sigmoid函数
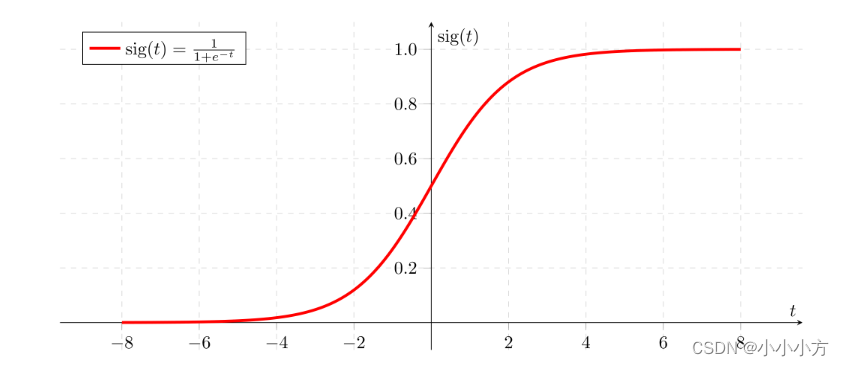
在深度学习中很少使用数学库,因为函数的输入是实数,深度学习主要使用的是矩阵和向量。
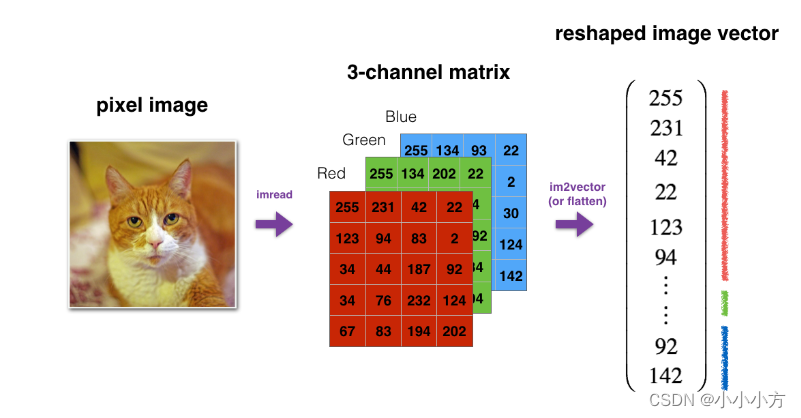
3D图像一般为(length,height,depth),作为算法输入时,转换为(length*height*depth,1)
对数据进行标准化之后,可以带来更好的性能,因为梯度下降在归一化后收敛的更快。将x更改为。
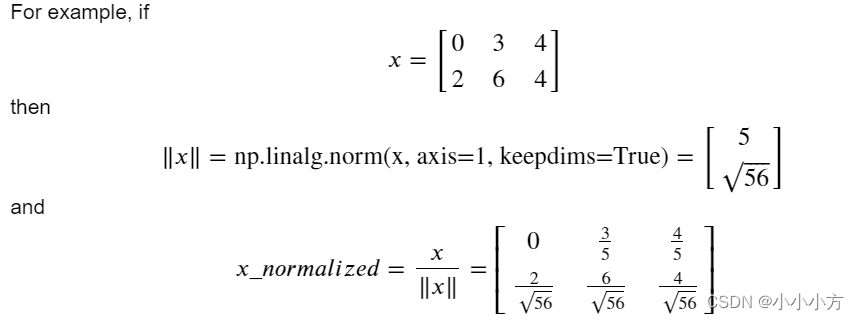
axis=1代表按照行进行标准化,keepdims=true代表应用广播机制。
softmax函数视为算法需要对两个或更多类进行分类时使用的归一化函数。
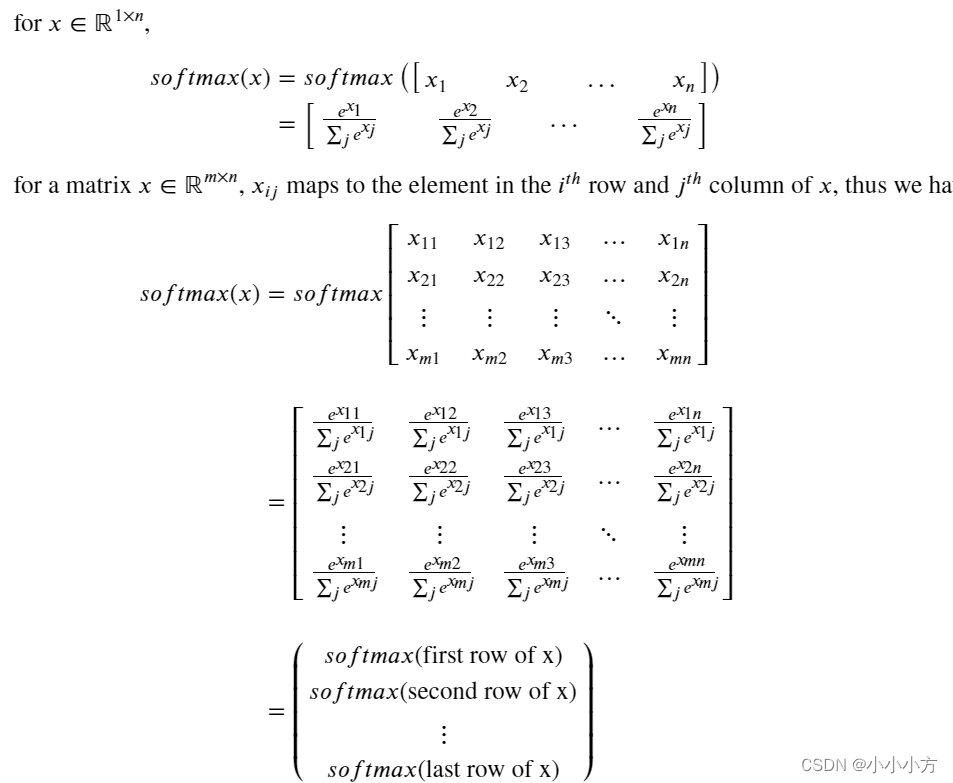
m代表训练示例的数量,每行都有相同特征的数据。应该对每个训练示例的所有特征进行归一化,因此应该对列执行softmax。
使用矢量化,确保代码的计算效率。
构建一个见到那的图像识别算法,改算法可以正确的将图片分类为猫或者非猫。
import numpy as np
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
from lr_utils import load_dataset
from public_tests import *
%matplotlib inline
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
m_train = train_set_x_orig.shape[0]
m_test = test_set_x_orig.shape[0]
num_px = train_set_x_orig.shape[1]
# 重塑训练和测试数据集
# 参数-1自行计算剩余维度
train_set_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0],-1).T
test_set_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0],-1).T
# 预处理步骤:集中和标准化数据集,从每个示例中减去整个numpy数组的平均值
# 然后将每个示例除以整个numpy数组的标准差
# 对于图片数据集,将数据集的每一行除以255就更简单
train_set_x = train_set_x_flatten / 255.
test_set_x = test_set_x_flatten / 255.
逻辑回归是最简单的神经网络
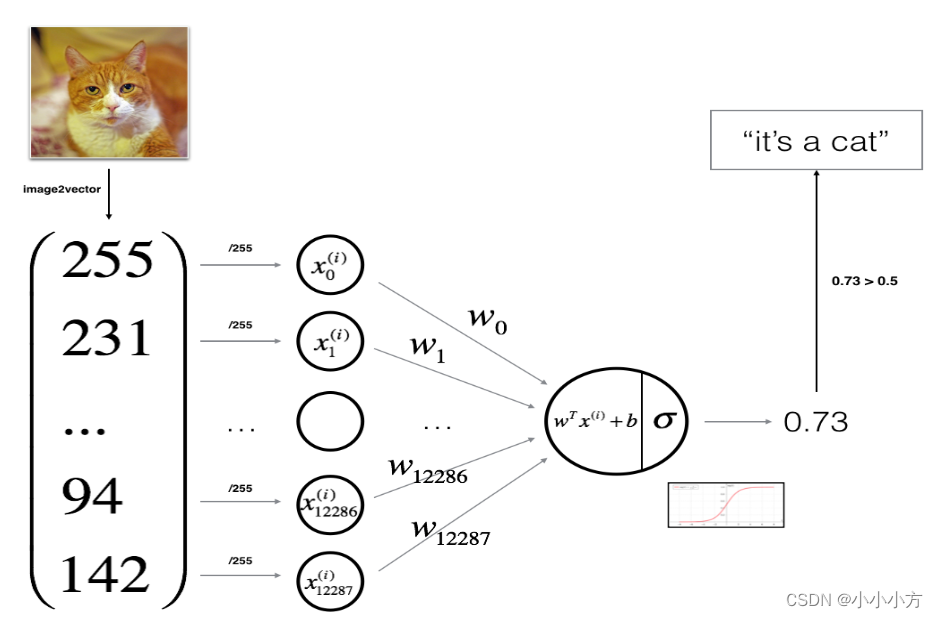
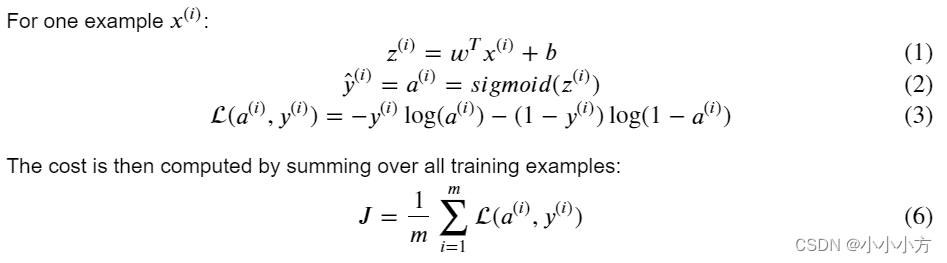
#sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(z):
s= 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
return s# 初始化参数
def initialize_with_zeros(dim):
w=np.zeros((dim,1))
b=0.0
return w,b
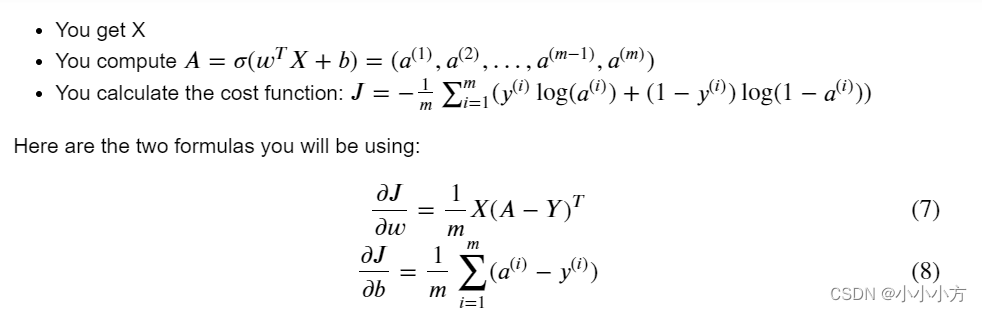
# 前向传播和后向传播
def propagate(w,b,X,Y):
m = X.shape[1]
A = sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,X)+b)
cost = -1/m*np.sum(Y*np.log(A)+(1-Y)*np.log(1-A))
dw=1/m*np.dot(X,(A-Y).T)
db=1/m*np.sum(A-Y)
cost = np.squeeze(np.array(cost))
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return grads, cost
# 优化
def optimize(w, b, X, Y, num_iterations=100, learning_rate=0.009, print_cost=False):
w = copy.deepcopy(w)
b = copy.deepcopy(b)
costs = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
grads,cost=propagate(w,b,X,Y)
dw = grads["dw"]
db = grads["db"]
w=w-learning_rate*dw
b=b-learning_rate*db
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
if print_cost:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
params = {"w": w,
"b": b}
grads = {"dw": dw,
"db": db}
return params, grads, costs# 预测
def predict(w,b,X):
m = X.shape[1]
Y_prediction = np.zeros((1, m))
w = w.reshape(X.shape[0], 1)
A=sigmoid(np.dot(w.T,X)+b)
for i in range(A.shape[1]):
if A[0,i] <= 0.5:
Y_prediction[0,i]=0
else:
Y_prediction[0,i]=1
return Y_prediction # 画出曲线
costs = np.squeeze(logistic_regression_model['costs'])
plt.plot(costs)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per hundreds)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(logistic_regression_model["learning_rate"]))
plt.show()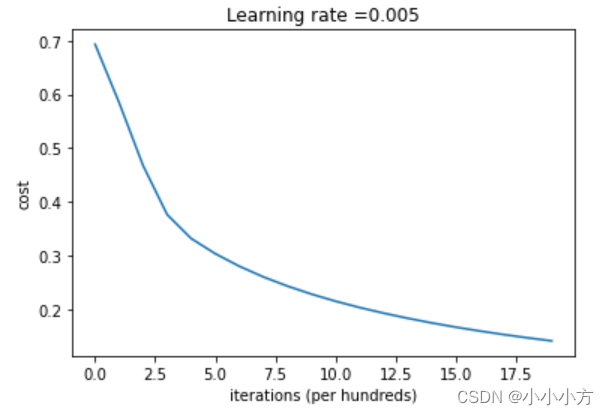
cost下降,表明正在学习参数,可以在训练集上进一步训练模型。尝试增加单元格中的迭代次数并重新运行单元格,会看到训练集准确度上升,但测试集准确度下降,这称为过拟合。
学习率决定了参数更新的速度,学习率太大会超过最优值,太小又会需要迭代太多次才能收敛到最佳值。
learning_rates = [0.01, 0.001, 0.0001]
models = {}
for lr in learning_rates:
print ("Training a model with learning rate: " + str(lr))
models[str(lr)] = model(train_set_x, train_set_y, test_set_x, test_set_y, num_iterations=1500, learning_rate=lr, print_cost=False)
print ('\n' + "-------------------------------------------------------" + '\n')
for lr in learning_rates:
plt.plot(np.squeeze(models[str(lr)]["costs"]), label=str(models[str(lr)]["learning_rate"]))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (hundreds)')
legend = plt.legend(loc='upper center', shadow=True)
frame = legend.get_frame()
frame.set_facecolor('0.90')
plt.show()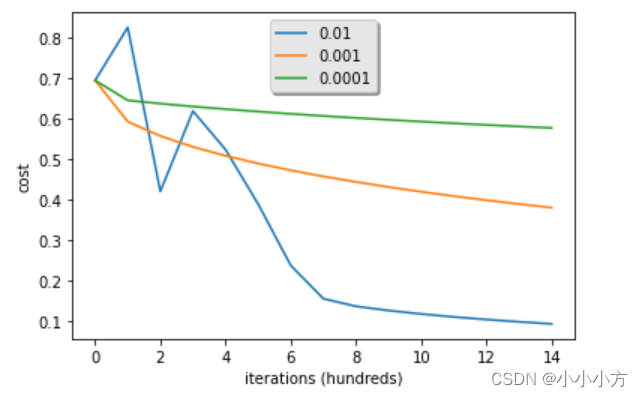
my_image = "my_image.jpg"
# We preprocess the image to fit your algorithm.
fname = "images/" + my_image
image = np.array(Image.open(fname).resize((num_px, num_px)))
plt.imshow(image)
image = image / 255.
image = image.reshape((1, num_px * num_px * 3)).T
my_predicted_image = predict(logistic_regression_model["w"], logistic_regression_model["b"], image)
print("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) + ", your algorithm predicts a \"" + classes[int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")y = 0.0, your algorithm predicts a "non-cat" picture.






















 1378
1378











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








