int maxUnique(String str) {
if (str == null || str.equals("")) {
return 0;
}
char[] chas = str.toCharArray();
//记录每个字符上次出现的位置
int[] map = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
map[i] = -1;// 上次出现初始为-1
}
int len = 0;// 结果值
int pre = -1;// 当前字符串最长向前伸长下标位置记录
int cur = 0;// 临时pre,用于pre的更新
for (int i = 0; i != chas.length; i++) {
// 前面的字符串最长位置,就是arr[i]上一次出现位置和满足其他字符的最长位置
pre = Math.max(pre, map[chas[i]-'a']);
cur = i - pre;// 此时字符串最长伸展位置,cur就是以arr[i]结尾的非重复最长字符串长度。
len = Math.max(len, cur);//max的len更新
map[chas[i]] = i;//记录此时字符的位置,用于下次查找重复位置
}
// 返回结果
return len;
}
}
时间效率和空间效率的平衡
- 一般来说我们追求时间效率比空间更加优秀,但是对于嵌入式来说,有时也会浪费一些时间来减少空间的消耗,因为嵌入式的内存是非常有限的。
丑数
题目:我们把只包含质因子2、3、5的数称为丑数,求正整数域上的第N个丑数。另外习惯上将1作为第一个丑数。
- 一般思路:第一整数1~N依次判断是否为丑数。
- 优化思路:和求质数不同,丑数有可预期性,可以直接通过丑数乘以2、3或5得到。所以我们只需要在1的基础之上寻找丑数。
- 值得注意的是:在得到第N-1个丑数后,并不能直接通过N-1来推导出第N个丑数,因为第N个丑数可能要通过第N-1前面的数获取。
public class Main {
public static int process(int N) {
if (N<=0) {
return 0;
}
int[] uglyNumber=new int[N];
uglyNumber[0]=1;
int index=1;
// multiply_2_3_5三个索引指向和uglyNumber[index]大小相近的值
int multiply_2=0;
int multiply_3=0;
int multiply_5=0;
int nextUglyNum;
while (index<N) {
nextUglyNum=Math.min(uglyNumber[multiply_2]*2
,Math.min(uglyNumber[multiply_3]*3, uglyNumber[multiply_5]*5));
uglyNumber[index]=nextUglyNum;
while (multiply_2!=index&&uglyNumber[multiply_2]*2<=nextUglyNum) {
++multiply_2;
}
while (multiply_3!=index&&uglyNumber[multiply_3]*3<=nextUglyNum) {
++multiply_3;
}
while (multiply_5!=index&&uglyNumber[multiply_5]*5<=nextUglyNum) {
++multiply_5;
}
++index;
}
return uglyNumber[N-1];
}
}
数组中的逆序对🔐
题目:数组中的两个数,若前面的一个数大于后面的一个数,那么这两个数组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,返回逆序对的个数。
- 归并排序过程,和求小数和相似。
- 关于为什么归并排序过程中能实现单方向的大小判断?实际上是因为归并排序在排序过程中保持了数据的局部有序性,当合并时,在两个子数组整体之间存在相对位置关系。这也是为什么只有在合并的时候才能进行单方向上的大小判断。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return divideTest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
}
private static int divideTest(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int m = (left + right) / 2;
return divideTest(arr, left, m, temp) // 左侧的总和
+ divideTest(arr, m + 1, right, temp)// 右侧的总和
+ mergeTest(arr, left, m, right, temp);// 左侧右侧组合过程中形成总和
}
return 0;
}
private static int mergeTest(int[] arr, int left, int m, int right, int[] temp) {
int i = left;
int j = m + 1;
int tempIndex = 0;
int res = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= right) {
// 和小数和就相差在大于小于符号和这里没有乘以arr[i]
res += arr[i] > arr[j] ? (right - j + 1) : 0;
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i++] : arr[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= right)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[j++];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, left, tempIndex);
return res;
}
}
基于归并排序的小数和🔐
附加题目:小和问题和逆序对问题 小和问题 在一个数组中,每一个数左边比当前数小的数累加起来,叫做这个数组 的小和。求一个数组 的小和。 例子:[1,3,4,2,5] 1左边比1小的数,没有; 3左边比3小的数,1; 4左 边比4小的数,1、3; 2左边比2小的数,1; 5左边比5小的数,1、3、4、 2; 所以小和为1+1+3+1+1+3+4+2=16
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
return divideTest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, new int[arr.length]);
}
private static int divideTest(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int m = (left + right) / 2;
return divideTest(arr, left, m, temp) // 左侧小数和的总和
+ divideTest(arr, m + 1, right, temp)// 右侧小数和的总和
+ mergeTest(arr, left, m, right, temp);// 左侧右侧组合过程中形成的小数和总和
}
return 0;
}
private static int mergeTest(int[] arr, int left, int m, int right, int[] temp) {
int i = left;
int j = m + 1;
int tempIndex = 0;
int res = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= right) {
// 若左小,就是会出现小数的位置。个数由右侧确定。
res += arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i] * (right - j + 1) : 0;
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i] < arr[j] ? arr[i++] : arr[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[i++];
while (j <= right)
temp[tempIndex++] = arr[j++];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, left, tempIndex);
return res;
}
}
两个链表的第一公共节点
题目:给定两个无环单链表,并且其中有公共部分,实现一个函数,返回相遇的第一公共节点。
- 均遍历一遍计算节点差值步,然后重新开始长链表走差值步后,短的和此时长的同时遍历,第一个相同节点就是第一个相遇节点。
public class Main {
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null || head2 == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
//计算链表差值
while (cur1.next != null) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != null) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if (cur1 != cur2) {
return null;
}
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
//长的走到和短的长度同位置
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
//判断是否有相同节点,若无就会走到最后返回null
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
public static class Node{
int value;
Node next;
}
}
面试中的各项能力
- 沟通能力
- 学习能力
知识迁移能力
排序数组中查找数字🔐
题目:给定一个有序数组和一个值,返回该值在该数组中出现的次数。
- 若遍历整个数组,时间复杂度 O(N)
- 若二分查找这个数,一般情况O(logN)+O(1),最坏的情况时间复杂度O(1)+ O(N)
- 二分查找该值的最左的值和最右的值,时间复杂度2*O(logN)
public class Main {
public static int theNumOfK(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int first = getFirstK(arr, k);
int last = getLastK(arr, k);
if (first != -1 && last != -1) {
return last - first + 1;
}
return 0;
}
private static int getFirstK(int[] arr, int k) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int med = (((end - start) >> 1) + start);
if (arr[med] == k) {
// 是该值,就判断是不是第一个,若是返回,否则end向左收敛
if ((med > 0 && arr[med - 1] != k) || med == 0) {
return med;
} else {
end = med - 1;
}
} else if (arr[med] > k) {
end = med - 1;
} else {
start = med + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static int getLastK(int[] arr, int k) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int med = (((end - start) >> 1) + start);
if (arr[med] == k) {
// 是该值,就判断是不是最后一个,若是返回,否则start向右收敛
if ((med < arr.length - 1 && arr[med + 1] != k) || med == arr.length - 1) {
return med;
} else {
start = med + 1;
}
} else if (arr[med] > k) {
end = med - 1;
} else {
start = med + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
0~N-1中缺失的数字
题目:一个长度为N-1的递增整数数组,其中每个整数都是唯一的,范围均在0~ N-1之间,那么0~N-1之间定有一个在数组中不存在的数,返回该数。
- 显然数据和下标有紧密关系要么相等,要么相差1,并且有序,显然用改造的二分查找。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int med = right + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (med == arr[med]) {
left = med + 1;
} else {
// 结果就是下标和值不同的组合中最左位置的下标值
// 所以只在下标不同时进行判断是否为最左位置。
if (med == 0 || arr[med - 1] == med - 1) {
return med;
} else {// 不是最左位置,继续二分
right = med - 1;
}
}
}
// 程序到这里有两种情况:
// - 所有下标和数相同 left直接走到了arr.length
// - 输入的数据不符合题意
if (left == arr.length) {
return arr.length;
}
// 若不符合题意
return -1;
}
}
数组中数值和下标相等的元素
题目:假设一个单调递增的数组中每个元素数组唯一,实现一个函数,给定一个该类型数组,找出任意一个数组等于下标的元素。
- 若数值比下标小,左边定不存在
- 若数值比下标大,右边定不存在
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int med = right + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (med == arr[med]) {
return med;
}
if (med < arr[med]) {
right = med - 1;
} else {
left = med + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
二叉树的最大深度
题目:给定一个根节点,返回二叉树最大深度。
public class Main {
public static int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root==null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.leftNode),maxDepth(root.rightNode))+1;
}
public static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}
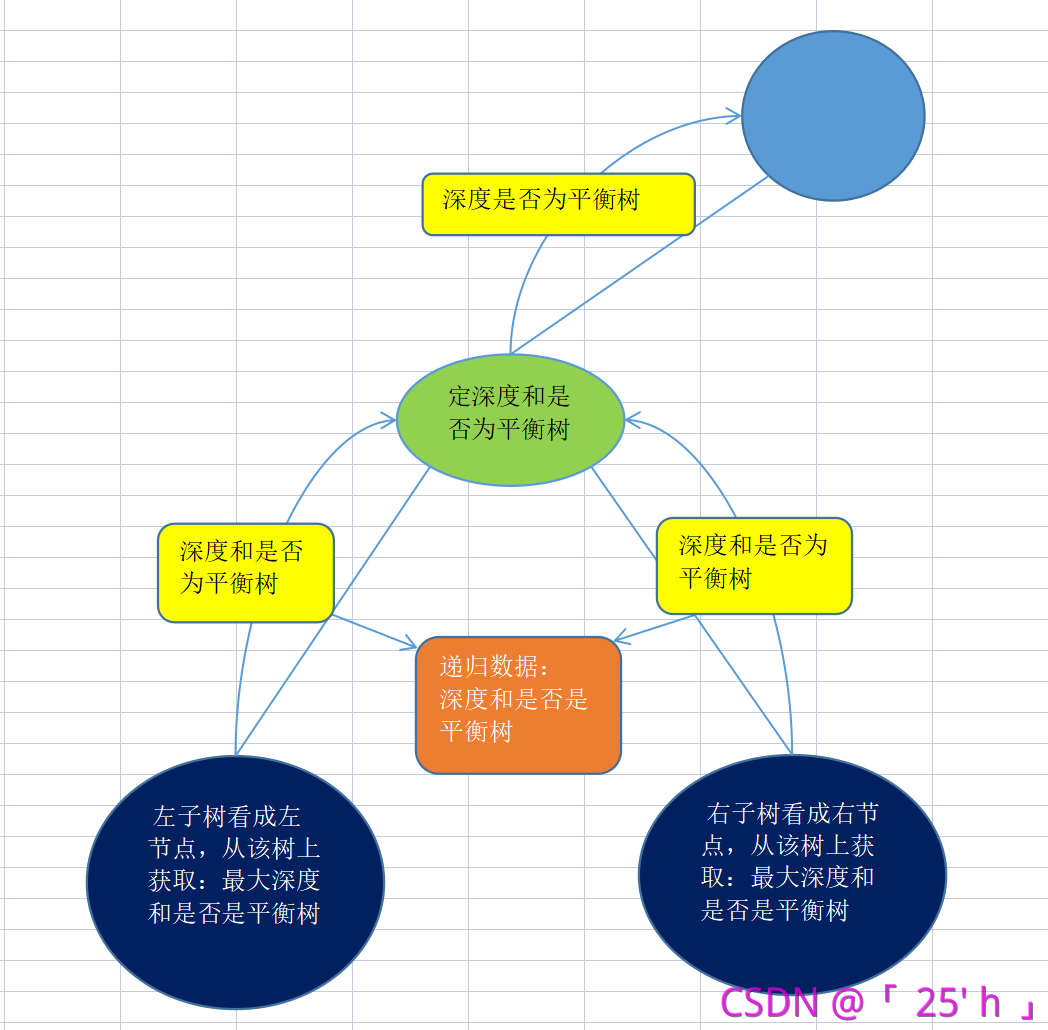
平衡二叉树
题目:给定一个根节点,判断是否为平衡二叉树。
树类递归思路:
public class Main {
public static Data isAVL(Node head) {
if (head == null)
return new Data(0, true);
Data lData = isAVL(head.left);
Data rData = isAVL(head.right);
int height = Math.max(lData.height, rData.height) + 1;
boolean flag = lData.isAVL && rData.isAVL && Math.abs(lData.height - rData.height) <= 1;
return new Data(height, flag);
}
static class Data {
int height;
boolean isAVL;
public Data(int height, boolean is) {
this.height = height;
this.isAVL = is;
}
}
}
数组中只出现一次的数字🔐
题目:给定一个整数数组,只有两个数出现了一次,其他数字均出现偶数次,输出这两个数出现一次的数。
- 根据两个值不同,定存在二进制位不同的情况,由此将数组分成两个部分,就转化成了在数组中查找有且仅有一个值出现一次的该值。
public class Main {
public static void twoSingleNum(int[] arr) {
int med = 0;
for (int a : arr) {
med ^= a;// 两个不同的单数^最后得到med
}
int rightOne = med & (~med + 1);// 取出med中二进制为1的位值(必存在,因为不同值)
int med1 = 0;
for (int a : arr) {
// 对应位为1的值取出进行^最后的到两个单数中对应位为1的值
// (a&rightOne)== 0得到对应位为0
if ((a & rightOne) == rightOne) {
med1 ^= a;
}
}
System.out.println(med1);// 两个单数其中一个值
System.out.println(med ^ med1);// 两个单数令一个值
}
}
数组中唯一只出现一次的数🔐
题目:给定一个整数数组,只有一个数出现了一次,其他数字均出现了三次,输出这一个只出现一次的数。
- 只看出现三次到数字,那么对于这些值的二进制位的累加和定能被3整除
- 现在出现了一个只出现一次的数,由于该数的存在,所有二进制位累加和除以3的余数就是该值的对应二进制位数。
public class Main {
public static int twoSingleNum(int[] arr) {
int[] bit = new int[32];// 每一位求和
for (int a : arr) {
int b = 1;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((a & b) != 0) {// 为1就累加
++bit[i];
}
b <<= 1;// 换位
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
res = res << 1;
res += (bit[i] % 3);// 取余数
}
return res;
}
}
和为s的两个数字
题目:给定一个整数递增数组和整数s,在数组中找出两个值相加为s,若存在就返回 true,不存在返回 false。
public class Main {
public static boolean process(int[] arr, int s) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return false;
}
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = arr[left] + arr[right];
if (sum == s) {
return true;
} else if (sum > s) {
--right;
} else {
++left;
}
}
return false;
}
}
和为s的连续正数序列
题目:给定一个整数s,打印所有和为s的连续正数序列。例如输入15,有1+2+3+4+5 = 4+5+6 = 7+8 = 15
public class Main {
public static void process(int s) {
if (s < 3) {
return;
}
int small = 1;
int big = 2;
int curSum = small + big;
while (small <= s / 2) {
if (curSum == s) {
Printer(small, big);
curSum -= small;
++small;
} else if (curSum < s) {
++big;
curSum += big;
} else {
curSum -= small;
++small;
}
}
}
private static void Printer(int small, int big) {
for (int i = small; i <= big; i++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
反转字符串🔐
题目:输入英文句子,返回单词的反转,例如:“I am a pig”,返回 “pig a am I"
- 整体逆序然后单独逆序。“I am a pig” --> “gip a ma I” --> “pig a am I"
public class Main {
public static String process(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
reverse(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
int begin = 0;
int end = 0;
while (begin < arr.length) {
if (end == arr.length || arr[end] == ' ') {
// arr[begin]和arr[end-1]均为字符
reverse(arr, begin, end - 1);
// 让begin指向下一个单词的第一个或越界退出
// end指向下一个单词的第一个并向后继续遍历
begin = ++end;
} else {
++end;
}
}
return new String(arr);
}
private static void reverse(char[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
while (left < right) {
char temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
++left;
--right;
}
}
}
左旋转字符串🔐
题目:给定一个字符串和一整数k,返回左旋转字符串,例如:k=3 “abcdefg” --> “defgabc”
- “abcdefg” --> “cbagfed” --> “defgabc”
public class Main {
public static String leftReverseString(String s,int k) {
if (s==null||s.length()==0) {
return null;
}
char[] arr=s.toCharArray();
reverse(arr, 0, k-1);
reverse(arr, k, arr.length-1);
reverse(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
return new String(arr);
}
private static void reverse(char[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
while (left < right) {
char temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
++left;
--right;
}
}
}
队列的最大值(双端队列)
题目:给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值例如,如果输入数组{2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,它们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5}
- 双端队列存放索引以便于数据唯一确定
- 并且对应的值的大小在双端队列中严格按照递减顺序
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int windowLen) {
int N = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[N - windowLen + 1];
// 实例化双端队列
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 先将nums前windowLen个数按照规则填入
for (int i = 0; i < windowLen; i++) {
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.getFirst()] <= nums[i]) {
deque.pollFirst();
}
deque.addFirst(i);// 填入的是索引,以便于唯一确定
}
res[0] = nums[deque.getLast()];
for (int i = windowLen; i < N; i++) {
// 保持双端队列中索引对应在nums中的数据是降序的。
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.getFirst()] <= nums[i]) {
deque.pollFirst();
}
deque.addFirst(i);// 将此时数据填入
// 当前双端队列第一个元素(最大值)是否还在滑动窗口中
if (deque.getLast() == i - windowLen) {
deque.pollLast();
}
res[i - windowLen + 1] = nums[deque.getLast()];
}
return res;
}
}
抽象建模能力
约瑟夫环🔐
public class Test {
/**
* @param N 当前元素总个数
* @param index 第index个死
* @return 最后存活的人的位次(非索引)当前该轮中的第几位
*/
public static int getLive(int N, int index) {
if (N == 1) return 1;//该1表示在最后还剩一个时的这个新一轮的索引
// 存活人在上一轮中的位次 = ( 存活人该轮中的位次 + index - 1 ) % N + 1
return (getLive(N - 1, index) + index - 1) % N + 1;
}
}
股票的最大利润
题目:假设把某股票的价格按照时间先后顺序存储在数组中,请问买卖该股票一次可能获得的最大利润是多少?例如,一只股票在某时间节点的价格为{9,1,8,5,7,12,16,14)。如果我们能在价格为5的时候买在价格为16时卖出,则能收获最大的利润11。
public class Main {
public static int process(int[] arr) {
if (arr==null||arr.length<2) {
return 0;
}
// 前面出现的最小值
int min=arr[0];
// 前面存在的最大差值
int maxSub=arr[1]-arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
maxSub=Math.max(maxSub, arr[i]-min);
// 計算差值后更新,因爲此時的最小值arr[i]不能減本身
min=Math.min(min,arr[i]);
}
return maxSub;
}
}
用位运算实现加減🔐
public class Main {
public static int add(int a, int b) {
int sum = a;
while (b != 0) {// 进位信息为0,此时sum就是结果
sum = a ^ b;// 不进位信息
b = (a & b) << 1;// 进位信息
a = sum;// 调整a值继续相加
}
return sum;
}
public static int sub(int a,int b) {
return add(a, add(~b, 1));// 取反加一就是一個數的相反數
}
}
查找树中两个节点的最近共父类节点🔐
- 该路径上不存在寻找的o1或o2,就回馈上一次递归null
- 路径上存在o1或o2,返回标记告诉上一次递归存在o1或o2
- 直到在某次递归时判断出左右路径都回馈了有o1或o2,就将该父节点返回
- 将返回的父节点以返回值的方式传给上一次递归直至结束递归。
public class Main {
/**
* @param header 根节点
* @param o1 节点一
* @param o2 节点二
* @return 最近共父节点
*
*/
public static Node ancestor(Node header, Node o1, Node o2) {
if (header == null || o1 == header || o2 == header)
return header;
Node lNode = ancestor(header.leftNode, o1, o2);
Node rNode = ancestor(header.rightNode, o1, o2);
// 该条件只会成功一次,返回的header就是我们所要找的节点
// 如何将这个节点返回第一次调用这个函数时?
// 由于我们不知道这个父节点是它的父节点的左还是右
// 但是我们知道成功进入该条件后的所有递归中只能出现一边为null,另一边为header节点
// 所以 返回: lNode != null ? lNode : rNode
// 另外这句话也会在找到目标节点前将o1或o2传到上一个递归中,代表着这个路径上存在o1或o2
// 当路径上没有o1或o2时,lNode和rNode均为空,随便返回一个
if (lNode != null && rNode != null)
return header;
return lNode != null ? lNode : rNode;
}
static class Node {
int value;
Node leftNode;
Node rightNode;
}
}






















 5033
5033











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










