Only for the Test 1 which include 4.2 4.3 4.4
Locomotion and Kinematics 运动和运动学
(4.2) Part 2: Wheeled Motion
1. Wheeled Robots
a. 省略控制双腿需要的计算复杂度
b. 只限于easy terrain (地形)
c. 不平坦uneven 不规则irregular 的地形需要很多计算
d. 轮子的选择根据应用的需要决定
2. Four basic wheel types
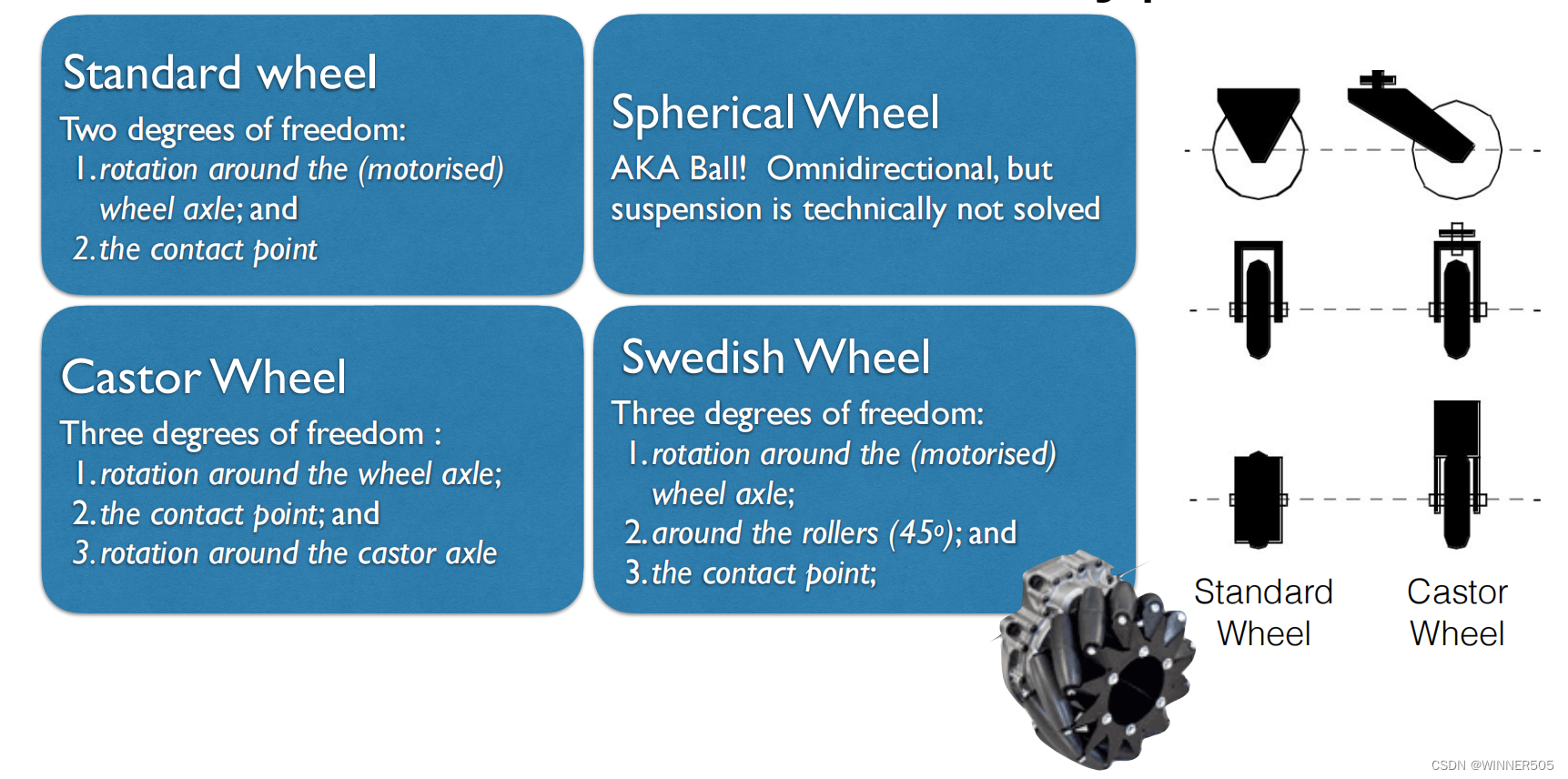
3. Features / characteristics
a.
Stability of a vehicle is be guaranteed with 3 wheels
. 机器人的稳定性需要三个轮子来保证
b. Stability is improved by 4 and more wheels
c. However, such arrangements with more thanthree contact points are
hyperstatic 超固定的 and requirea
flexible suspension system 灵活的悬挂系统.
d.
Bigger wheels
allow robot to
overcome higher obstacles
.
e. Combining
actuation 驱动 and
steering 转向 on one wheel makesthe design complex and
adds additional errors forodometry
f. 计算速度 v = 2 r * w/2
r * w/2 = wr
= wr
g. Four wheels
1. 高机动性 难控制
h. Three wheels
1. Differential drive 差速器驱动器
plus caster 脚轮 or omnidirectional wheel.
Highly manoeuvrable, but limited to moving forwards/ backwards and rotating 高机动性,但仅限制于向前、向后和转向
2.
Connected drive wheels at rear,
steered wheel at front 前面是转向轮,后面是驱动轮
3.
Two free wheels in rear,
steered
drive wheel in front. 后轮是自由的, 前轮是需要操纵的
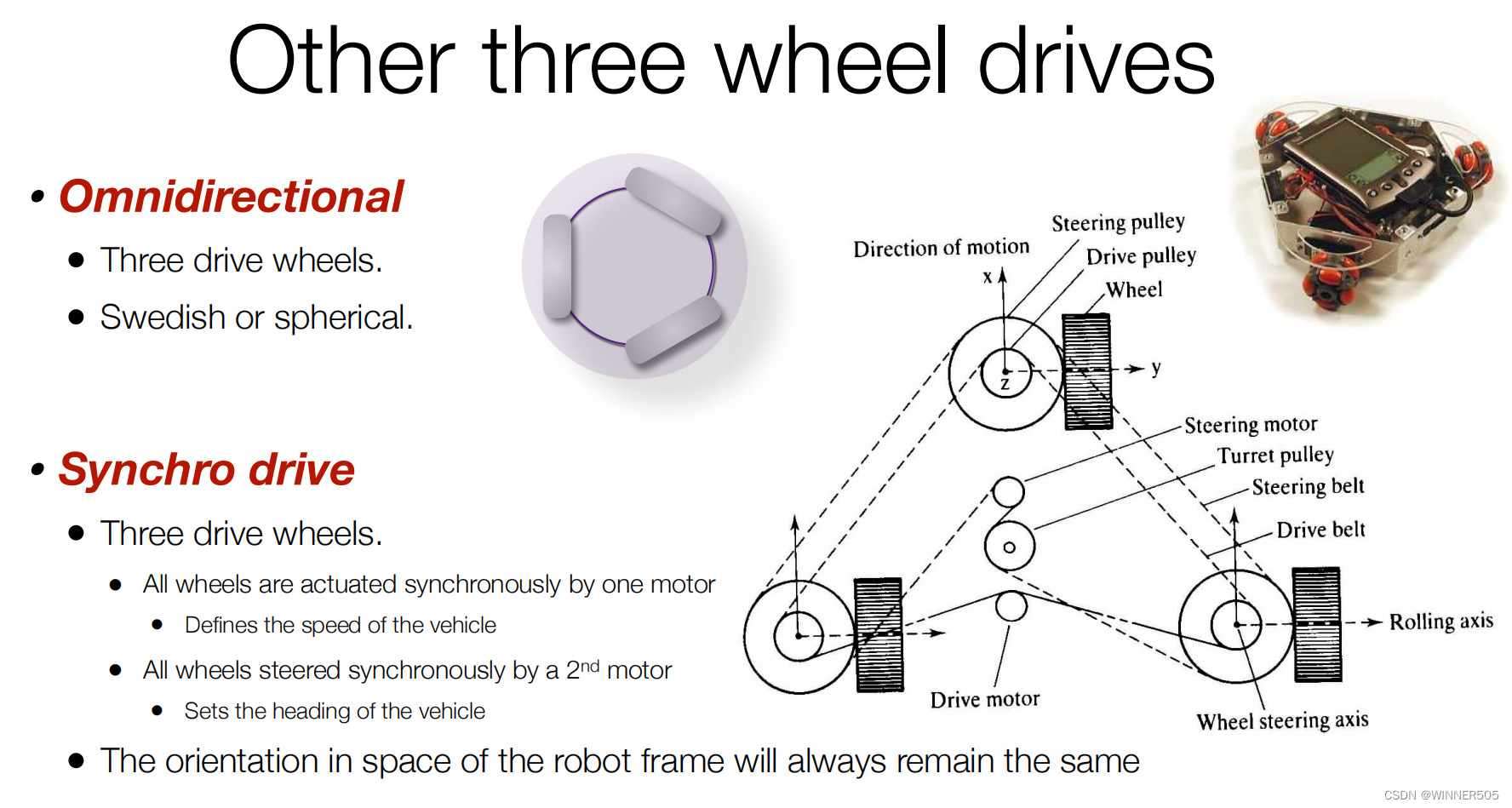
(4.3)Part 3: Two wheeled Vehicles and Manoeuvrability
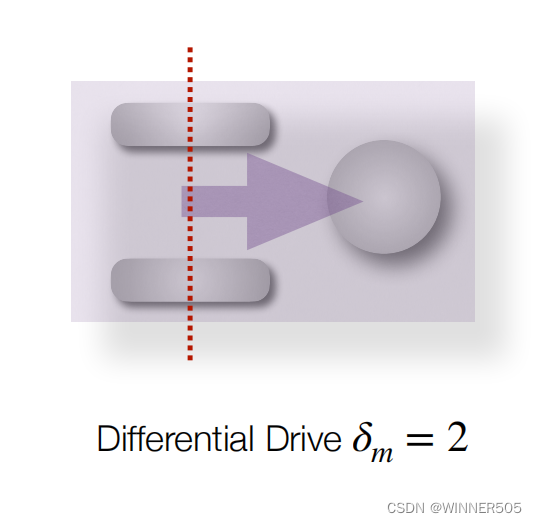
1. Two Wheels
Steering wheel
at front, drive wheel at back.
Stability issues, not that common
Differential drive
Turning achieved by varying the individual velocity / speed of each wheel
转向通过改变单个轮胎的速度来实现
Centre of mass above or below axle
Highly manoeuvrable, but limited to moving forwards/ backwards and rotating 高机动性,但仅限制于向前、向后和转向
 2. Degree of mobility
2. Degree of mobility
the number of
independent
fixed or steerable standard wheels
简而言之,就是独立固定的或者是可操纵的轮胎
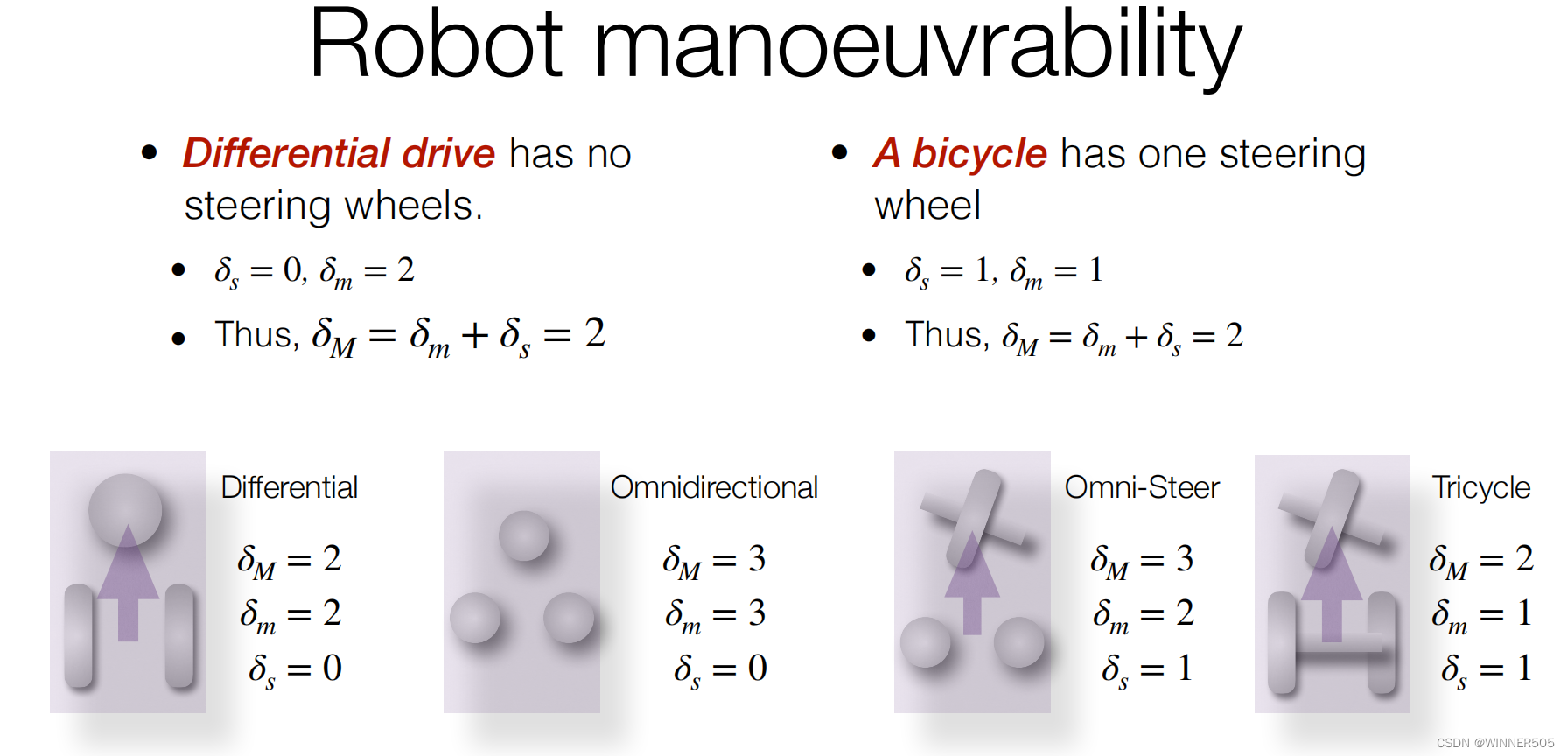
例子1:differential drive 什么差速器

例子2:tricycle 三轮车

例子3:bicycle 自行车

3. Mobility vs Steerability
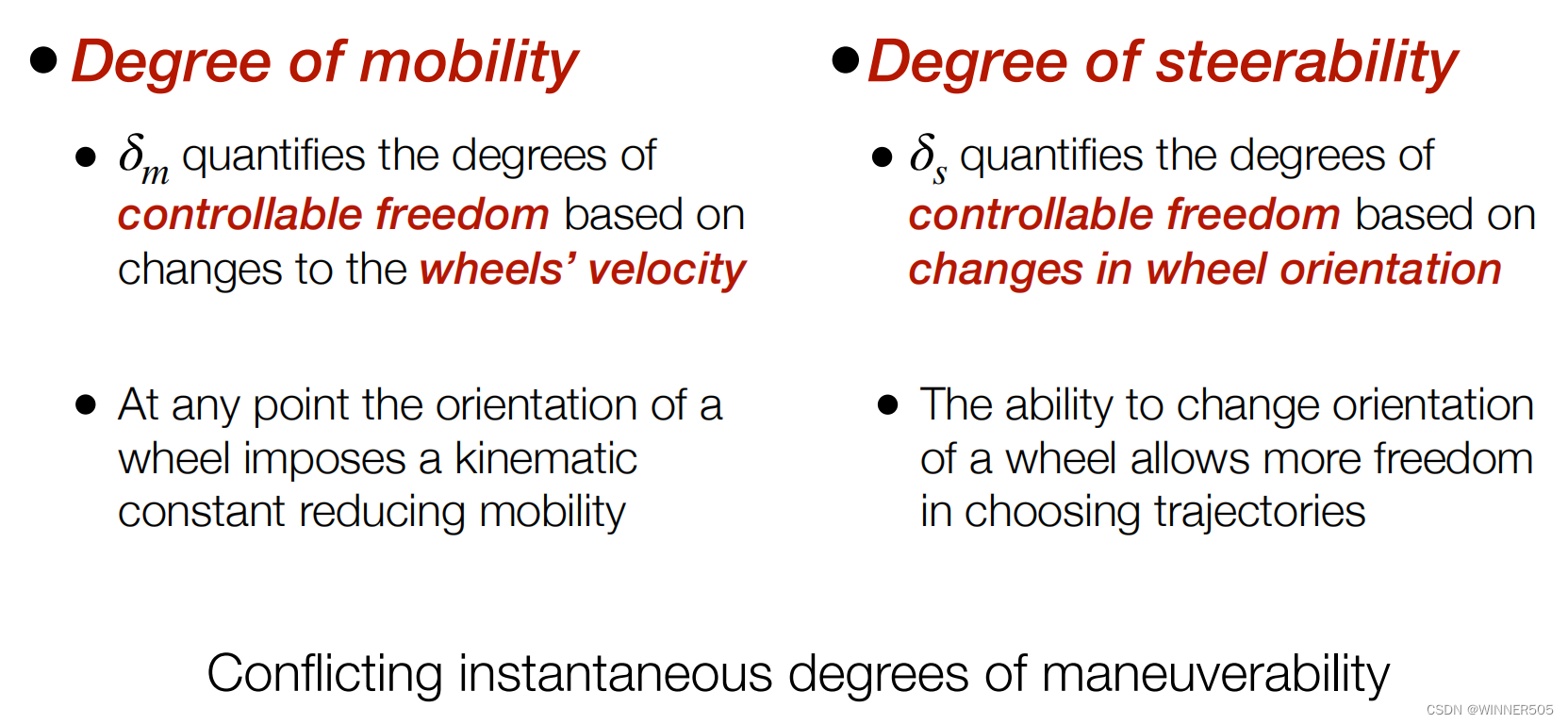
4. Degree of Steerability

5. Degree of Manoeuvrability

机器人可以通过改变车轮的速度(直接移动)和车轮的方向(间接移动)来操纵的整体自由度
两个具有相同 manoeuvrability 特性的机器人并不一定是相等的,但由于可移动性或可操纵性,它们可以以不同的方式进行操纵
6. Non-Holonomic Constraints 非人体工程学约束
(4.4)Part 4 Kinematics of Differential Drives
So far we have looked at different kinds of motion in a qualitative way
•
One way to program robots to move is
trial and error 试错法 反复实验
1.定义:
A somewhat better way is to establish mathematically how the robot
should
move, this is
kinematics
•
Rather
kinematics
is the business of figuring how a robot will move if it’s motors work in a given way.
运动学的任务是计算如果机器人的马达在特定的方式工作,它将如何移动
固定马达----计算移动
•
Inverse-kinematics
then tells us how to move the motors to get the robot to do what we want.
然后,逆运动学告诉我们如何移动马达来让机器人去做我们想做的事情
改变马达-----促使移动
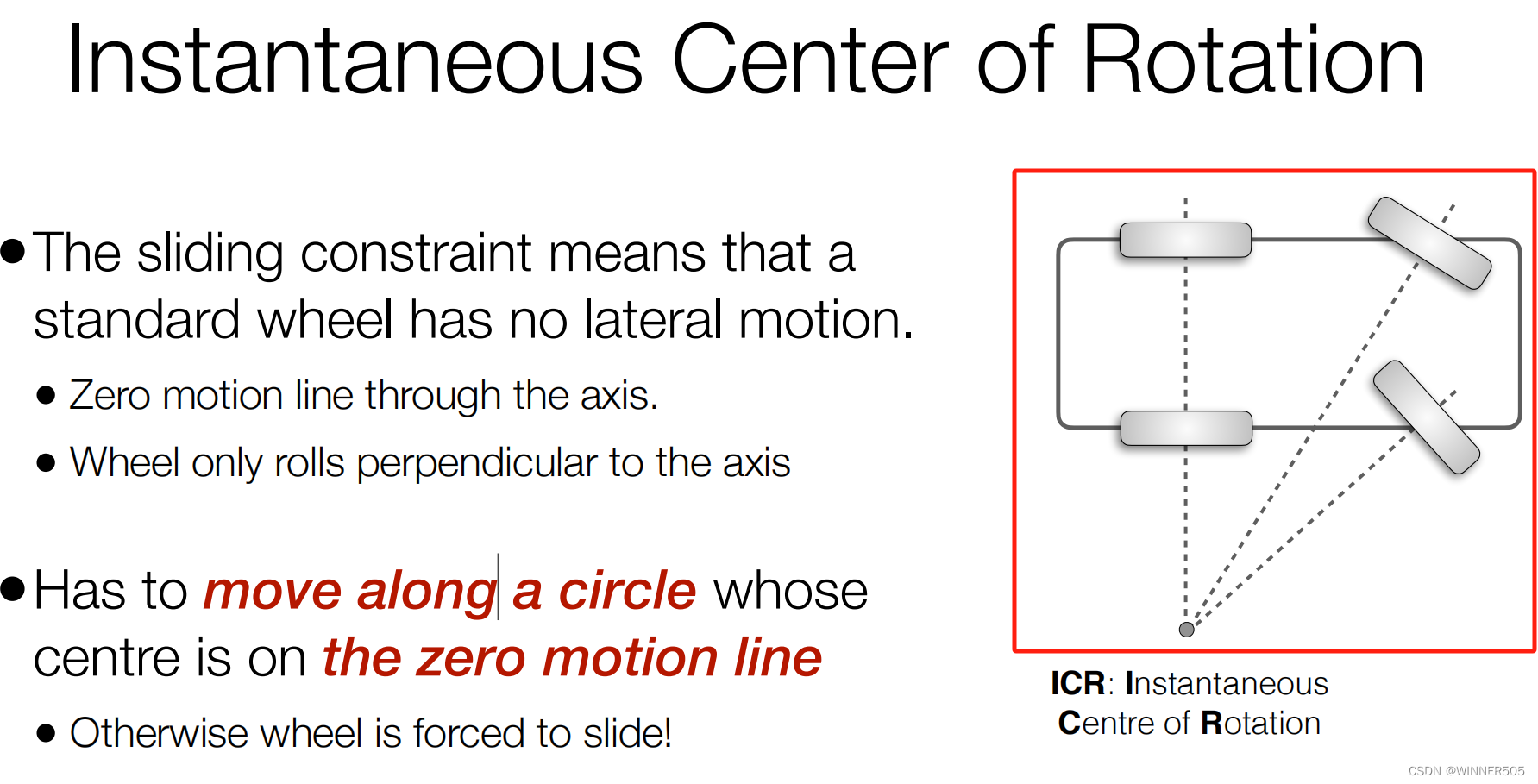
没有横向移动条件下的转向
31 / 54 明天在学 学闷了






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








