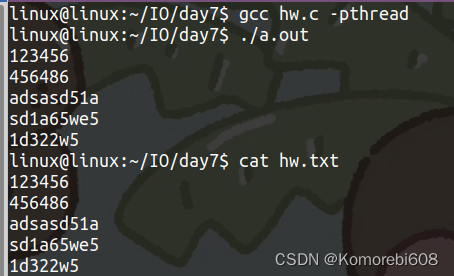
1.创建两个线程,实现将一个文件的内容打印到终端上,类似cat一个文件
一个线程读取文件中的内容
另一个线程将读取到的内容打印到终端上。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
//临界资源
int fd;
char c=0;
sem_t sem1,sem2;
void *callBack1(void* arg)
{
//char c=0;
off_t size=lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);
off_t offset = 0;
int i=0;
while(i++<size)
{
sem_wait(&sem1);
lseek(fd,offset,SEEK_SET);
if(read(fd,(char*)arg,sizeof(*(char*)arg))<0)
{
perror("read");
break;
}
offset=lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);
sem_post(&sem2);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callBack2(void* arg)
{
off_t size=lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);
off_t offset = size/2;
int i=0;
while(i++<size)
{
sem_wait(&sem2);
lseek(fd,offset,SEEK_SET);
if(write(stdout->_fileno,(char*)arg,sizeof(*(char*)arg))<0)
{
perror("write");
}
offset=lseek(fd,0,SEEK_CUR);
sem_post(&sem1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
fd=open("./hw.txt",O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
if(sem_init(&sem1,0,1)<0)
{
perror("sem_init");
return -1;
}
if(sem_init(&sem2,0,0)<0)
{
perror("sem_init");
return -1;
}
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,callBack1,(void *)&c);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,callBack2,(void *)&c);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
return 0;
}
结果:
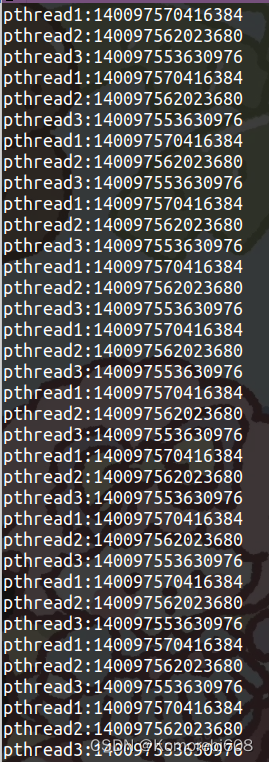
2.现有ID号为a b c的三个线程,每个线程的任务都是循环打印自己id号,要求打印的顺序为abc
//信号灯的方式实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
sem_t sem1,sem2,sem3;
void *callBack1(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem1);
printf("pthread1:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
sem_post(&sem2);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callBack2(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem2);
printf("pthread2:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
sem_post(&sem3);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callBack3(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem3);
printf("pthread3:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
sem_post(&sem1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(sem_init(&sem1,0,1)<0)
{
perror("sem_init");
return -1;
}
if(sem_init(&sem2,0,0)<0)
{
perror("sem_init");
return -1;
}
if(sem_init(&sem3,0,0)<0)
{
perror("sem_init");
return -1;
}
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,callBack1,(void*)&tid1);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,callBack2,(void*)&tid2);
pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,callBack3,(void*)&tid3);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
sem_destroy(&sem3);
return 0;
}
//条件变量的方式实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_cond_t cond1,cond2,cond3;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int flag = 1;
void *callBack1(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(1)
{
while(flag != 1)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond1, &mutex);
}
printf("pthread1:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
flag = 2;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond2);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callBack2(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(1)
{
while(flag != 2)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond2, &mutex);
}
printf("pthread2:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
flag = 3;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond3);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callBack3(void* arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(1)
{
while(flag != 3)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&cond3, &mutex);
}
printf("pthread3:%ld\n",*(pthread_t *)arg);
flag = 1;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_cond_init(&cond1,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond2,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond3,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,callBack1,(void*)&tid1);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,callBack2,(void*)&tid2);
pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,callBack3,(void*)&tid3);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond1);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond2);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond3);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
结果:





















 1215
1215











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








