1、模板实现顺序栈

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class Stack
{
T* S; //数组
int size;//栈容量
int top; //栈顶元素下标
public:
//有参构造
Stack(int size):S(new T[size]),size(size),top(-1){}
//初始化时直接将栈顶元素下标设置为-1
//析构函数
~Stack(){delete[] S;}
//判空
bool empty(){return top == -1;}
//判满
bool full(){return top == size-1;}
//入栈
void push(const T &item)
{
if(full())
{
cout<<"栈满!无法入栈!";
}else
{
S[++top] = item;
cout<<"入栈成功"<<endl;
}
}
//出栈
void pop()
{
if(empty())
{
cout<<"栈空!无法出栈!"<<endl;
}else
{
top--;
cout<<"出栈成功!"<<endl;
}
}
//输出栈中元素
void show()
{
int i=0;
if(empty())
{
cout<<"栈空"<<endl;
}
else
{
for(i=top;i>=0;i--)
{
cout<<S[i]<<endl;
}
}
}
//获取当前栈内元素个数
void num()
{
cout<<"当前栈中元素个数:"<<top+1<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Stack<int> sta(5);
sta.empty();
sta.push(1);
sta.push(2);
sta.push(3);
sta.push(4);
sta.push(5);
sta.full();
sta.show();
sta.pop();
sta.pop();
sta.num();
sta.show();
return 0;
}2、异常处理
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun(int a, int b)
{
if(b == 0)//判断可能发生的异常
{
throw int(2);//抛出异常
}else if(b == 2)
{
throw int(3);
}
return a/b;
}
int main()
{
//cout<<fun(2,0)<<endl; //除数为零导致程序无法运行
//尝试使用try...catch对异常进行处理
try
{
//存放所有可能抛出异常的代码
fun(2,0);
fun(2,2); //catch中只能接收一条异常,建议try中只放一条代码
} catch (int ret) //catch中对具体的异常类型进行判断
{
if(ret ==2)
{
cout<<"除数为零"<<endl;
}else if(ret ==3)
{
cout<<"test"<<endl;
}
}
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
return 0;
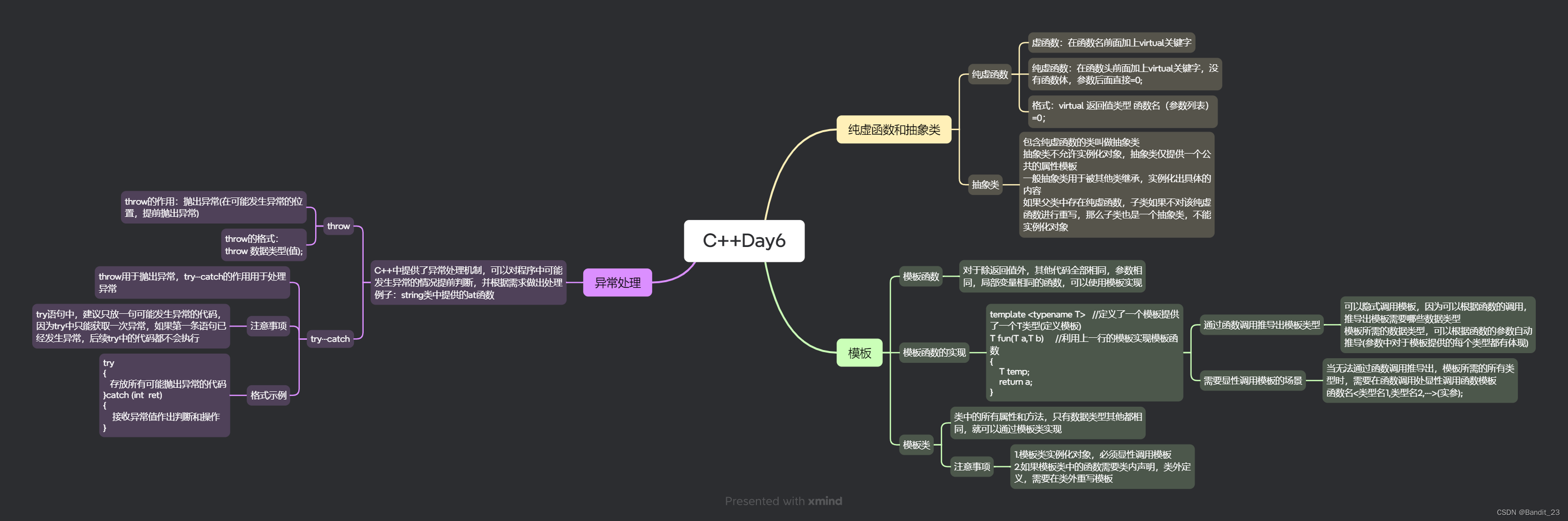
}3、思维导图





















 104
104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








